J Korean Soc Radiol.
2010 Apr;62(4):389-392. 10.3348/jksr.2010.62.4.389.
Arteriographic and MR Imaging Findings of a High-Voltage Electrical Burn in the Upper Extremity: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Hallym University College of Medicine, Hangang Sacred Heart Hospital, Korea. lgkhope@nate.com
- 2Department of Radiology, Dongguk University College of Medicine, Gyeongju Hospital, Korea.
- 3Department of Surgery, Burn Center, Hallym University College of Medicine, Hangang Sacred Heart Hospital, Korea.
- KMID: 1460075
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2010.62.4.389
Abstract
- An electrical injury is defined as sequelae caused by accidental contact with human-made or generated electrical power. A high-voltage electrical burn can cause many complications of numerous body systems within an individual's body, including the cardiac, respiratory, musculoskeletal, and central nervous systems. The radiologic features of this rare and sometimes life-threatening injury have occasionally been described in the literature. However, to the best of our knowledge, there have been no reports in Korea on the arteriographic and MR imaging findings of high-voltage electrical burn involving the body's upper extremity. In this article, we describe the imaging findings of a case involving a high-voltage electrical burn in the upper extremity, with an emphasis on the arteriographic and MR imaging findings and a review of the literature.
MeSH Terms
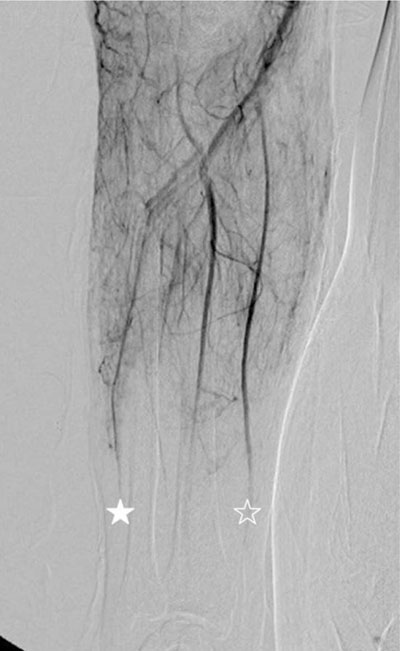
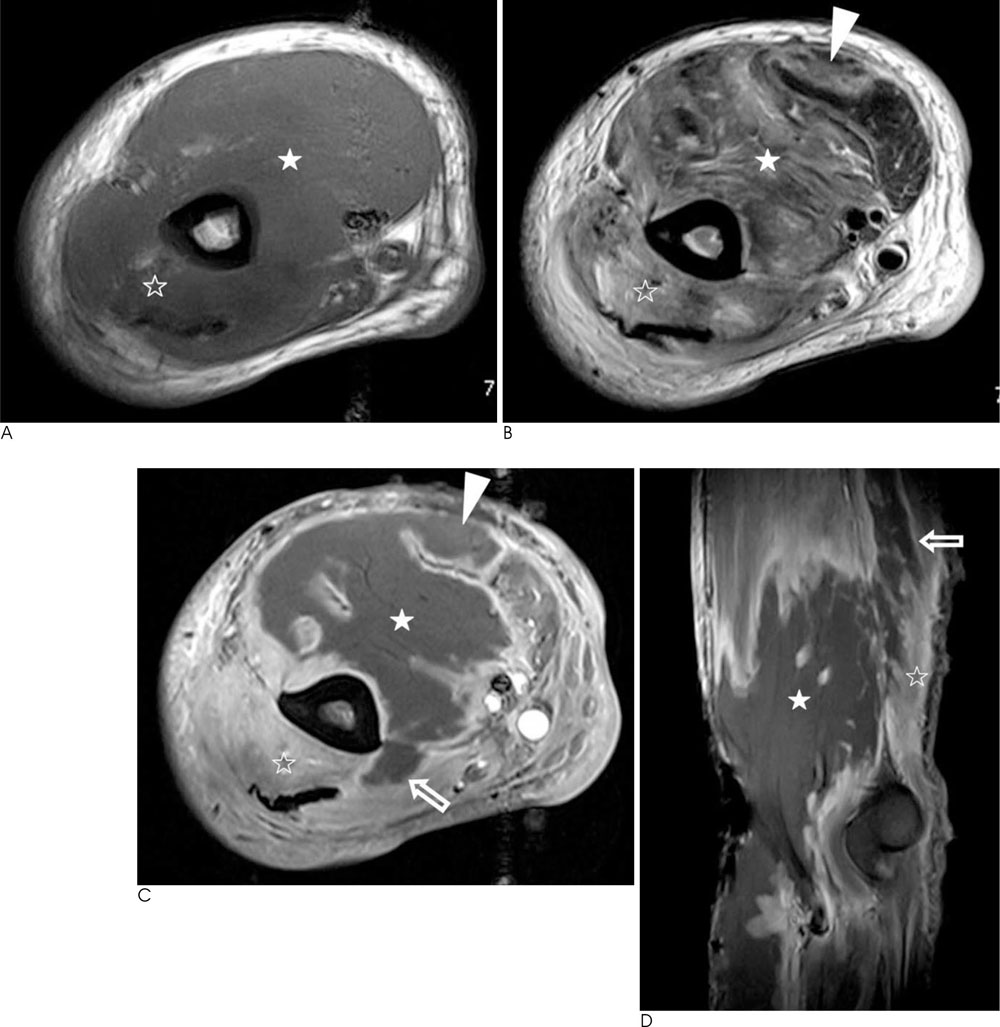
Figure
Reference
-
1. Rouse RG, Dimick AR. The treatment of electrical injury compared to burn injury: a clinical review of pathophysiology and comparison of patient management protocols. J Trauma. 1978; 18:43–47.2. Fleckenstein JL, Chason DP, Bonte FJ, Parkey RW, Hunt JL, Purdue GF, et al. High-voltage electric injury: assessment of muscle viability with MR imaging and Tc-99m pyrophosphate scintigraphy. Radiology. 