Lab Anim Res.
2012 Jun;28(2):131-136. 10.5625/lar.2012.28.2.131.
Pain modality and spinal glia expression by streptozotocin induced diabetic peripheral neuropathy in rats
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Animal Medicine, College of Veterinary Medicine, Chonbuk National University, Jeonju, Korea.
- 2Department of Pharmacology, Institute for Medical Science, Chonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju, Korea. 1972y@jbnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1436712
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5625/lar.2012.28.2.131
Abstract
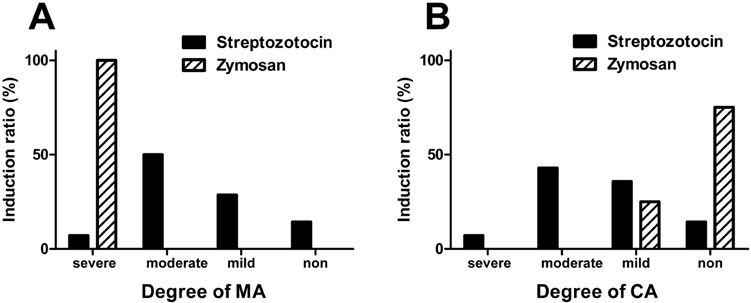
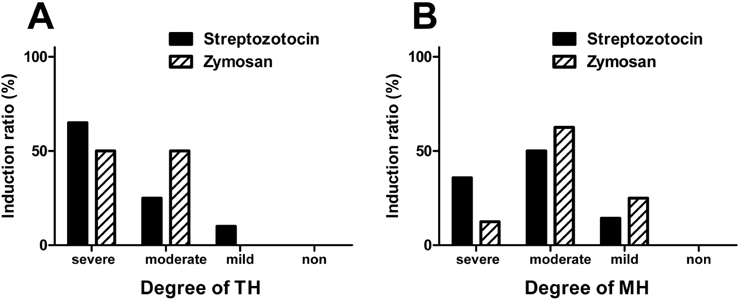
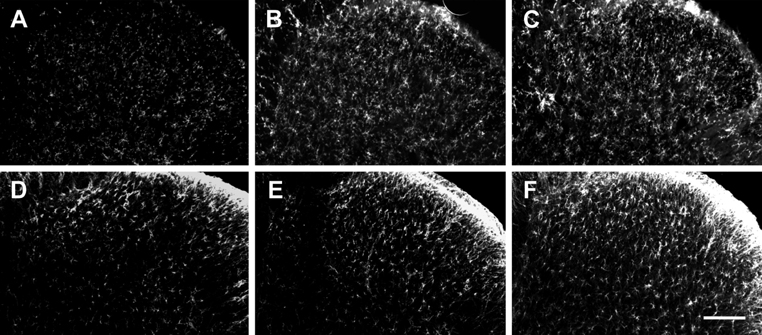
- Pain symptoms are a common complication of diabetic peripheral neuropathy or an inflammatory condition. In the most experiments, only one or two evident pain modalities are observed at diabetic peripheral neuropathy according to experimental conditions. Following diabetic peripheral neuropathy or inflammation, spinal glial activation may be considered as an important mediator in the development of pain. For this reason, the present study was aimed to address the induction of pain modalities and spinal glial expression after streptozotocin injection as compared with that of zymosan inflammation in the rat. Evaluation of pain behavior by either thermal or mechanical stimuli was performed at 3 weeks or 5 hours after either intravenous streptozotocin or zymosan. Degrees of pain were divided into 4 groups: severe, moderate, mild, and non-pain induction. On the mechanical allodynia test, zymosan evoked predominantly a severe type of pain, whereas streptozotocin induced a weak degree of pain (severe+moderate: 57.1%). Although zymosan did not evoke cold allodynia, streptozotocin evoked stronger pain behavior, compared with zymosan (severe+moderate: 50.0%). On the other hand, the high incidence of thermal hyperalgesia (severe+moderate: 90.0%) and mechanical hyperalgesia (severe+moderate: 85.7%) by streptozotocin was observed, as similar to that of zymosan. In the spinal cord, the increase of microglia and astrocyte was evident by streptozotocin, only microglia was activated by zymosan. Therefore, it is recommended that the selection of mechanical and thermal hyperalgesia is suitable for the evaluation of streptozotocin induced diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Moreover, spinal glial activation may be considered an important factor.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Effects of Nefopam on Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Neuropathic Pain in Rats
Jae Sik Nam, Yu Seon Cheong, Myong Hwan Karm, Ho Soo Ahn, Ji Hoon Sim, Jin Sun Kim, Seong Soo Choi, Jeong Gil Leem
Korean J Pain. 2014;27(4):326-333. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2014.27.4.326.
