J Korean Soc Radiol.
2011 Jan;64(1):71-74. 10.3348/jksr.2011.64.1.71.
Calcific Myonecrosis of the Lower Extremities: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Seoul Veterans Hospital, Korea. orabykim@paran.com
- 2Department of Pathology, Seoul Veterans Hospital, Korea.
- KMID: 1443585
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2011.64.1.71
Abstract
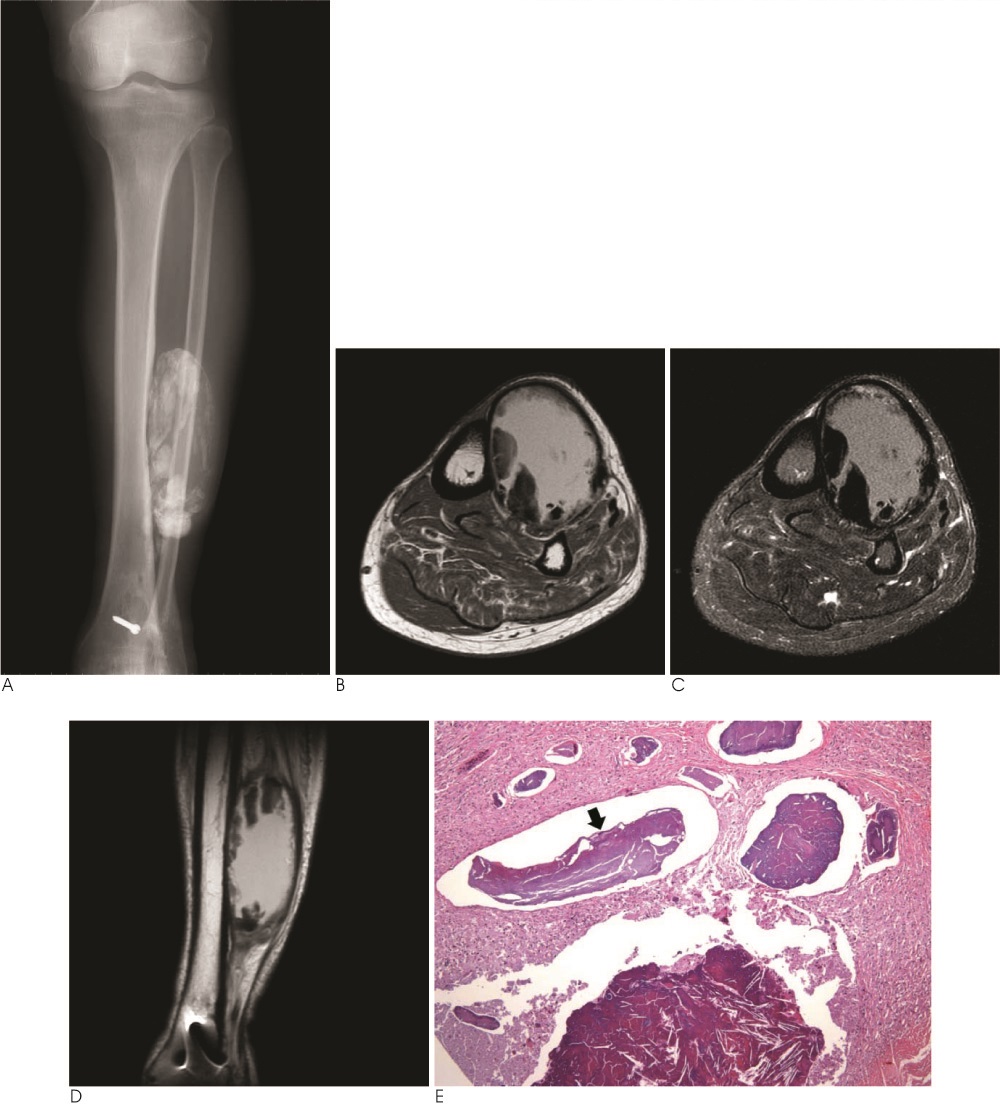
- Calcific myonecrosis is a rare and latent condition of the lower extremities after a trauma and is characterized by the formation of a fusiform mass lesion in the anterior compartment of the leg showing peripheral dystrophic calcification and central liquefaction. We report the radiologic findings of calcific myonecrosis in a patient with a lower extremity calcified mass lesion.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Holobinko JN, Damron TA, Scerpella PR, Hojnowski L. Calcific myonecrosis: keys to early recognition. Skeletal Radiol. 2003; 32:35–40.2. Muramatsu K, Ihara K, Seki T, Imagama T, Taguchi T. Calcific myonecrosis of the lower leg: diagnosis and options of treatment. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2009; 129:935–939.3. Larson RC, Sierra RJ, Sundaram M, Inwards C, Scully SP. Calcific myonecrosis: a unique presentation in the upper extremity. Skeletal Radiol. 2004; 33:306–309.4. O'Dwyer HM, Al-Nakshabandi NA, Al-Muzahmi K, Ryan A, O'Connell JX, Munk PL. Calcific myonecrosis: keys to recognition and management. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006; 187:W67–W76.5. Tuncay IC, Demirors H, Isiklar ZU, Agildere M, Demirhan B, Tandogan RN. Calcific myonecrosis. Int Orthop. 1999; 23:68–70.6. Janzen DL, Connell DG, Vaisler BJ. Calcific myonecrosis of the calf manifesting as an enlarging soft-tissue mass: imaging features. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1993; 160:1072–1074.7. Dhillon M, Davies AM, Benham J, Evans N, Mangham DC, Grimer RJ. Calcific myonecrosis: a report of ten new cases with an emphasis on MR imaging. Eur Radiol. 2004; 14:1974–1979.8. Viau MR, Pedersen HE, Salciccioli GG, Manoli A 2nd. Ectopic calcification as a late sequela of compartment syndrome. Report of two cases. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1983; 178–180.9. Snyder BJ, Oliva A, Buncke HJ. Calcific myonecrosis following compartment syndrome: report of two cases, review of the literature, and recommendations for treatment. J Trauma. 1995; 39:792–795.10. Wang JW, Chen WJ. Calcific myonecrosis of the leg: a case report and review of the literature. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001; 185–190.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Calcific Myonecrosis of the Calf
- Calcific Myonecrosis of the Antetibial Area
- Extensive calcific myonecrosis of the lower leg treated with free tissue transfer
- Thoracolumbar Paraspinal Myonecrosis after Aortic Dissection
- Arthroscopic treatment of chronic calcific tendinitis with intraosseous migration: a case report