Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr.
2010 Sep;13(2):193-198. 10.5223/kjpgn.2010.13.2.193.
A Case of Ascending Colon Diverticulitis with Perforation in a Child
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, College of Medicine, Hallym University, Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital, Seoul, Korea. jhped@hallym.or.kr
- 2Department of Surgery, College of Medicine, Hallym University, Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiology, College of Medicine, Hallym University, Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Pathology, College of Medicine, Hallym University, Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1459435
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5223/kjpgn.2010.13.2.193
Abstract
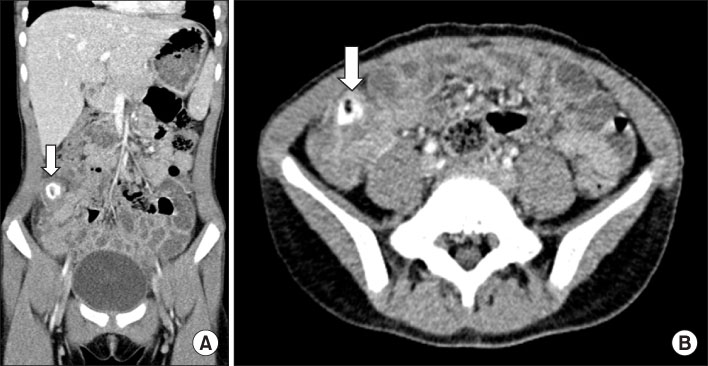
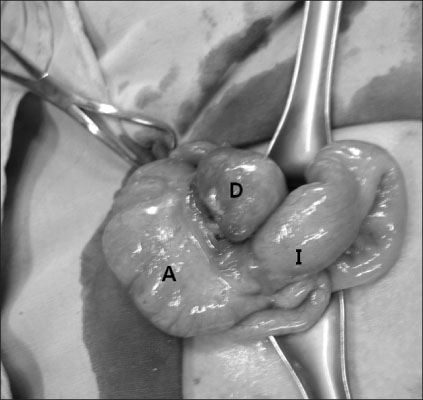
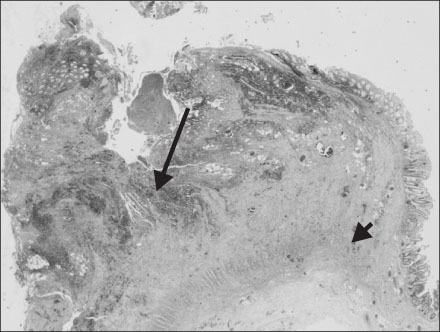
- A diverticulum is a blind pouch communicating with the gut. The term "diverticulitis" indicates inflammation of a diverticulum or diverticula, which is commonly accompanied by gross or microscopic perforation. Acute diverticuitis is a rare disorder in early childhood. Itis difficult to diagnose acute right colon diverticulitis from common causes of RLQ pain. We report a case of acute diverticulitis in the right colon in a 6-year-old girl. She complained of typical RLQ pain mimicking acute appendicitis,but was diagnosed with acute diverticulitis by CT scanning. Conservative treatment failed because of peritonitis due to perforation of an inflamed diverticulum. After the diverticulcetomy, the symptoms resolved.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sugihara K, Muto T, Morioka Y, Asano A, Yamamoto T. Diverticular disease of the colon: a review of 615 cases. Dis Colon Rectum. 1984. 27:531–537.2. Buchanan GN, Nicholas J, Kenefick J, Richard C, Cohen G. Diverticulitis. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2002. 16:635–647.
Article3. Stollman NH, Raskin JB. Diverticular disease of the colon. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1999. 29:241–252.
Article4. Hwang KY, Yang HW, Kim SH, Kim AN, Jung SH, Lee YJ, et al. Clinical characteristics of colonic diverticulitis in young patients. Korean J Med. 2008. 74:250–257.5. Sim JH, Song KH, Sim YJ, Cho DJ, Kim DH, Min KS, et al. A clinical study of acute colonic diverticulitis in children. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 2003. 46:1095–1100.6. Lane JS, Sarkar R, Schmit PJ, Chandler CF, Thompson JE. Surgical approach to cecal diverticulitis. J Am Coll Surg. 1999. 188:629–635.
Article7. Jacobs DO. Diverticulitis. N Engl J Med. 2007. 357:2057–2662.
Article8. Nakaji S, Danjo K, Munakata A, Sugawara K, MacAuley D, Kernohan G. Comparison of etiology of right sided diverticula in Japan with that of left sided diverticula in the West. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2002. 17:365–373.
Article9. Chan CC, Lo KK, Chung EC, Lo SS, Hon TY. Colonic diverticulitis in Hong Kong: distribution pattern and clinical significance. Clin Radiol. 1998. 53:842–844.
Article10. Miura S, Kodaira S, Shatari T, Nishioka M, Hosoda Y, Hisa TK. Recent trends in diverticulosis of the right colon in Japan: retrospective review in a regional hospital. Dis Colon Rectum. 2000. 43:1383–1392.11. Yoon HY, Kim BC. Clinical analysis of 42 cases who underwent colectomy for suspected acute appendicitis. J Korean Soc Coloproctol. 2005. 21:357–361.12. Lipton S, Estrin J, Glasser I. Diverticular disease of the appendix. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1989. 168:13–16.13. Lee IK, Kim SH, Lee YS, Kim HJ, Lee SK, Kang WK, et al. Diverticulitis of the right colon: tips for preoperative diagnosis and treatment strategy. J Korean Soc Coloproctol. 2007. 23:223–231.
Article14. Bogue CO, Mann EH. Imaging findings in right-sided diverticulitis in a child. Pediatr Radiol. 2008. 38:1125–1127.
Article15. Sreenivasan N, Kalyanpur A, Bhat A, Sridhar PG, Singh J. CT diagnosis of cecal diverticulitis. Ind J Radiol Imag. 2006. 16:451–452.
Article16. Matsushima K. Management of right-sided diverticulitis: a retrospective review from a hospital in Japan. Surg Today. 2010. 40:321–325.
Article17. Kim KY, Kim IK, Jung SW, Park KH, Park YJ. Analysis on the surgical treatment of colonic diverticulitis. J Korean Surg Soc. 2007. 73:36–41.18. Jang JI, Lim YS, Choi JW, Lee YS. Management of right colon diverticulitis. J Korean Soc Coloproctol. 2010. 26:22–82.
Article19. Moon BC, Kim HS. Developmental pattern and treatment in colon diverticular disease. J Korean Soc Coloproctol. 2007. 23:305–311.
Article