Reference
-
1. Coppey LJ, Davidson EP, Dunlap JA, Lund DD, Yorek MA. Slowing of motor nerve conduction velocity in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats is preceded by impaired vasodilation in arterioles that overlie the sciatic nerve. Int J Exp Diabetes Res. 2000. 1(2):131–143.2. Obrosova IG. Diabetic painful and insensate neuropathy: pathogenesis and potential treatments. Neurotherapeutics. 2009. 6(4):638–647.3. Morrow TJ. Animal models of painful diabetic neuropathy: the STZ rat model. Curr Protoc Neurosci. 2004. Chapter 9:Unit 9. 18.4. Chen SR, Samoriski G, Pan HL. Antinociceptive effects of chronic administration of uncompetitive NMDA receptor antagonists in a rat model of diabetic neuropathic pain. Neuropharmacology. 2009. 57(2):121–126.5. Mixcoatl-Zecuatl T, Jolivalt CG. A spinal mechanism of action for duloxetine in a rat model of painful diabetic neuropathy. Br J Pharmacol. 2011. 164(1):159–169.6. Xu GY, Li G, Liu N, Huang LY. Mechanisms underlying purinergic P2X3 receptor-mediated mechanical allodynia induced in diabetic rats. Mol Pain. 2011. 7:60.7. Fuchs D, Birklein F, Reeh PW, Sauer SK. Sensitized peripheral nociception in experimental diabetes of the rat. Pain. 2010. 151(2):496–505.8. Nirogi R, Jabaris SL, Jayarajan P, Abraham R, Shanmuganathan D, Rasheed MA, Royapalley PK, Goura V. Antinociceptive activity of α4β2* neuronal nicotinic receptor agonist A-366833 in experimental models of neuropathic and inflammatory pain. Eur J Pharmacol. 2011. 668(1-2):155–162.9. Manni L, Florenzano F, Aloe L. Electroacupuncture counteracts the development of thermal hyperalgesia and the alteration of nerve growth factor and sensory neuromodulators induced by streptozotocin in adult rats. Diabetologia. 2011. 54(7):1900–1908.10. Talbot S, Chahmi E, Dias JP, Couture R. Key role for spinal dorsal horn microglial kinin B1 receptor in early diabetic pain neuropathy. J Neuroinflammation. 2010. 7(1):36.11. Pabreja K, Dua K, Sharma S, Padi SS, Kulkarni SK. Minocycline attenuates the development of diabetic neuropathic pain: possible anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant mechanisms. Eur J Pharmacol. 2011. 661(1-3):15–21.12. Bianchi R, Cervellini I, Porretta-Serapiglia C, Oggioni N, Burkey B, Ghezzi P, Cavaletti G, Lauria G. Beneficial effects of PKF275-055, a novel, selective, orally bioavailable, long-acting dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor in streptozotocin-induced diabetic peripheral neuropathy. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012. 340(1):64–72.13. Messinger RB, Naik AK, Jagodic MM, Nelson MT, Lee WY, Choe WJ, Orestes P, Latham JR, Todorovic SM, Jevtovic-Todorovic V. In vivo silencing of the Ca(V)3.2 T-type calcium channels in sensory neurons alleviates hyperalgesia in rats with streptozocin-induced diabetic neuropathy. Pain. 2009. 145(1-2):184–195.14. Naruse K, Sato J, Funakubo M, Hata M, Nakamura N, Kobayashi Y, Kamiya H, Shibata T, Kondo M, Himeno T, Matsubara T, Oiso Y, Nakamura J. Transplantation of bone marrow-derived mononuclear cells improves mechanical hyperalgesia, cold allodynia and nerve function in diabetic neuropathy. PLoS One. 2011. 6(11):e27458.15. Graeber MB, Christie MJ. Multiple mechanisms of microglia: a gatekeeper's contribution to pain states. Exp Neurol. 2012. 234(2):255–261.16. Dixon WJ. Efficient analysis of experimental observations. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1980. 20:441–462.17. Hwang HS, Yang EJ, Lee SM, Lee SC, Choi SM. Antiallodynic Effects of Electroacupuncture Combined with MK-801 Treatment through the Regulation of p35/p25 in Experimental Diabetic Neuropathy. Exp Neurobiol. 2011. 20(3):144–152.18. Liao YH, Zhang GH, Jia D, Wang P, Qian NS, He F, Zeng XT, He Y, Yang YL, Cao DY, Zhang Y, Wang DS, Tao KS, Gao CJ, Dou KF. Spinal astrocytic activation contributes to mechanical allodynia in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes. Brain Res. 2011. 1368:324–335.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Role of Nitric Oxide on the Neuropathic Pain in Streptozotocin-induced Diabetic Rats
- Protective Effect of Melatonin on Neuropathy in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats
- Increased Nociceptive Responses in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats and the Related Expression of Spinal NR2B Subunit of N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Receptors
- Analgesic Effects of DA-5018, a New Capsaicin Derivative, in Hyperalgesia of Experimental Diabetic Neuropathy
- Effect of Empagliflozin, a Selective Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor, on Kidney and Peripheral Nerves in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats