J Korean Surg Soc.
2011 Oct;81(4):291-294. 10.4174/jkss.2011.81.4.291.
Huge carotid body paraganglioma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Ulsan University Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Ulsan, Korea. ud3012md@medimail.co.kr
- 2Department of Vascular Surgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1445752
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2011.81.4.291
Abstract
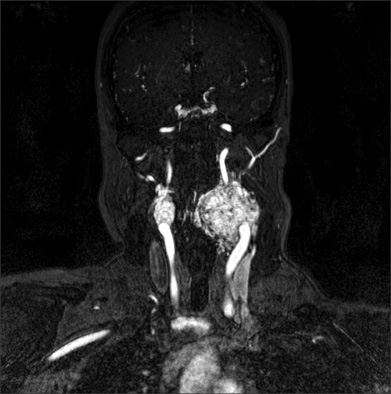
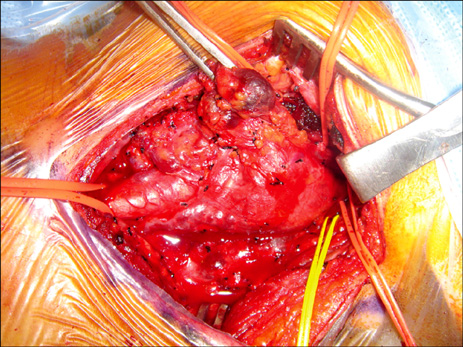
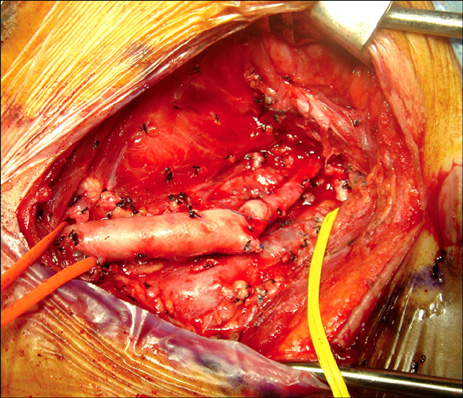
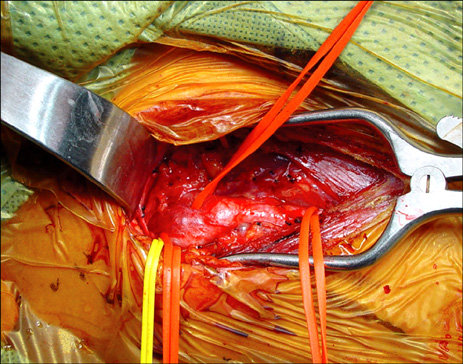
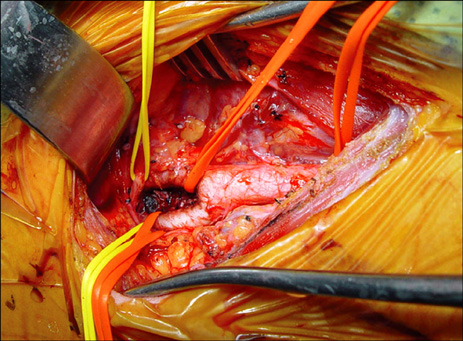
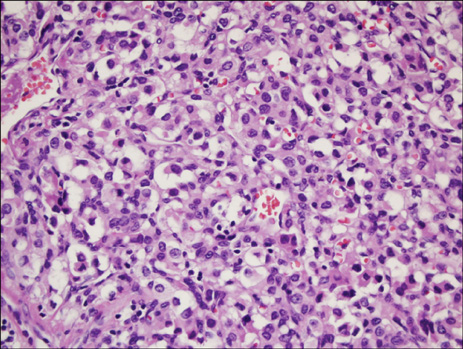
- A 33-year-old woman was admitted to our hospital with a slow-growing mass in the left side of her neck. The mass was found to be a huge (73 x 56 x 54 mm) carotid body paraganglioma. Another 21 mm-size tumor was incidentally detected at the right carotid bifurcation. She had hoarseness and Horner's syndrome of her left side. Both tumors were surgically removed. There were no cerebrovascular complications but some neurologic complications occurred when the left tumor was removed.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Linder F. Tumoren der Karotisdrüse. Langenbecks Arch Chir Suppl Kongressbd. 1953. 276:156–162.2. Shamblin WR, ReMine WH, Sheps SG, Harrison EG Jr. Carotid body tumor (chemodectoma). Clinicopathologic analysis of ninety cases. Am J Surg. 1971. 122:732–739.3. Dimakakos PB, Kotsis TE. Carotid body paraganglioma: review and surgical management. Eur J Plast Surg. 2001. 24:58–65.4. Carroll W, Stenson K, Stringer S. Malignant carotid body tumor. Head Neck. 2004. 26:301–306.5. van den Berg R. Imaging and management of head and neck paragangliomas. Eur Radiol. 2005. 15:1310–1318.6. Persky MS, Setton A, Niimi Y, Hartman J, Frank D, Berenstein A. Combined endovascular and surgical treatment of head and neck paragangliomas: a team approach. Head Neck. 2002. 24:423–431.7. van der Bogt KE, Vrancken Peeters MP, van Baalen JM, Hamming JF. Resection of carotid body tumors: results of an evolving surgical technique. Ann Surg. 2008. 247:877–884.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Bilateral Carotid Body Tumor with Functional Paraganglioma of the Retroperitoneum
- Carotid body paraganglioma showing multiple spinal metastases
- Synchronous Intra-Thyroid Paraganglioma with Carotid Body Tumor
- Breast Metastasis from Malignant Paraganglioma: A Case Report
- Multiple Metastases of Paraganglioma: A case report