J Korean Hip Soc.
2011 Dec;23(4):275-281. 10.5371/jkhs.2011.23.4.275.
Cementless Total Hip Arthroplasty Using a Modular Femoral Component in Patients with Femoral Head Osteonecrosis: Comparison of Metal-on-Metal and Ceramic-on-Ceramic Articulation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, SM Christianity Hospital, Pohang, Korea.
- 2Department of ImmunoMicrobiology, College of Pharmacy, Dongduk Women's University, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, College of Medicine, Chung-Ang University, Seoul, Korea. babyjack@empas.com
- KMID: 1452635
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5371/jkhs.2011.23.4.275
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the clinical and radiological outcomes after total hip arthroplasty using the S-ROM modular system for osteonecrosis of the femoral head, and to compare the results between the groups using metal-on-metal articulation and ceramic-on-ceramic articulation.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sixty-six patients (78 hips) with osteonecrosis of the femoral head were evaluated after primary total hip arthroplasty between January 2001 and December 2004, using an S-ROM proximal modular femoral stem. The average follow-up was 77 months (range, 60 to 122 months) and all patients were followed for more than five years.
RESULTS
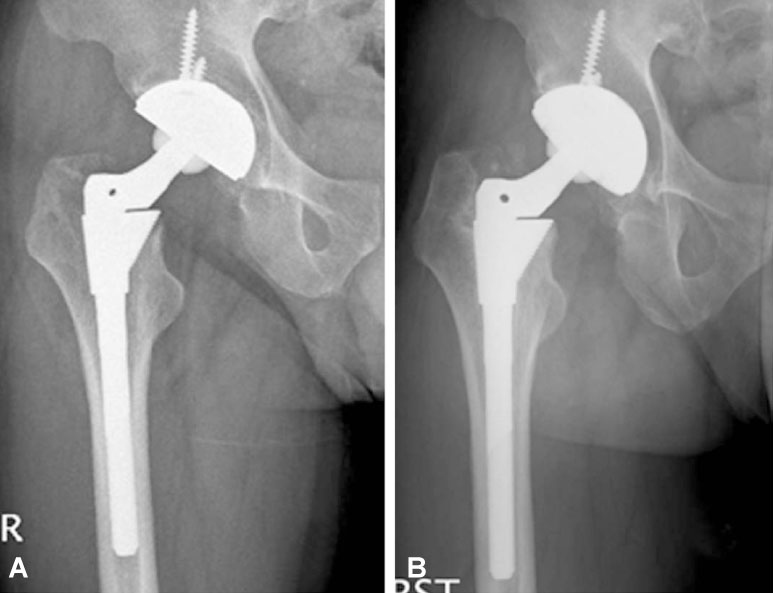
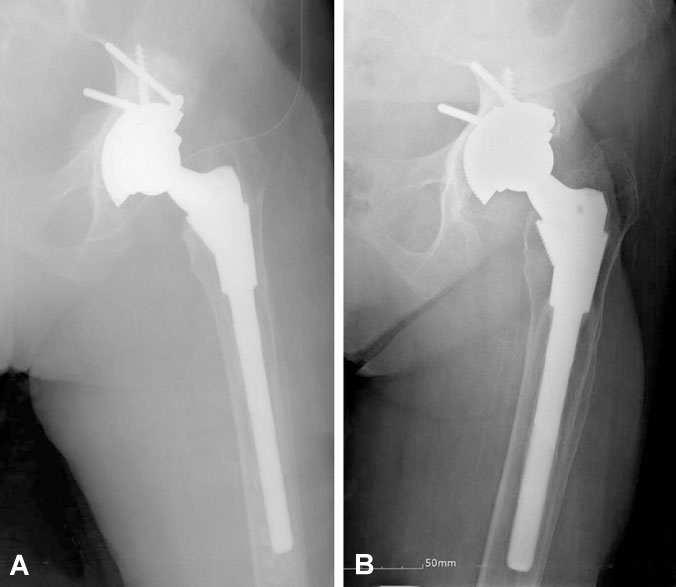
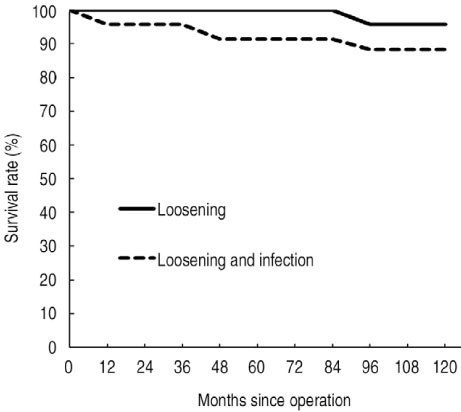
The average Harris hip score improved from 53 points to 88.5 points at the final follow-up. At the latest radiologic evaluation, sixty-seven stems had bony ingrowth stability, and 10 stems had stable fibrous ingrowth. However, one stem had diffuse extensive osteolysis and loosening, which was revised at 9 years. Postoperative complications included 4 cases of heterotrophic ossificiation, 1 case of linear fracture after insertion of the femoral stem, 1 case of dislocation, 2 cases of infection, and 1 case of extensive osteolysis and loosening. There were 3 cases of revision and Kaplan-Meier survivorship analysis with revision estimated at a 95.7% chance of survival for the femoral component during 122 months.
