J Korean Soc Spine Surg.
2012 Sep;19(3):116-121. 10.4184/jkss.2012.19.3.116.
Selective Laminoplasty For Cervical Myelopathy: 3 Cases Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Inje University, Seoul Paik Hospital, Seoul, Korea. hd1404@hanafos.com
- KMID: 1435589
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4184/jkss.2012.19.3.116
Abstract
- STUDY DESIGN: 3 cases report.
OBJECTIVES
We present 3 cases of cervical myelopathy treated successfully by selective laminoplasty on 2 levels or less, using Kurokawa technique with a review of the relevant articles. SUMMARY OF LITERATURE REVIEW: As there were no clear criteria for the numbers of the laminae that require decompression in a standard laminoplasty, a wide level laminoplasty from C3 to C7 has been generally done. As a result, complications such as axial pain, C5 root paresis, and loss of range of motion have been reported commonly. To reduce these complications, recent studies have attempted less invasive procedures, such as selective laminoplasty or preservation of posterior ligament and muscle components.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
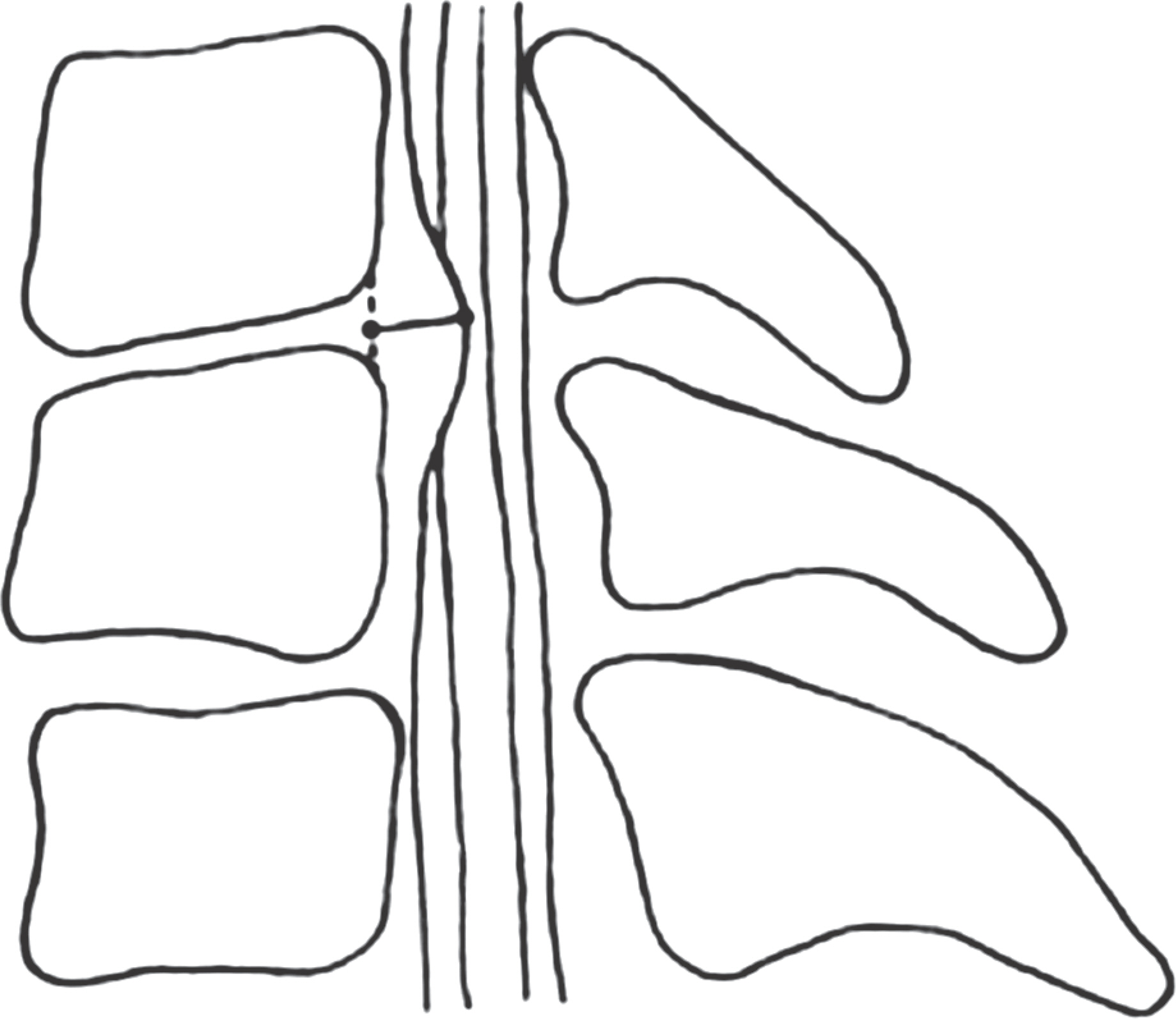
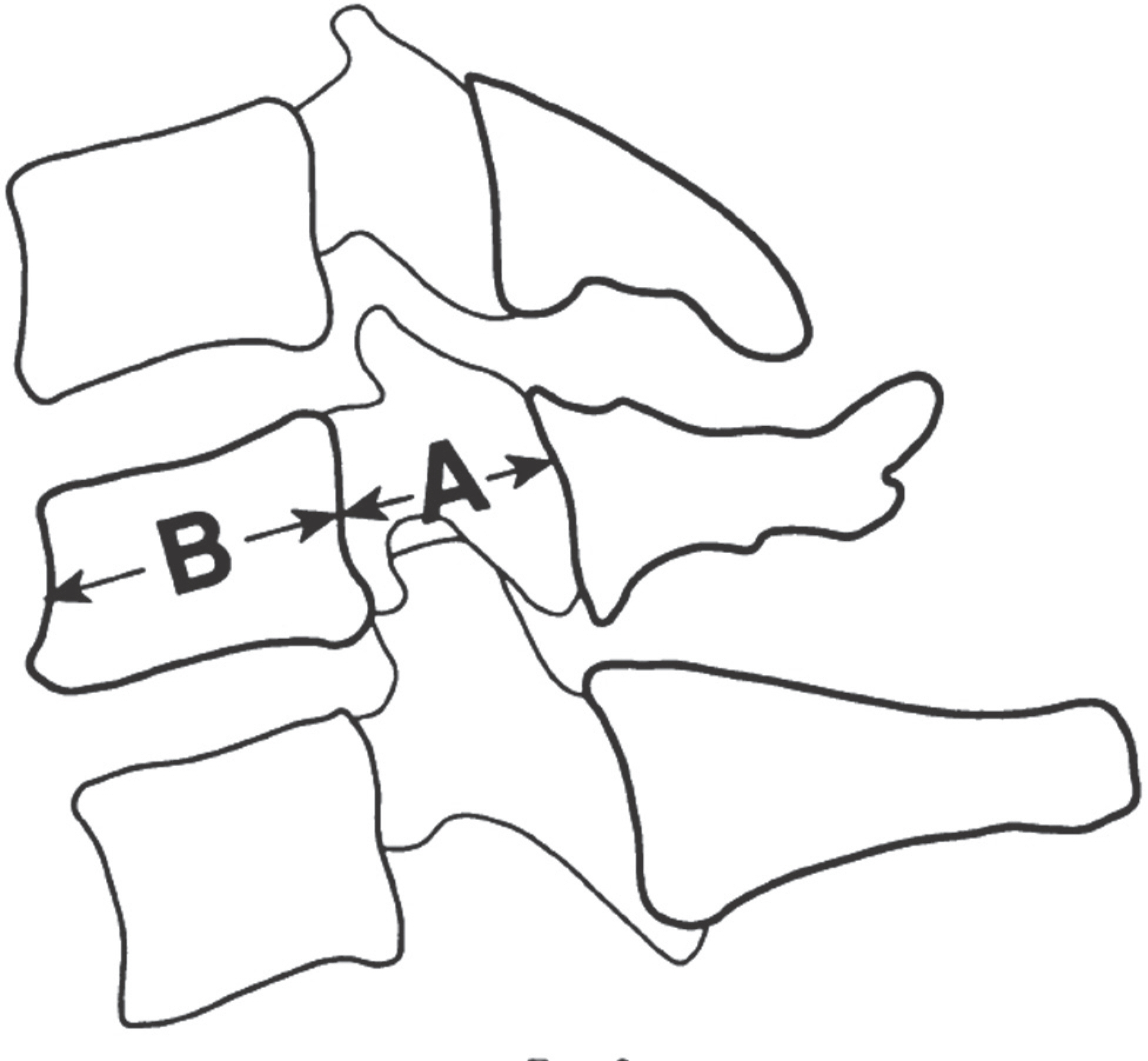
