J Korean Soc Radiol.
2011 Apr;64(4):333-339. 10.3348/jksr.2011.64.4.333.
Treatment of Spinal Osseous Metastasis with Combined Percutaneous Radiofrequency Ablation and Vertebroplasty
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Korea University Guro Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hongsj@korea.ac.kr
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Korea University Guro Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1443536
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2011.64.4.333
Abstract
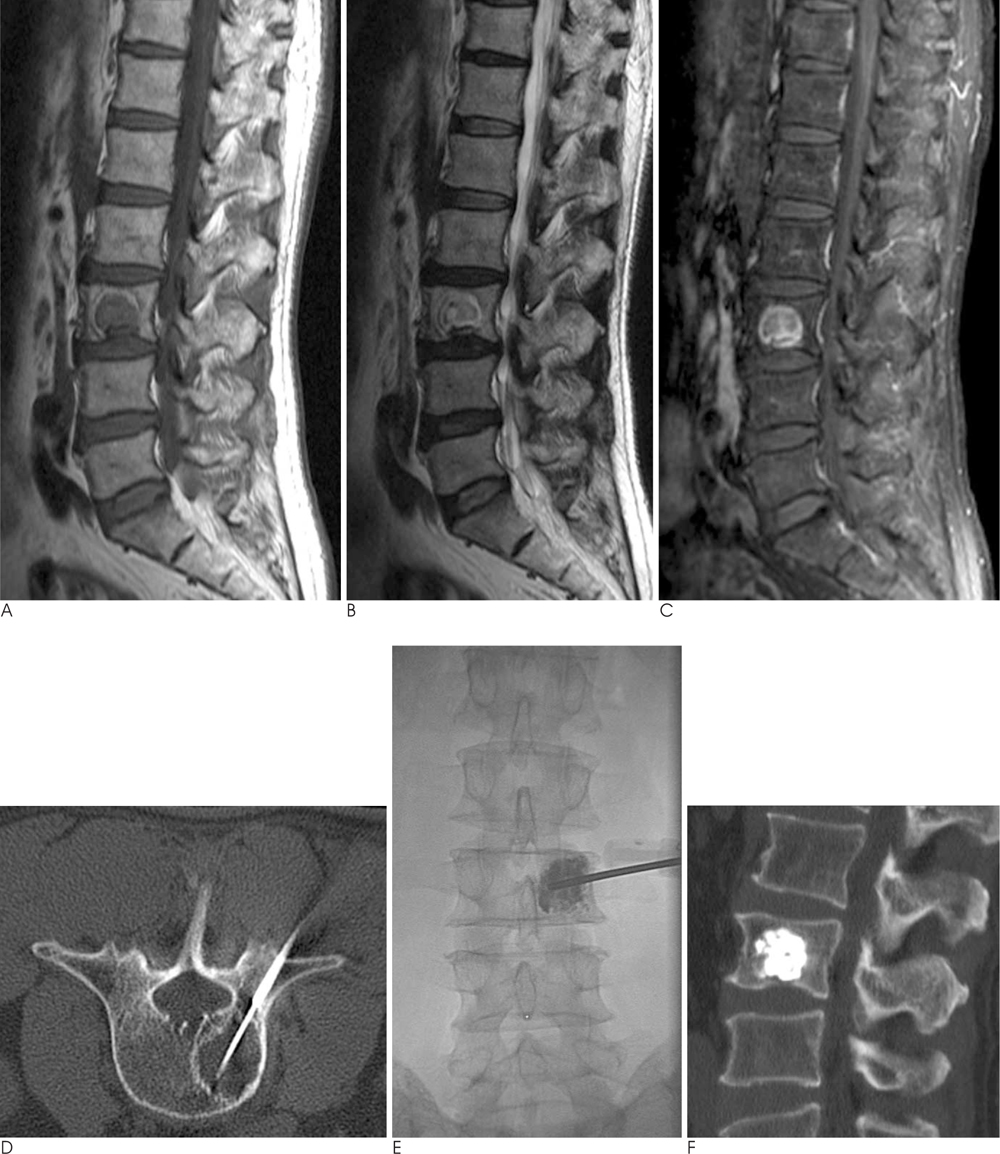
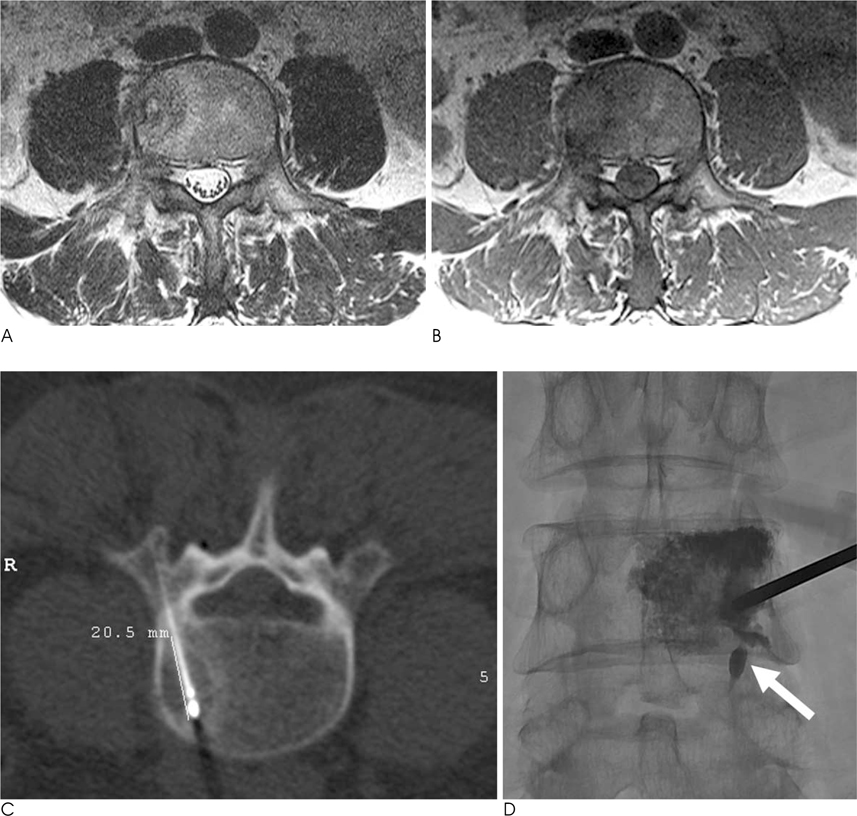
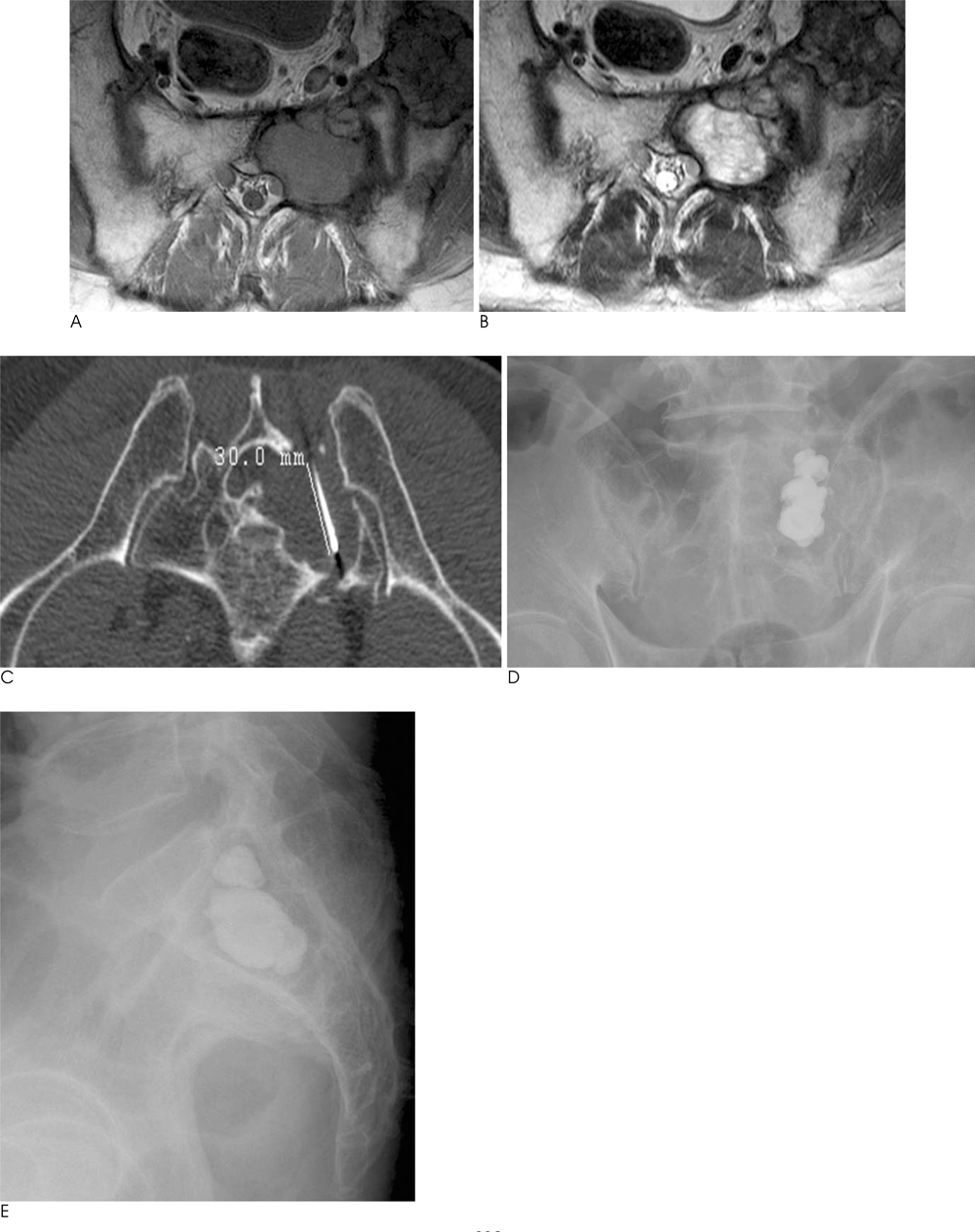
- Recent introduction of image-guided percutaneous methods to treat unresectable bone tumors including metastases that do not respond to conventional radiotherapy or chemotherapy has proven to be effective. Here we present three successfully treated cases of metastatic bone lesions: two cases of malignant bone metastases in the lumbar spine and one in the sacral bone, using combined percutaneous radiofrequency ablation and percutaneous vertebroplasty/cementoplasty. A brief review of literature is also included.