CONCLUSION
Our study showed that total hip arthroplasty using the S-ROM modular system with metal-on-metal articulation or ceramic-on-ceramic articulation had favorable clinical and radiological mid- to long-term results.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ortiguera CJ, Pulliam IT, Cabanela ME. Total hip arthroplasty for osteonecrosis: matched-pair analysis of 188 hips with long-term follow-up. J Arthroplasty. 1999. 14:21–28.2. Ritter MA, Meding JB. A comparison of osteonecrosis and osteoarthritis patients following total hip arthroplasty. A long-term follow-up study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986. 206:139–146.3. Saito S, Saito M, Nishina T, Ohzono K, Ono K. Long-term results of total hip arthroplasty for osteonecrosis of the femoral head. A comparison with osteoarthritis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989. 244:198–207.4. Salvati EA, Cornell CN. Long-term follow-up of total hip replacement in patients with avascular necrosis. Instr Course Lect. 1988. 37:67–73.5. Kim YH, Choi Y, Kim JS. Cementless total hip arthroplasty with alumina-on-highly cross-linked polyethylene bearing in young patients with femoral head osteonecrosis. J Arthroplasty. 2011. 26:218–223.
Article6. Kim YH, Choi Y, Kim JS. Cementless total hip arthroplasty with ceramic-on-ceramic bearing in patients younger than 45 years with femoral-head osteonecrosis. Int Orthop. 2010. 34:1123–1127.
Article7. Kim YH, Kim JS, Park JW, Joo JH. Contemporary total hip arthroplasty with and without cement in patients with ssteonecrosis of the femoral head: a concise follow-up, at an average of seventeen years, of a previous report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011. 93:1806–1810.
Article8. Millar NL, Halai M, McKenna R, McGraw IW, Millar LL, Hadidi M. Uncemented ceramic-on-ceramic THA in adults with osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Orthopedics. 2010. 33:795.
Article9. Buly R. The S-ROM stem: versatility of stem/sleeve combinations and head options. Orthopedics. 2005. 28:s1025–s1032.
Article10. Goldstein WM, Branson JJ. Modular femoral component for conversion of previous hip surgery in total hip arthroplasty. Orthopedics. 2005. 28:s1079–s1084.
Article11. Spitzer AI. The S-ROM cementless femoral stem: history and literature review. Orthopedics. 2005. 28:s1117–s1124.
Article12. Christie MJ, DeBoer DK, Trick LW, et al. Primary total hip arthroplasty with use of the modular S-ROM prosthesis. Four to seven-year clinical and radiographic results. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999. 81:1707–1716.
Article13. Harris WH. Traumatic arthritis of the hip after dislocation and acetabular fractures: treatment by mold arthroplasty. An end-result study using a new method of result evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1969. 51:737–755.
Article14. Widmer KH, Zurfluh B. Compliant positioning of total hip components for optimal range of motion. J Orthop Res. 2004. 22:815–821.
