J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2011 Dec;18(4):268-272. 10.4184/jkss.2011.18.4.268.
Gelfoam Granuloma Formation and Myelopathy after Posterior Decompression in Thoracic Spine: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, College of Medicine, Dong-A University, Busan, Korea. gylee@dau.ac.kr
- KMID: 1448007
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2011.18.4.268
Abstract
- STUDY DESIGN: A case report.
OBJECTIVES
To document that Gelfoam(R) (Pharmacia & Upjohn, Kalamazoo, MI) contributes to granuloma formation and spinal cord irritation by immune response. SUMMARY OF LITERATURE REVIEW: The Gelfoam(R) or microfibrillar collagen applied during various operation for hemostasis. Some complications of Gelfoam(R), such as mechanical cord compression, postoperative swelling and mass effect in closed cavity have been reported.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
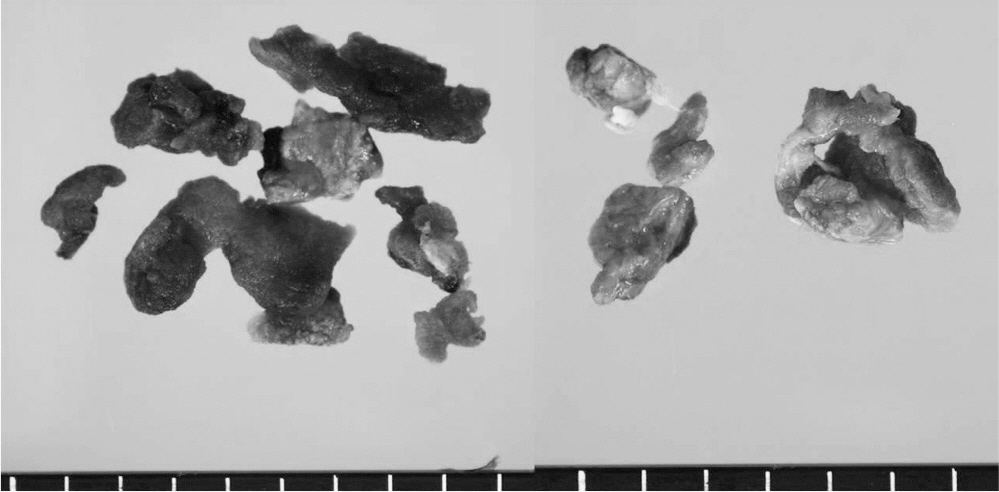
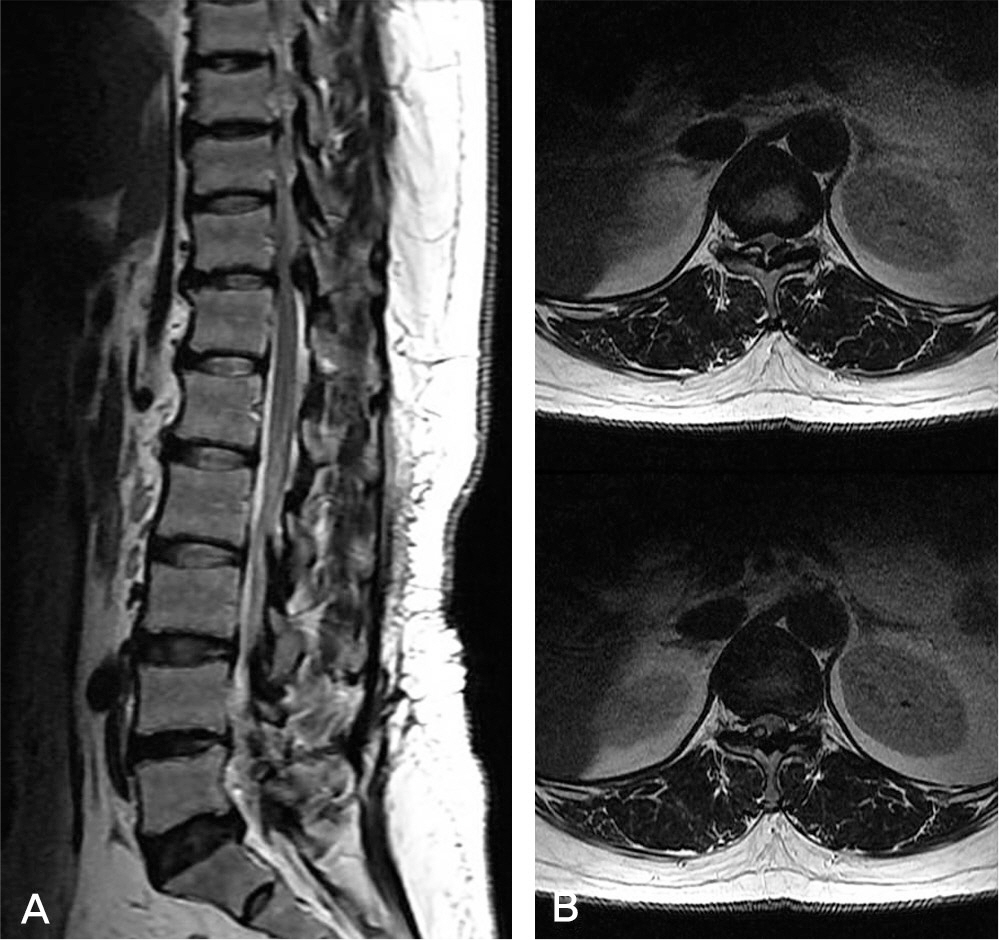
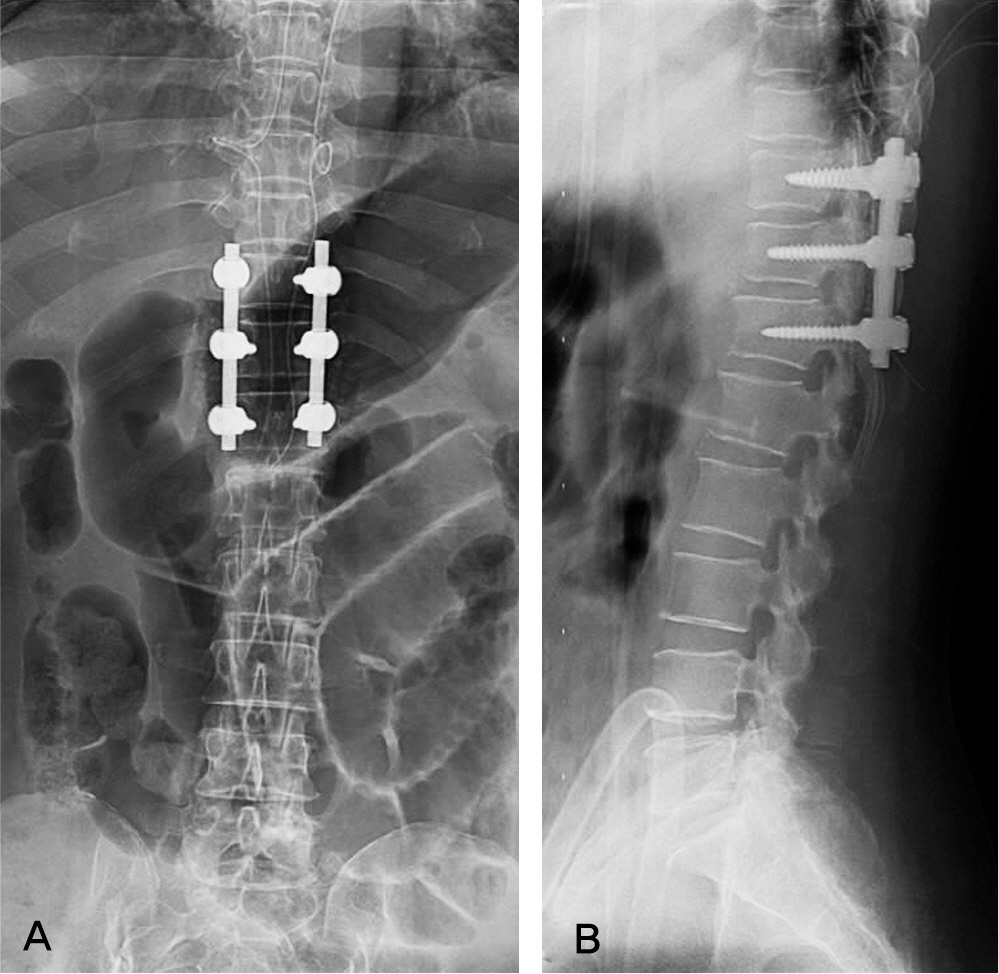