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Callstrom MR, Charboneau JW, Goetz MP, Rubin J, Atwell TD, Farrell MA, et al. Image-guided ablation of painful metastatic bone tumors: a new and effective approach to a difficult problem. Skeletal Radiol. 2006; 35:1–15.2. Dupuy DE, Hong R, Oliver B, Goldberg SN. Radiofrequency ablation of spinal tumors: temperature distribution in the spinal canal. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000; 175:1263–1266.3. Goetz MP, Callstrom MR, Charboneau JW, Farrell MA, Maus TP, Welch TJ, et al. Percutaneous image-guided radiofrequency ablation of painful metastases involving bone: a multicenter study. J Clin Oncol. 2004; 22:300–306.4. Hoffmann RT, Jakobs TF, Trumm C, Weber C, Helmberger TK, Reiser MF. Radiofrequency ablation in combination with osteoplasty in the treatment of painful metastatic bone disease. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2008; 19:419–425.5. Gronemeyer DH, Schirp S, Gevargez A. Image-guided radiofrequency ablation of spinal tumors: preliminary experience with an expandable array electrode. Cancer J. 2002; 8:33–39.6. Toyota N, Naito A, Kakizawa H, Hieda M, Hirai N, Tachikake T, et al. Radiofrequency ablation therapy combined with cementoplasty for painful bone metastases: initial experience. