J Adv Prosthodont.
2010 Jun;2(2):46-49. 10.4047/jap.2010.2.2.46.
Full mouth rehabilitation of destroyed dentition with rotational path removable partial denture: a case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Prosthodontics and Dental Research Institute, School of Dentistry, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea. young21c@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1456754
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jap.2010.2.2.46
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
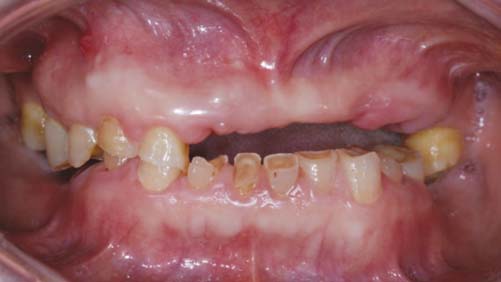
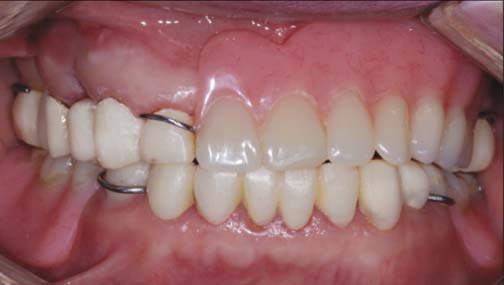
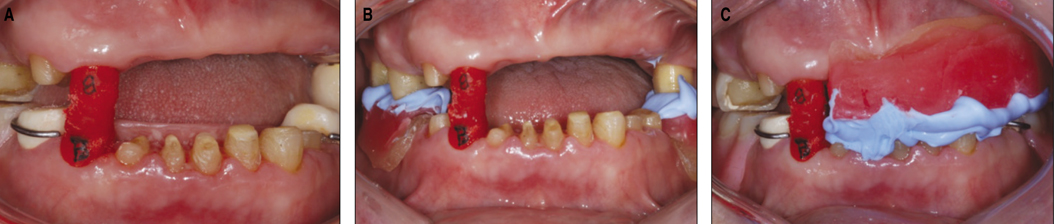
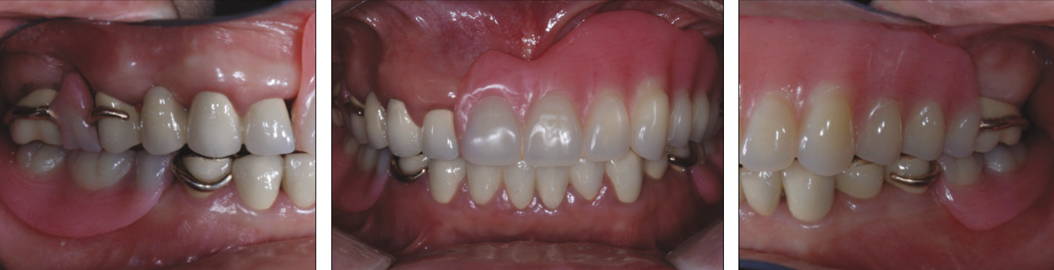
Though implant dentistry is very successful and predictable in treatment of patients with destroyed dentition, there are some cases with limitations to implant therapy. In these cases, alternative treatment modality should be considered. CASE DESCRIPTION: A patient with destroyed dentition was rehabilitated with a lateral rotational path removable partial denture. According to the diagnosis, we determined to raise vertical dimension for esthetic and functional restoration. The final restoration was performed after four months of provisional period. CLINICAL IMPLICATION: The edentulous patients with compromised esthetics and functions can be successfully treated with a rotational path removable partial denture through adequate treatment planning and precise laboratory procedure.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Dawson PE. Functional Occlusion - From TMJ to smile design. 2007. 1st ed. N.Y.: Mosby;18–26. 114–129. 430–452.2. Ancowitz S. Esthetic removable partial dentures. Gen Dent. 2004. 52:453–459. quiz 460.3. King GE. Dual-path design for removable partial dentures. J Prosthet Dent. 1978. 39:392–395.4. Carreiro Ada F, Machado AL, Giampaolo ET, Santana IL, Vergani CE. Dual path: a concept to improve the esthetic replacement of missing anterior teeth with a removable partial denture. J Prosthodont. 2008. 17:586–590.5. Byron R Jr, Frazer RQ, Herren MC. Rotational path removable partial denture: an esthetic alternative. Gen Dent. 2007. 55:245–250.6. Suh JS, Billy EJ. Rotational path removable partial denture (RPD): conservative esthetic treatment option for the edentulous mandibular anterior region: a case report. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2008. 20:98–105. discussion 106-7.7. Grageda E. Achieving an aesthetic anterior-posterior rotational path partial denture: case report. Dent Today. 2007. 26:130132–135.8. Donovan T. Use of the rotational path removable partial denture concept in a Kennedy Class II patient: a case report. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2008. 20:294–298.9. Jacobson TE. Rotational path partial denture design: a 10-year clinical follow-up-Part I. J Prosthet Dent. 1994. 71:271–277.10. Halberstam SC, Renner RP. The rotational path removable partial denture: the over-looked alternative. Compendium. 1993. 14:544546–552.11. Jacobson TE, Krol AJ. Rotational path removable partial denture design. J Prosthet Dent. 1982. 48:370–376.12. Firtell DN, Jacobson TE. Removable partial dentures with rotational paths of insertion: problem analysis. J Prosthet Dent. 1983. 50:8–15.13. McCracken WL, Carr AB, McGivney GP. McCracken's removable partial prosthodontics. 2000. 10th ed. St. Louis: Mosby;356–360.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Three-year follow-up of full mouth rehabilitation with anterior implant surveyed bridges and distal extension removable partial denture
- Full mouth rehabilitation of severely worn dentition with implants and removable partial dentures
- Full mouth rehabilitation of the patient with crossed occlusion using removable partial denture restoration: A case report
- Full mouth rehabilitation using removable partial denture in patient with loss of vertical dimension due to worn dentition
- Full mouth rehabilitation with a few remaining teeth and implants for a patient with chronic periodontitis: a case report