J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg.
2012 Mar;14(1):5-10. 10.7461/jcen.2012.14.1.5.
Intraarterial Tirofiban Thrombolysis for Thromboembolisms During Coil Embolization for Ruptured Intracranial Aneurysms
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Chuncheon Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea. neurosheen@gmail.com
- KMID: 1441679
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2012.14.1.5
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
Thromboembolus can occur during endovascular coil embolization. The aim of our study was to show our experience of intraarterial (IA) tirofiban infusion for thromboembolism during coil embolization for ruptured intracranial aneurysms.
METHODS
This retrospective analysis was conducted in 64 patients with ruptured aneurysms who had emergent endovascular coil embolization from May 2007 to April 2011 at a single institute. Thromboembolic events were found in ten patients (15.6%). Anticoagulation treatment with intravenous heparin was started after the first coil deployment in ruptured aneurysmal sac. When a thrombus or embolus was found during the procedure, we tried to resolve them without delay with an initial dosage of 0.3 mg of tirofiban up to 1.2 mg.
RESULTS
Three patients of four with total occlusion had recanalizations of thrombolysis in myocardial infarction (TIMI) grade III and five of six with partial occlusion had TIMI grade III recanalizations. Eight patients showed good recovery, with modified Rankin Scale (mRS) score of 0 and one showed poor outcome (mRS 3 and 6). There was no hemorrhagic or hematologic complication.
CONCLUSION
IA tirofiban can be feasible when thromboembolic clots are found during coil embolization in order to get prompt recanalization, even in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage.
MeSH Terms
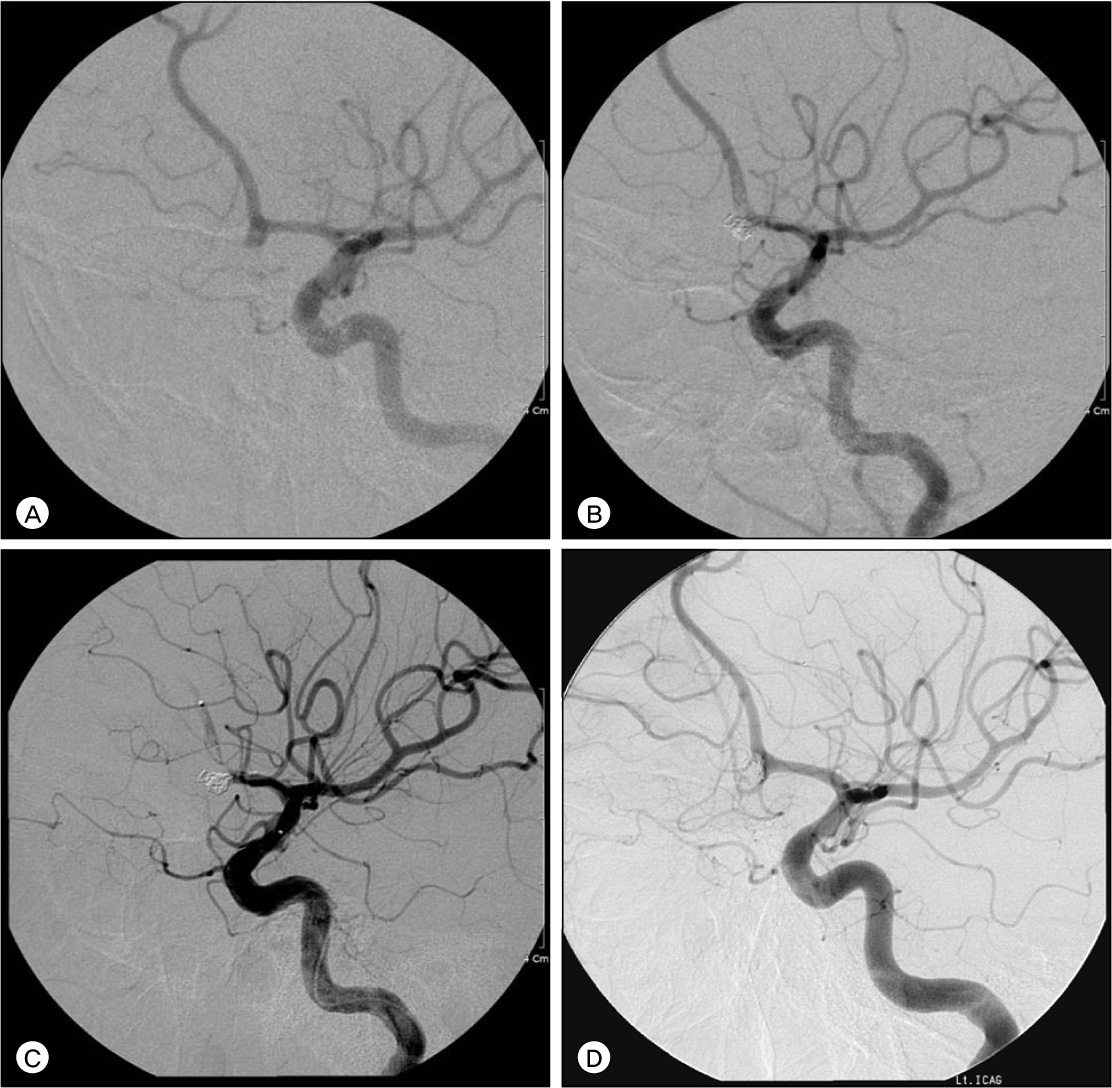
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Intra-arterial and Intravenous Tirofiban Infusion for Thromboembolism during Endovascular Coil Embolization of Cerebral Aneurysm
Sang Heum Kim, Tae Gon Kim, Min Ho Kong
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2017;60(5):518-526. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2016.1212.006.