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2005; 28:578–583.7. Schaefer O, Lohrmann C, Herling M, Uhrmeister P, Langer M. Combined radiofrequency thermal ablation and percutaneous cementoplasty treatment of a pathologic fracture. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2002; 13:1047–1050.8. Nakatsuka A, Yamakado K, Maeda M, Yasuda M, Akeboshi M, Takaki H, et al. Radiofrequency ablation combined with bone cement injection for the treatment of bone malignancies. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2004; 15:707–712.9. van der Linden E, Kroft LJ, Dijkstra PD. Treatment of vertebral tumor with posterior wall defect using image-guided radiofrequency ablation combined with vertebroplasty: preliminary results in 12 patients. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2007; 18:741–747.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Tageted bipolar radiofrequency decompression with vertebroplasty for intractable radicular pain due to spinal metastasis: a case report
- Two Cases of Percutaneous Vertebroplasty for Spinal Metastatic Cancer: A case report
- Percutaneous Vertebroplasty in Spinal Metastasis and Myeloma:25 Cases Experience
- Lumbar Root Injury by the Leakage of Bone Cement after the Percutaneous Vertebroplasty: A case report
- The Comparision of the Radiofrequency Ablasion Therapy with Vertebroplasty and Radiotherapy in Metastatic Spine Tumor