J Korean Fract Soc.
2011 Jan;24(1):23-27. 10.12671/jkfs.2011.24.1.23.
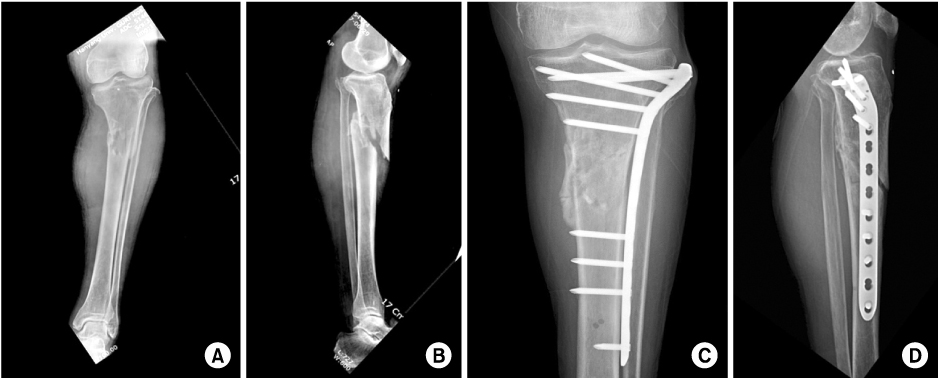
Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis for Proximal Tibial Shaft Fracture
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Guri Hospital, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Guri, Korea. kcpark@hanyang.ac.kr
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Daegu Fatima Hospital, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 1449412
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2011.24.1.23
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To report the results of patients treated by minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) for proximal tibial shaft fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From September 2003 to June 2008, thirty-two patients with proximal tibial shaft fractures weretreated by MIPO. There were 22 men and 10 women and mean age was 43.8 years (range; 21~72 years). Follow-up was available for all patients and the mean follow-up period was 19.5 months (range; 12~40 months). Duration of union, range of knee motion and postoperative complications were evaluated.
RESULTS
Twenty-nine patients (90.6%) healed after the MIPO technique. The mean duration of radiographic union was 18.3 weeks (range; 10~28 weeks). The mean range of knee motion was 134 degrees at the last follow-up. There were 1 non-union, 2 delayed unions, 1 superficial infection, 1 deep infection, 2 malunions with more than 5 degrees of malalignment and 14 cases of skin irritation by plate.
CONCLUSION
MIPO is an effective treatment for closed, proximal tibialshaft fractures. More aggressive treatment such as dual plating should be considered in fractures with severe comminution or bone loss.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Stabilization Using a Medial Locking Plate for Proximal Tibial Fractures - Technical Note -
Jae Ang Sim, Beom Koo Lee, Kwang Hui Kim, Yong Seuk Lee
J Korean Fract Soc. 2013;26(4):327-332. doi: 10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.4.327.Medial Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis in Proximal Tibial Comminuted Fractures
Jae-Ang Sim, Kwang-Hui Kim, Yong-Seuk Lee, Sang-Jin Lee, Beom-Koo Lee
J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2014;49(4):278-284. doi: 10.4055/jkoa.2014.49.4.278.
Reference
-
1. Boldin C, Fankhauser F, Hofer HP, Szyszkowitz R. Three-year results of proximal tibia fractures treated with the LISS. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006. 445:222–229.
Article2. Böstman O, Hänninen A. The fibular reciprocal fracture in tibial shaft fractures caused by indirect violence. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1982. 100:115–121.
Article3. Cole PA, Zlowodzki M, Kregor PJ. Treatment of proximal tibia fractures using the less invasive stabilization system: surgical experience and early clinical results in 77 fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2004. 18:528–535.
Article4. Collinge C, Sanders R, DiPasquale T. Treatment of complex tibial periarticular fractures using percutaneous techniques. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000. 375:69–77.
Article5. D'Aubigne RM, Maurer P, Zucman J, Masse Y. Blind intramedullary nailing for tibial fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1974. 105:267–275.6. Egol KA, Tejwani NC, Capla EL, Wolinsky PL, Koval KJ. Staged management of high-energy proximal tibia fractures (OTA types 41): the results of a prospective, standardized protocol. J Orthop Trauma. 2005. 19:448–455.7. Gerber A, Ganz R. Combined internal and external osteosynthesis a biological approach to the treatment of complex fractures of the proximal tibia. Injury. 1998. 29:Suppl 3. C22–C28.
Article8. Helfet DL, Suk M. Minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis of fractures of the distal tibia. Instr Course Lect. 2004. 53:471–475.9. Kim JW, Oh CW, Oh JK, et al. Staged minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis of proximal tibial fracture. J Korean Fract Soc. 2009. 22:6–12.
Article10. Lachiewicz PF, Funcik T. Factors influencing the results of open reduction and internal fixation of tibial plateau fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990. 259:210–215.
Article11. Laflamme GY, Heimlich D, Stephen D, Kreder HJ, Whyne CM. Proximal tibial fracture stability with intramedullary nail fixation using oblique interlocking screws. J Orthop Trauma. 2003. 17:496–502.
Article12. Lang GJ, Cohen BE, Bosse MJ, Kellam JF. Proximal third tibial shaft fractures. Should they be nailed? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995. 315:64–74.13. Littenberg B, Weinstein LP, McCarren M, et al. Closed fractures of the tibial shaft. A meta-analysis of three methods of treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998. 80:174–183.14. Oh CW, Oh JK, Jeon IH, et al. Double plating of proximal tibial fractures using minimally invasive percutaneous osteosynthesis technique. J Korean Fract Soc. 2005. 18:250–255.
Article15. Oh CW, Oh JK, Jeon IH, et al. Minimally invasive percutaneous plate stabilization of proximal tibial fractures. J Korean Fract Soc. 2004. 17:224–229.
Article16. Peindl RD, Zura RD, Vincent A, Coley ER, Bosse MJ, Sims SH. Unstable proximal extraarticular tibia fractures: a biomechanical evaluation of four methods of fixation. J Orthop Trauma. 2004. 18:540–545.17. Perren SM. Evolution of the internal fixation of long bone fractures. The scientific basis of biological internal fixation: choosing a new balance between stability and biology. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002. 84:1093–1110.18. Phisitkul P, McKinley TO, Nepola JV, Marsh JL. Complications of locking plate fixation in complex proximal tibia injuries. J Orthop Trauma. 2007. 21:83–91.
Article19. Sarmiento A, Gersten LM, Sobol PA, Shankwiler JA, Vangsness CT. Tibial shaft fractures treated with functional braces. Experience with 780 fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1989. 71:602–609.
Article20. Schatzker J, Lambert DC. Supracondylar fractures of the femur. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1979. 138:77–83.
Article21. Schatzker J, McBroom R, Bruce D. The tibial plateau fracture. The Toronto experience 1968--1975. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1979. 138:94–104.22. Tejwani NC, Achan P. Staged management of high-energy proximal tibia fractures. Bull Hosp Jt Dis. 2004. 62:62–66.23. Whiteside LA, Lesker PA. The effects of extraperiosteal and subperiosteal dissection. II. On fracture healing. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1978. 60:26–30.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Stabilization Using a Medial Locking Plate for Proximal Tibial Fractures: Technical Note
- Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis for Humeral Proximal or Distal Shaft Fractures Using a 3.5/5.0 Metaphyseal Locking Plate
- Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis for Distal Tibial Shaft Fracture
- Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis Using a Lateral Plate in Distal Tibial Fracture
- The Comparison of Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis and Intramedullary Nailing in the Treatment of the Proximal and Distal Tibia Fracture