Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr.
2011 Mar;14(1):67-73. 10.5223/kjpgn.2011.14.1.67.
An Epidemiologic Study on the Seropositive Rate of Hepatitis A Virus in Children of Gwangju and Jeonnam
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, School of Medicine, Chosun University, Gwangju, Korea. krmoon@chosun.ac.kr
- 2Department of Medical Education, School of Medicine, Chosun University, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 1451208
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5223/kjpgn.2011.14.1.67
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Recently, the incidence of acute hepatitis A has increased nationwide and is related to a low rate of IgG anti-HAV production. To establish effective measures for preventing hepatitis A virus infection, an epidemiologic study on the seroprevalence of anti-HAV is needed. Thus, we investigated the seroprevalence of IgG anti-HAV in children living in Gwangju and Jeonnam.
METHODS
IgG anti-HAV levels were measured in a total of 1,435 patients who visited Chosun University Hospital between January 2009 and December 2009.
RESULTS
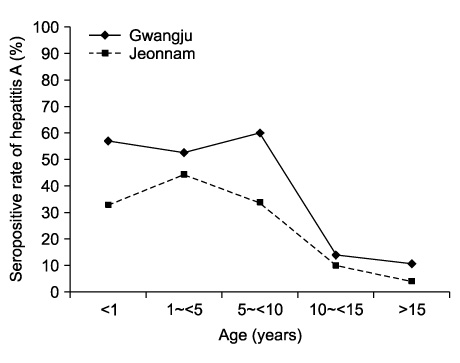
The overall seropositve rate was 40.8% (586/1,435). The seropositive rates were 41% among children under the age of 1 year, 49.9% for children 1~5 years old, 51.1% among individuals 5~10 years old, 12.9% for individuals 10~15 years old, and 8.2% for subjects over 15 years old. There was no significant difference between genders in any group. The seropositive rates in Gwangju and Jeonnam were 57.3% and 32.9% for children under the age of 1 year, 52.5% and 44.3% for children 1~5 years old, 60.2% and 33.9% among children 5~10 years old, 14.1% and 9.7% for children 10~15 years old, and 10.8% and 4.2% for individuals over 15 years old.
CONCLUSION
The results demonstrated the low rates of IgG anti-HAV, particularly among subjects over 10 years old, which suggests the possibility of increasing clinical HAV infection rates among adults in the near future. We should actively prevent the spread of hepatitis A virus. Vaccination is the most effective means of preventing hepatitis A virus transmission among persons at risk for infection. Hepatitis A vaccination is recommended for children who have low IgG anti-HAV seropositive rates.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Cuthbert JA. Hepatitis A: old and new. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2001. 14:38–58.
Article2. Hong WS, Kim CY. Seroepidemoiology of type A and type B hepatitis in Seoul Area. Korean J Intern Med. 1982. 25:19–26.3. Choi W, Eom HS, Kim IH, Lee DH, Kim PS, Kim HG, et al. Patterns of acute hepatitis A and anti-HAV sero-prevalence of Kyungin Province. Korean J Gastroenterol. 1999. 34:69–75.4. Kim NJ, Sung JK, Lee SW. An outbreak of hepatitis A in Taejeon city. Korean J Gastroenterol. 1999. 34:205–212.5. Glikson M, Galun E, Oren R, Tur-Kaspa R, Shouval D. Relapsing hepatitis A. Review of 14 cases and literature survey. Medicine. 1992. 71:14–23.
Article6. Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). Fiore AE, Wasley A, Bell BP. Prevention of hepatitis A through active or passive immunization: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR Recomm Rep. 2006. 55:1–23.7. Hadler SC, Webster HM, Erben JJ, Swanson JE, Maynard JE. Hepatitis A in day care centers. A community-wide assessment. N Engl J Med. 1980. 302:1222–1227.8. Choi HJ, Lee SY, Ma SH, Kim JH, Hur JK, Kang JH. Age related prevalence of antibodies to hepatitis A virus performed in Korea in 2005. Korean J Pediatr Infect Dis. 2005. 12:186–194.
Article9. Feinstone SM, Kapikian AZ, Purceli RH. Hepatitis A:detection by immune electron microscopy of a viruslike antigen associated with acute illness. Science. 1973. 182:1026–1028.
Article10. Moon KR. Hepatitis A. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2008. 11:44–49.11. Youn HS. Current status of hepatitis A virus infections in Korea. Korean J Pediatr. 2008. 51:690–695.
Article12. Nelson KE. Global changes in the epidemiology of hepatitisA virus infections. Clin Infect Dis. 2006. 42:1151–1152.13. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Prevention of hepatitis A through active or passive immunization: Recommendation of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR Recomm Rep. 1999. 48(RR-12):1–37.14. Kim CY, Hong WS. Seroepidemiology of type A and type B hepatitis in Seoul area. Korean J Intern Med. 1982. 25:19–27.15. Lee JI, Kim JY, Kim ST, Yoo SY, Chung SM, Kim YK, et al. Epidemiologic study of antibody to hepatitis A antigen in Choong Chung area. Korean J Gastroenterol. 1982. 14:87–91.16. Kim TW, Lee KJ. Antibody of hepatitis A antigen in children and adolescents in Korea. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1982. 25:36–40.17. Lee KY, Song KH, Kang JH. Seroepidemiology of hepatitis A in Taejon, Korea 1996. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1998. 41:53–61.18. Park CH. Changes in teh age-specific prevalence of hepatitis A virus antibodies: a 10 year cohort study in Jinju, South Korea. Clin Infect Dis. 2006. 42:1148–1150.
Article19. Kim SY. Concordance of Seropositivity between Helicobacter pylori and Hepatitis A virus IgG in children of Gwangju and Chonnam Area. Korean J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2001. 4:191–198.
Article20. Kim H, Kim JH, Kim DH, Heo JK, Lee WB, Seo BK, et al. Epidemiologic changes and clinical features of hepatitis A in children; living in Kyung-gi province, since 1988 to 1998. Korean J Pediatr Infect Dis. 1998. 5:230–236.
Article21. Duval B, De Serres G, Ochnio J, Scheifele D, Gilca V. Nationwide Canadian study of hepatitis A antibody prevalence among children eight to thirteen years old. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2005. 24:514–519.
Article22. Song YB, Lee JH, Choi MS, Koh KC, Paik SW, Yoo BC, et al. The age-specific seroprevalence of hapatitis A virus antibody in Korea. Korean J Hepatol. 2007. 13:27–33.23. CDC. Prevention of hepatitis A through active or passive immunization. Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR Recomm Rep. 2006. 55:1–23.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- An epidemiologic study on the seropositive rate of hepatitis A virus among a selected group of children and adults in Busan
- Epidemiologic Study on Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Childhood
- Epidemiologic study for serologic markers of hepatitis B virus ininstitutionalized population
- Molecular and Clinical Characterization of Hepatitis A Virus in Gwangju and Jeonnam Province
- Prevention of Viral Hepatitis and Vaccination