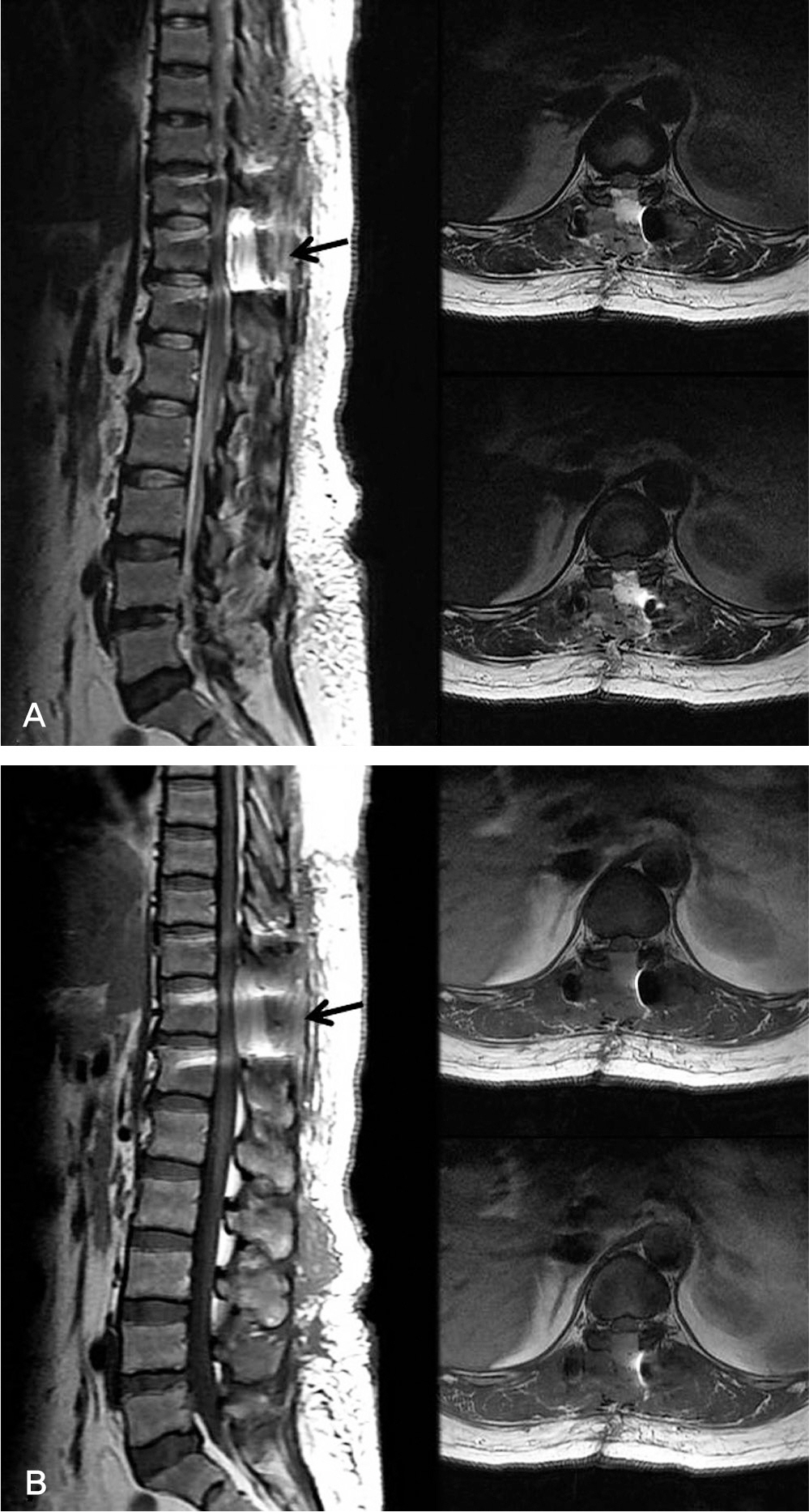
The patient was underwent posterior decompression and instrumented posterolateral fusion under the diagnosis of the ossification of ligamentum flavum at T10-11 and T11-12. In operation, Gelfoam(R) was used at epidural space. She complained of sensory deterioration and muscle weakness around lower extremities after 10days postoperatively. A second operation was performed.
RESULTS
Postoperatively, the patient immediately improved motor grade except spasticity. She is under observation.
