Korean J Pain.
2010 Dec;23(4):230-235. 10.3344/kjp.2010.23.4.230.
Analgesic Effect of Intrathecal Ginsenosides in a Murine Bone Cancer Pain
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Chonnam National University, Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. mhyoon@chonnam.ac.kr
- 2The Brain Korea 21 Project, Center for Biomedical Human Resources at Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 1454705
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2010.23.4.230
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Bone cancer pain has a disruptive effect on the cancer patient's quality of life. Although ginsenosides have been used as traditional medicine in Eastern Medicine, the effect on bone cancer pain has not been thoroughly studied. The aim of this study was to determine whether ginsenosides may alter the bone cancer pain at the spinal level.
METHODS
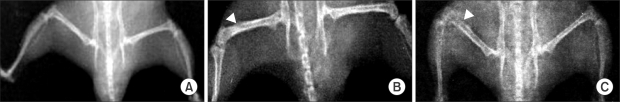
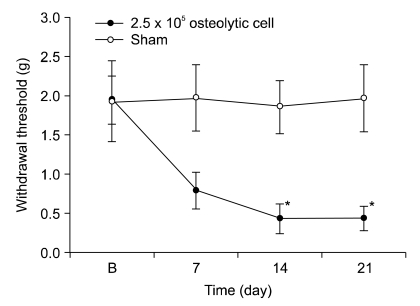
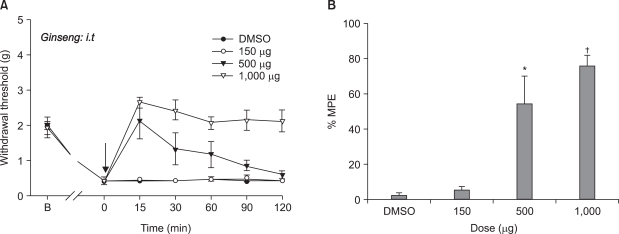
NCTC 2472 tumor cells (2.5 x 10(5)) were injected into the femur of adult male C3H/HeJ mice to evoke bone tumor and bone cancer pain. To develop bone tumor, radiologic pictures were obtained. To assess pain, the withdrawal threshold was measured by applying a von Frey filament to the tumor cells inoculation site. The effect of intrathecal ginsenosides was investigated. Effect of ginsenosides (150, 500, 1,000 microgram) was examined at 15, 30, 60, 90, 120 min after intrathecal delivery.
RESULTS
The intrafemoral injection of NCTC 2472 tumor cells induced a radiological bone tumor. The withdrawal threshold with tumor development was significantly decreased compared to the sham animals. Intrathecal ginsenosides effectively increased the withdrawal threshold in the bone cancer site.
CONCLUSIONS
NCTC 2472 tumor cells injection into the mice femur caused bone tumor and bone cancer pain. Intrathecal ginsenosides attenuated the bone cancer-related pain behavior. Therefore, spinal ginsenosides may be an alternative analgesic for treating bone cancer pain.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Portenoy RK, Lesage P. Management of cancer pain. Lancet. 1999; 353:1695–1700. PMID: 10335806.
Article2. Banning A, Sjøgren P, Henriksen H. Pain causes in 200 patients referred to a multidisciplinary cancer pain clinic. Pain. 1991; 45:45–48. PMID: 1861877.
Article3. Coleman RE, Houston S, Purohit OP, Rubens RD, Kandra A, Ford J. A randomised phase II study of oral pamidronate for the treatment of bone metastases from breast cancer. Eur J Cancer. 1998; 34:820–824. PMID: 9797692.
Article4. Coleman RE. How can we improve the treatment of bone metastases further? Curr Opin Oncol. 1998; 10(Suppl 1):S7–S13. PMID: 9801853.5. Mercadante S, Arcuri E. Breakthrough pain in cancer patients: pathophysiology and treatment. Cancer Treat Rev. 1998; 24:425–432. PMID: 10189409.
Article6. Mercadante S. Malignant bone pain: pathophysiology and treatment. Pain. 1997; 69:1–18. PMID: 9060007.
Article7. Portenoy RK, Payne D, Jacobsen P. Breakthrough pain: characteristics and impact in patients with cancer pain. Pain. 1999; 81:129–134. PMID: 10353500.
