J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2012 Feb;47(1):28-34. 10.4055/jkoa.2012.47.1.28.
Femoral Head Size of 36 mm against Highly Cross-linked Polyethylene in Patients Younger than 60 Years: Minimun Three Years of Follow Up
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Daegu Catholic University Medical Center, Catholic University of Daegu School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. cmr0426@cu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1439989
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2012.47.1.28
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the early results of total hip arthroplasty (THA) performed using large diameter femoral head against with highly cross-linked polyethylene as a bearing surface in patients less than sixty years of age.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Seventy patients were enrolled and retrospectively reviewed. The mean age of patients at index surgery was 49 years and the mean follow-up period was 61 months. Clinical follow-up involved implementing the Harris hip score (HHS) and a radiographic evaluation that included linear radiolucency, osteolysis, and loosening. An annual wear rate was performed at 6 weeks; at 3, 6, and 12 months; and on a yearly basis thereafter.
RESULTS
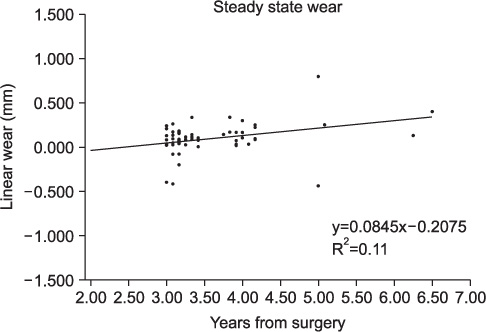
The average HHS at last follow-up was 94 (range: 82-98). Radiographically, no osteolysis in the pelvis or proximal femur was observed in any patient. No acetabular cup or femoral stem failed due to aseptic loosening. No eccentric wear was observed on any liner, and no liner fracture occurred. However, one patient experienced hip dislocation. The average femoral head penetration rate during the first postoperative year was 0.077+/-0.026 mm/year, and the average steady-state wear rate was 0.033+/-0.023 mm/year.
CONCLUSION
THA with a large diameter femoral head of highly cross-linked polyethylene in patients younger than 60 years of age was found to produce results comparable to previous in vitro laboratory hip simulation studies. In particular, patient satisfaction was high due to no limitation in range of motion or hip posture during the early post-operative period. Longer-term follow-up is required to demonstrate the clinical benefits of this new material more comprehensively.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Results of Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty with 36-mm Femoral Heads on Highly Cross-linked Polyethylene-Minimum Seven-years Follow-up
Won-Kee Choi, Myung-Rae Cho, Joo-Hwan Lee
Hip Pelvis. 2014;26(4):220-226. doi: 10.5371/hp.2014.26.4.220.
Reference
-
1. Burroughs BR, Rubash HE, Harris WH. Femoral head sizes larger than 32 mm against highly cross-linked polyethylene. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002. (405):150–157.
Article2. Geller JA, Malchau H, Bragdon C, Greene M, Harris WH, Freiberg AA. Large diameter femoral heads on highly cross-linked polyethylene: minimum 3-year results. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006. 447:53–59.3. Harris WH. Highly cross-linked, electron-beam-irradiated, melted polyethylene: some pros. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004. (429):63–67.4. Harris WH. Traumatic arthritis of the hip after dislocation and acetabular fractures: treatment by mold arthroplasty. An end-result study using a new method of result evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1969. 51:737–755.5. Engh CA, Bobyn JD, Glassman AH. Porous-coated hip replacement. The factors governing bone ingrowth, stress shielding, and clinical results. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1987. 69:45–55.
Article6. Barrack RL, Mulroy RD Jr, Harris WH. Improved cementing techniques and femoral component loosening in young patients with hip arthroplasty. A 12-year radiographic review. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1992. 74:385–389.
Article7. Hammerberg EM, Wan Z, Dastane M, Dorr LD. Wear and range of motion of different femoral head sizes. J Arthroplasty. 2010. 25:839–843.
Article8. D'Antonio JA, Manley MT, Capello WN, et al. Five-year experience with Crossfire highly cross-linked polyethylene. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005. 441:143–150.9. Martell JM, Verner JJ, Incavo SJ. Clinical performance of a highly cross-linked polyethylene at two years in total hip arthroplasty: a randomized prospective trial. J Arthroplasty. 2003. 18:7 Suppl 1. 55–59.
Article10. Cho MR, Lee JK, Lee HS. Comparison of bipolar hemiarthroplasty and total hip arthroplasty using large heads in patients with femoral neck fractures. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2009. 44:514–519.