Reference
-
1. Aster RH, Curtis BR, Bougie DW, Dunkley S, Greinacher A, Warkentin TE, et al. Thrombocytopenia associated with the use of GPIIb/IIIa inhibitors: position paper of the ISTH working group on thrombocytopenia and GPIIb/IIIa inhibitors. J Thromb Haemost. 2006. 03. 4(3):678–679.
Article2. Aviv RI, O'Neill R, Patel MC, Colquhoun IR. Abciximab in patients with ruptured intracranial aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005. 08. 26(7):1744–1750.3. Bougie DW, Wilker PR, Wuitschick ED, Curtis BR, Malik M, Levine S, et al. Acute thrombocytopenia after treatment with tirofiban or eptifibatide is associated with antibodies specific for ligand-occupied GPIIb/IIIa. Blood. 2002. 09. 100(6):2071–2076.
Article4. Bruening R, Mueller-Schunk S, Morhard D, Seelos KC, Brueckmann H, Schmid-Elsaesser R, et al. Intraprocedural thrombus formation during coil placement in ruptured intracranial aneurysms: treatment with systemic application of the glycoprotein IIb/IIIa antagonist tirofiban. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006. Jun-Jul. 27(6):1326–1331.5. Cronqvist M, Pierot L, Boulin A, Cognard C, Castaings L, Moret J. Local intraarterial fibrinolysis of thromboemboli occurring during endovascular treatment of intracerebral aneurysm: a comparison of anatomic results and clinical outcome. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1998. 01. 19(1):157–165.6. Harder S, Klinkhardt U, Alvarez JM. Avoidance of bleeding during surgery in patients receiving anticoagulant and/or antiplatelet therapy: pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic considerations. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2004. 43(14):963–981.7. Hayashi K, Takahata H, Kitagawa N. Ruptured cerebral aneurysm complicated with rebleeding following thrombolysis during endovascular embolization: two case reports. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2007. 06. 47(6):261–264.8. Kang HS, Kwon BJ, Roh HG, Yoon SW, Chang HW, Kim JE, et al. Intra-arterial tirofiban infusion for thromboembolism during endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms. Neurosurgery. 2008. 08. 63(2):230–237. discussion 237-8.
Article9. Kwon OK, Lee KJ, Han MH, Oh CW, Han DH, Koh YC. Intraarterially administered abciximab as an adjuvant thrombolytic therapy: report of three cases. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2002. 03. 23(3):447–451.10. Liebeskind DS, Pollard JR, Schwartz ED, Cucchiara BL, McGarvey ML, Hurst RW. Vertebrobasilar thrombolysis with intravenous tirofiban: case report. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2002. 04. 13(2):81–84.11. McClellan KJ, Goa KL. Tirofiban. A review of its use in acute coronary syndromes. Drugs. 1998. 12. 56(6):1067–1080.12. Park JH, Kim JE, Sheen SH, Jung CK, Kwon BJ, Kwon OK, et al. Intraarterial abciximab for treatment of thromboembolism during coil embolization of intracranial aneurysms: outcome and fatal hemorrhagic complications. J Neurosurg. 2008. 03. 108(3):450–457.
Article13. Ries T, Siemonsen S, Grzyska U, Zeumer H, Fiehler J. Abciximab is a safe rescue therapy in thromboembolic events complicating cerebral aneurysm coil embolization: single center experience in 42 cases and review of the literature. Stroke. 2009. 05. 40(5):1750–1757.14. Song JK, Niimi Y, Fernandez PM, Brisman JL, Buciuc R, Kupersmith MJ, et al. Thrombus formation during intracranial aneurysm coil placement: treatment with intra-arterial abciximab. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2004. 08. 25(7):1147–1153.15. Yi HJ, Gupta R, Jovin TG, Tayal A, Genevro J, Gologorsky Y, et al. Initial experience with the use of intravenous eptifibatide bolus during endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006. 10. 27(9):1856–1860.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Intra-arterial and Intravenous Tirofiban Infusion for Thromboembolism during Endovascular Coil Embolization of Cerebral Aneurysm
- Single-session Coil Embolization of Multiple Intracranial Aneurysms
- Clinical Experience of Thromboembolic Complications of Coil Embolization for Intracranial Aneurysms with Literature Review
- Ruptured Very Small Cerebral Aneurysms and the Usefulness of Coil Embolization
- Rebleeding of Ruptured Intracranial Aneurysms in the Immediate Postoperative Period after Coil Embolization