CONCLUSIONS
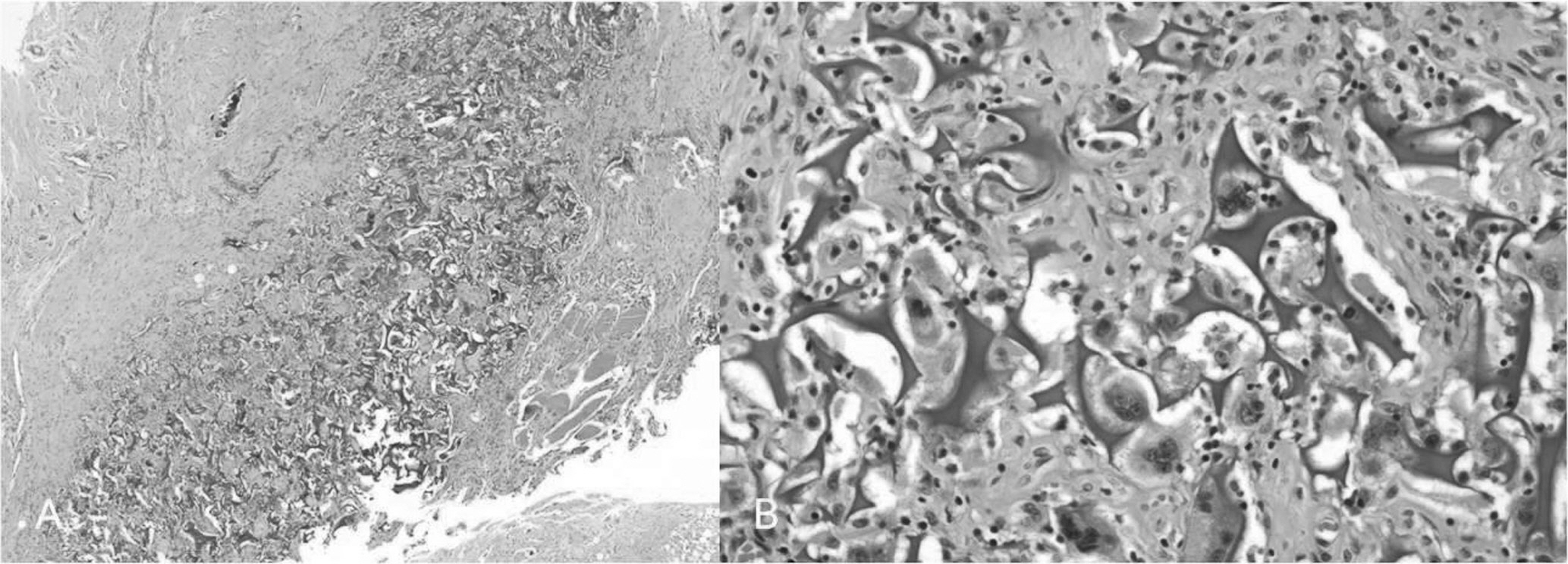
Gelfoam(R) at epidural space after posterior decompression can result hyperactive immune reaction and irritate spinal cord.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Harris WH, Crothers OD, Moyen BJ. Topical hemostatic agents for bone bleeding in humans. A quantitative comparison of gelatin paste, gelatin sponge plus bovine thrombin, and microfibrillar collagen. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1978; 60:454–6.
Article2. Tomizawa Y. Clinical benefits and risk analysis of topical hemostats: a review. J Artif Organs. 2005; 8:137–42.
Article3. Friedman J, Whitecloud TS. Lumbar cauda equina syndrome associated with the use of Gelfoam: case report. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001; 26:E485–7.4. Herndon JH, Grillo HE, Roseborough EJ, Rich JC. Compression of the brain and spinal cord following use of Gelfoam. Arch Surg. 1972; 104:107.
Article5. Epstein NE, Silvergleid RS, Hollingsworth R. Increased postoperative cervical myelopathy and cord compression resulting from the use of Gelfoam. Spine J. 2009; 9:E19–21.
Article6. Shenoi PM, Ballantyne JC, Bredberg G. Absorbable gelatin sponge B.P. (sterispon) and poststapedectomy sensorineural hearing loss: a phase contrast microscopic report on the human temporal bone. J Laryngol Otol. 1975; 89:159–68.
Article7. Knowlson GT. Gelfoam granuloma in the brain. J Neuro Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1974; 37:971–3.
Article8. Blaine G. Absorbable gelatin sponge in experimental surgery. Lancet. 1951; 2:427–9.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Fracture of Ossification of the Yellow Ligament Causing Thoracic Myelopathy: A Case Report
- Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy: Pathophysiology and Current Treatment Strategies
- Treatment of Ossification of Posterior Longitudinal Ligament in Cervical Spine with Anterior Fusion and Anterior Decompression: Report of 3 Cases
- Thoracic Myelopathy Caused by Multiple Ossified Ligamentum flavum Combined with Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament
- Eosinophilic Granuloma in an Adult Thoracic Spine: A Case Report