Article11. Cho MR, Kim SS, Lee HS. Total hip arthroplasty using a large femoral head: the short-term follow-up results and the early complications. J Korean Hip Soc. 2009. 21:232–237.
Article12. Cho MR, Lee HS. Early results after the treatment with total hip arthroplasty with larger diameter femoral head versus bipolar arthroplasty in patients with femoral neck fractures. J Korean Hip Soc. 2007. 19:463–467.
Article13. Engh CA, Griffin WL, Marx CL. Cementless acetabular components. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1990. 72:53–59.
Article14. Kennedy JG, Rogers WB, Soffe KE, Sullivan RJ, Griffen DG, Sheehan LJ. Effect of acetabular component orientation on recurrent dislocation, pelvic osteolysis, polyethylene wear, and component migration. J Arthroplasty. 1998. 13:530–534.
Article15. Widmer KH. A simplified method to determine acetabular cup anteversion from plain radiographs. J Arthroplasty. 2004. 19:387–390.
Article16. Engh CA, Hooten JP Jr, Zettl-Schaffer KF, Ghaffarpour M, McGovern TF, Bobyn JD. Porous-coated total hip replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994. (298):89–96.
Article17. DeLee JG, Charnley J. Radiological demarcation of cemented sockets in total hip replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1976. (121):20–32.
Article18. Gruen TA, McNeice GM, Amstutz HC. "Modes of failure" of cemented stem-type femoral components: a radiographic analysis of loosening. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1979. (141):17–27.19. Brooker AF, Bowerman JW, Robinson RA, Riley LH Jr. Ectopic ossification following total hip replacement. Incidence and a method of classification. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1973. 55:1629–1632.20. Bradford L, Kurland R, Sankaran M, Kim H, Pruitt LA, Ries MD. Early failure due to osteolysis associated with contemporary highly cross-linked ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene. A case report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004. 86-A:1051–1056.21. Heisel C, Silva M, dela Rosa MA, Schmalzried TP. Short-term in vivo wear of cross-linked polyethylene. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004. 86:748–751.
Article22. Dowd JE, Sychterz CJ, Young AM, Engh CA. Characterization of long-term femoral-head-penetration rates. Association with and prediction of osteolysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000. 82:1102–1107.23. Schmalzried TP, Szuszczewicz ES, Northfield MR, et al. Quantitative assessment of walking activity after total hip or knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998. 80:54–59.
Article24. McKellop H, Shen FW, Lu B, Campbell P, Salovey R. Development of an extremely wear-resistant ultra high molecular weight polyethylene for total hip replacements. J Orthop Res. 1999. 17:157–167.25. Furmanski J, Anderson M, Bal S, et al. Clinical fracture of cross-linked UHMWPE acetabular liners. Biomaterials. 2009. 30:5572–5582.
Article26. Lachiewicz PF, Heckman DS, Soileau ES, Mangla J, Martell JM. Femoral head size and wear of highly cross-linked polyethylene at 5 to 8 years. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009. 467:3290–3296.
Article27. McCalden RW, MacDonald SJ, Rorabeck CH, Bourne RB, Chess DG, Charron KD. Wear rate of highly cross-linked polyethylene in total hip arthroplasty. A randomized controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009. 91:773–782.28. d'aubigne RM, Postel M. Functional results of hip arthroplasty with acrylic prosthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1954. 36:451–475.29. Estok DM 2nd, Bragdon CR, Plank GR, Huang A, Muratoglu OK, Harris WH. The measurement of creep in ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene: a comparison of conventional versus highly cross-linked polyethylene. J Arthroplasty. 2005. 20:239–243.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Results of Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty with 36-mm Femoral Heads on Highly Cross-linked Polyethylene-Minimum Seven-years Follow-up
- Results of Total Hip Arthroplasty with 36-mm Metallic Femoral Heads on 1st Generation Highly Cross Linked Polyethylene as a Bearing Surface in Less than Forty Year-old Patients: Minimum Ten-year Results
- Results of Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty Using 36 mm Femoral Heads on 1st Generation Highly Cross Linked Polyethylene in Patients 50 Years and Less with Minimum Five Year Follow-up
- Total Hip Arthroplasty Using Metal Head on a Highly Cross-linked Polyethylene Liner
- A Liner Breakage in Total Hip Arthroplasty after Using 1st Generation Highly Cross Linked Polyethylene Mated against 36-mm Metal Head: A Case Report