Article15. Khalily C, Lester DK. Results of a tapered cementless femoral stem implanted in varus. J Arthroplasty. 2002. 17:463–466.
Article16. Martell JM, Pierson RH 3rd, Jacobs JJ, Rosenberg AG, Maley M, Galante JO. Primary total hip reconstruction with a titanium fiber-coated prosthesis inserted without cement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993. 75:554–571.
Article17. Engh CA, Massin P, Suthers KE. Roentgenographic assessment of the biologic fixation of porous-surfaced femoral components. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990. 257:107–128.
Article18. Latimer HA, Lachiewicz PF. Porous-coated acetabular components with screw fixation. Five to ten-year results. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1996. 78:975–981.
Article19. Engh CA, Hooten JP Jr, Zettl-Schaffer KF, et al. Porous-coated total hip replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994. 298:89–96.
Article20. DeLee JG, Charnley J. Radiological demarcation of cemented sockets in total hip replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1976. 121:20–32.
Article21. Gruen TA, McNeice GM, Amstutz HC. "Modes of failure" of cemented stem type femoral components: a radiographic analysis of loosening. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1979. 141:17–27.22. Brooker AF, Bowerman JW, Robinson RA, Riley LH Jr. Ectopic ossification following total hip replacement. Incidence and a method of classification. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1973. 55:1629–1632.23. Kaplan EL, Meier P. Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc. 1958. 53:457–481.
Article24. Brinker MR, Rosenberg AG, Kull L, Galante JO. Primary total hip arthroplasty using noncemented porous-coated femoral components in patients with osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Arthroplasty. 1994. 9:457–468.
Article25. Cornell CN, Salvati EA, Pellicci PM. Long-term follow-up of total hip replacement in patients with osteonecrosis. Orthop Clin North Am. 1985. 16:757–769.
Article26. Haddad RJ, Cook SD, Brinker MR. A comparison of three varieties of noncemented porous-coated hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1990. 72:2–8.
Article27. Taylor AH, Shannon M, Whitehouse SL, Lee MB, Learmonth ID. Harris Galante cementless acetabular replacement in avascular necrosis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2001. 83:177–182.
Article28. Yoo MC, Cho YJ, Kim KI, et al. Long term follow up study of cementless total hip arthroplasty for osteonecrosis of the femoral head: minimum 10-year follow up study. J Korean Hip Soc. 2004. 16:1–9.29. Han CD, Choi WS, Lee WS, Cho JH. Cementless total hip arthroplasty for osteonecrosis in patients forty-five years old and less:minimum 5-year follow-up result. J Korean Hip Soc. 1999. 11:134–141.30. Willert HG, Buchhorn GH, Fayyazi A, et al. Metal-on-metal bearings and hypersensitivity in patients with artificial hip joints. A clinical and histomorphological study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005. 87:28–36.
Article31. Davies AP, Willert HG, Campbell PA, Learmonth ID, Case CP. An unusual lymphocytic perivascular infiltration in tissues around contemporary metal-on-metal joint replacements. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005. 87:18–27.
Article32. Kim SY, Kyung HS, Ihn JC, Cho MR, Koo KH, Kim CY. Cementless Metasul metal-on-metal total hip arthroplasty in patients less than fifty years old. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004. 86-A:2475–2481.
Article33. Park YS, Moon YW, Lim SJ, Yang JM, Ahn G, Choi YL. Early osteolysis following second-generation metal-on-metal hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005. 87:1515–1521.
Article34. Bourne RB, Rorabeck CH, Ghazal ME, Lee MH. Pain in the thigh following total hip replacement with a porous-coated anatomic prosthesis for osteoarthrosis. A five-year follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1994. 76:1464–1470.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Failure of a Ceramic Head in Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Case Report
- Failure of a Metal Femoral Head after Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty for a Ceramic Liner Fracture
- The Early Results of a Cementless Total Hip Arthroplasty in Femoral Head Necrosis in Renal Transplant Recipients
- Arthroplasty in Femoral Head Osteonecrosis
- Ceramic on Ceramic Cementless Total Hip Arthroplasty with a 36 mm Diameter Femoral Head: More than Three Years Follow up