Article8. Mercadante S, Fulfaro F. Management of painful bone metastases. Curr Opin Oncol. 2007; 19:308–314. PMID: 17545792.
Article9. O'Connor JP, Lysz T. Celecoxib, NSAIDs and the skeleton. Drugs Today (Barc). 2008; 44:693–709. PMID: 19137124.10. Vanderah TW, Gardell LR, Burgess SE, Ibrahim M, Dogrul A, Zhong CM, et al. Dynorphin promotes abnormal pain and spinal opioid antinociceptive tolerance. J Neurosci. 2000; 20:7074–7079. PMID: 10995854.
Article11. Liu CX, Xiao PG. Recent advances on ginseng research in China. J Ethnopharmacol. 1992; 36:27–38. PMID: 1501490.
Article12. Attele AS, Wu JA, Yuan CS. Ginseng pharmacology: multiple constituents and multiple actions. Biochem Pharmacol. 1999; 58:1685–1693. PMID: 10571242.13. Nah JJ, Hahn JH, Chung S, Choi S, Kim YI, Nah SY. Effect of ginsenosides, active components of ginseng, on capsaicin-induced pain-related behavior. Neuropharmacology. 2000; 39:2180–2184. PMID: 10963761.
Article14. Shin DJ, Yoon MH, Lee HG, Kim WM, Park BY, Kim YO, et al. The effect of treatment with intrathecal ginsenosides in a rat model of postoperative pain. Korean J Pain. 2007; 20:100–105.
Article15. Kim SY, Yoon MH, Lee HG, Kim WM, Lee JD, Kim YO, et al. The role of adrenergic and cholinergic receptors on the antinociception of Korean red ginseng in the spinal cord of rats. Korean J Pain. 2008; 21:27–32.
Article16. Schwei MJ, Honore P, Rogers SD, Salak-Johnson JL, Finke MP, Ramnaraine ML, et al. Neurochemical and cellular reorganization of the spinal cord in a murine model of bone cancer pain. J Neurosci. 1999; 19:10886–10897. PMID: 10594070.
Article17. Hylden JL, Wilcox GL. Intrathecal morphine in mice: a new technique. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980; 67:313–316. PMID: 6893963.
Article18. Dixon WJ. Efficient analysis of experimental observations. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1980; 20:441–462. PMID: 7387124.
Article19. Yoon MH, Choi JI, Jeong SW. Antinociception of intrathecal cholinesterase inhibitors and cholinergic receptors in rats. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2003; 47:1079–1084. PMID: 12969099.
Article20. Nah SY. Ginseng; recent advances and trends. Korean J Ginseng Sci. 1997; 21:1–12.21. Kaku T, Miyata T, Uruno T, Sako I, Kinoshita A. Chemico-pharmacological studies on saponins of Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer. II. Pharmacological part. Arzneimittelforschung. 1975; 25:539–547. PMID: 239732.22. Lee JH, Jeong SM, Lee BH, Kim DH, Kim JH, Kim JI, et al. Differential effect of bovine serum albumin on ginsenoside metabolite-induced inhibition of alpha3beta4 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Arch Pharm Res. 2003; 26:868–873. PMID: 14609137.
Article23. Nah SY, McCleskey EW. Ginseng root extract inhibits calcium channels in rat sensory neurons through a similar path, but different receptor, as mu-type opioids. J Ethnopharmacol. 1994; 42:45–51. PMID: 8046943.
Article24. Nah SY, Park HJ, McCleskey EW. A trace component of ginseng that inhibits Ca2+ channels through a pertussis toxin-sensitive G protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995; 92:8739–8743. PMID: 7568008.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of Intrathecal Ginsenosides on Mechanical Allodynia in a Neuropathic Rat Model
- Effect of ginsenosides in a mouse model of bone cancer pain
- The role of spinal adrenergic receptors on the antinociception of ginsenosides in a rat postoperative pain model
- The Effect of Treatment with Intrathecal Ginsenosides in a Rat Model of Postoperative Pain
- Additive interaction of intrathecal ginsenosides and neostigmine in the rat formalin test