1995; 195:205–210.3. Timmons JH, Hartshorne MF, Peters VJ, Cawthon MA, Bauman JM. Muscle necrosis in the extremities: evaluation with Tc-99m pyrophosphate scanning-a retrospective review. Radiology. 1988; 167:173–178.4. Li L, Chai J, Sheng ZC, Guo Z, Chen Y, Ouyang Z. A comparative study on the predictive value of digital subtraction angiography and B-mode ultrasonography in evaluating arterial injury in high-voltage electrical burn of the forearm. J Burn Care Res. 2006; 27:502–507.5. Jang TY, Jo YG, Moon JH, Kim HC, Jo JH. Arteriographic features in patients with high-voltage electric burn. J Korean Burn Soc. 2007; 10:131–134.6. Ohashi M, Koizumi J, Hosoda Y, Fujishiro Y, Tuyuki A, Kikuchi K. Correlation between magnetic resonance imaging and histopathology of an amputated forearm after an electrical injury. Burns. 1998; 24:362–368.7. Nettelblad H, Thuomas KA, Sjöberg F. Magnetic resonance imaging: a new diagnostic aid in the care of high-voltage electrical burns. Burns. 1996; 22:117–119.8. Kim CS, Hong SH, Lee MJ, Cho SW, Lee ES, Kang IW. MRI findings of the brain in high-voltage electrical burn Patient: case report. J Korean Radiol Soc. 2003; 48:387–389.9. Moon SY, Kim HC. Investigation of amputations related to electrical burns. J Korean Burn Soc. 2002; 5:38–56.10. Song SE, Kim HC, Jang YS, Lee DR. Epidemiologic analysis of electric burns. J Korean Burn Soc. 2007; 10:1–12.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pyogenic Arthritis of the Ankle Joint Following a High-Voltage Electrical Burn in the Lower Extremity: A Case Report
- A Retrospective Analysis of 645 Burn Patients Following High Voltage Electrical Injuries - 8 Years of Experience
- Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy For Treatment of Intractable Stump Pain
- Early-Onset Myelopathy after High-voltage Electrical Burn: Case Report
- MRI Findings of the Brain in High-Voltage Electrical Burn Patient: Case Report