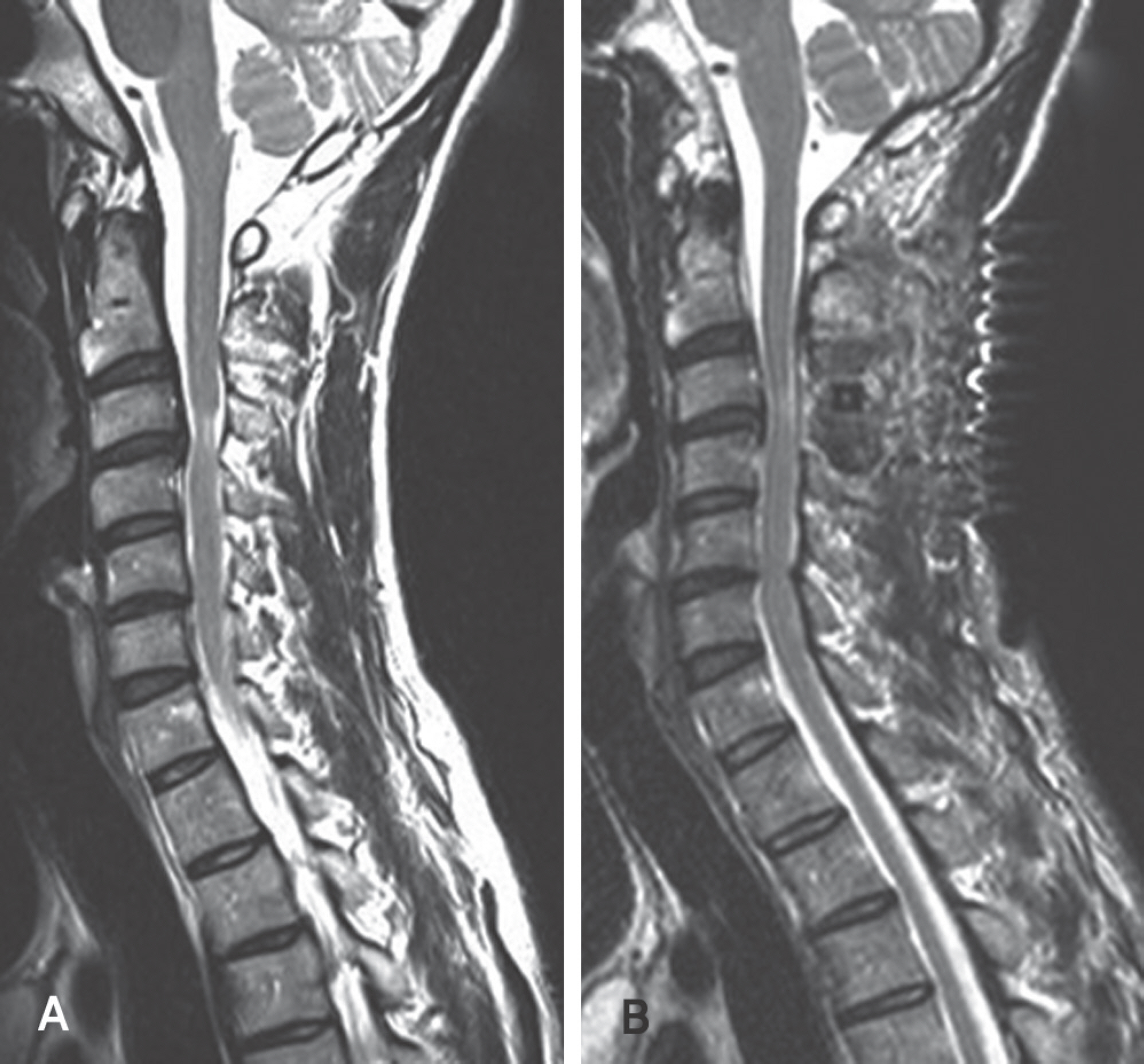
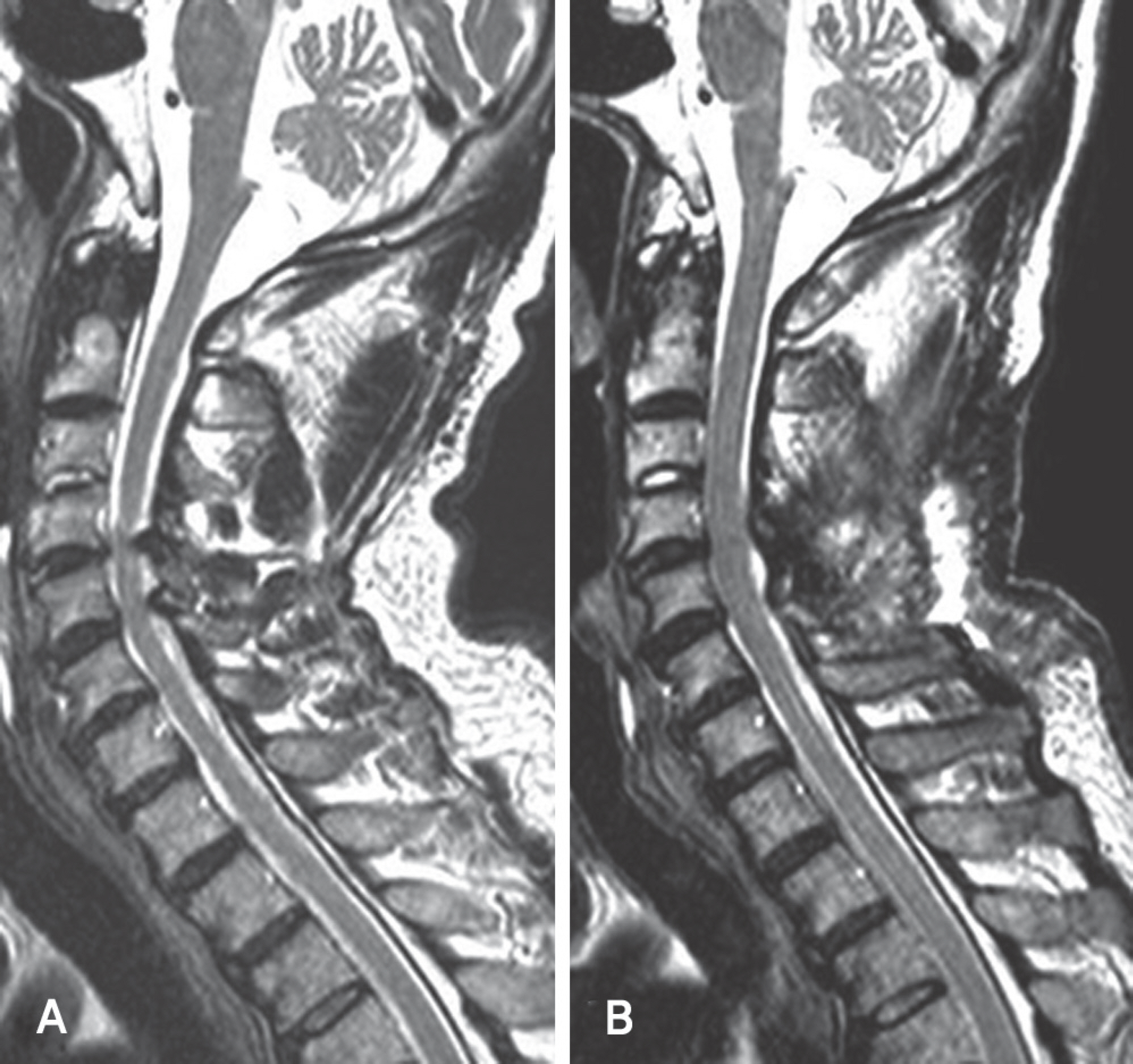
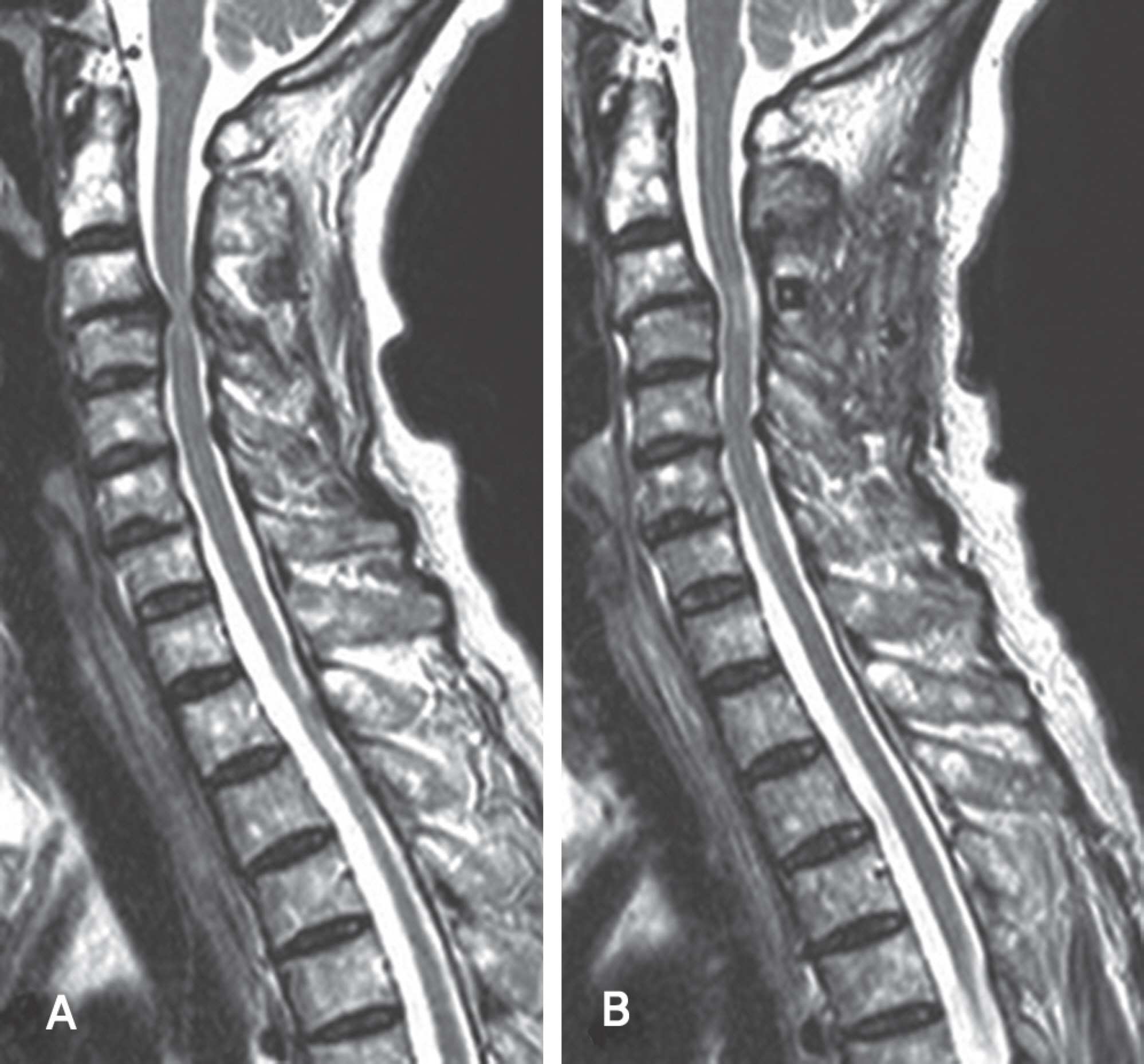
There were two cases of developmental stenosis and one posterior compressive stenosis that underwent selective laminoplasty. The posterior shift of the spinal cord and the dural expansion were measured by magnetic resonance imaging at 3 or 4 weeks after surgery. Clinical outcomes were evaluated by Japanese Orthopedic Association (JOA) score. Axial pain was classified as follows; never: Grade 0; mild: Grade 1; moderate: Grade 2; and severe: Grade 4.
RESULTS
The spinal cord had a tendency to shift posterioly and the dura mater was expanded in all cases. Clinical outcomes and axial pain were also improved in all.
CONCLUSIONS
Selective laminoplasty that enabled the surgeon to perform a less invasive surgery preserving operative time and the patient to have a lower risk of C5 root paresis is effective for the developmental stenosis or posterior compressive stenosis less than 3 levels.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1.Tsuji T., Asazuma T., Masuoka K, et al. Retrospective cohort study between selective and standard C3-7 lami-noplasty. Minimum 2-year follow-up study. Eur Spine J. 2007. 16:2072–7.
Article2.Seichi A., Takeshita K., Ohishi I, et al. Long-term results of double-door laminoplasty for cervical stenotic myelopathy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001. 26:479–87.
Article3.Kawaguchi Y., Kanamori M., Ishihara H., Ohmori K., Nakamura H., Kimura T. Minimum 10-year followup after en bloc cervical laminoplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003. 411:129–39.
Article4.Hale JJ., Gruson KI., Spivak JM. Laminoplasty: a review of its role in compressive cervical myelopathy. Spine J. 2006. 6(6 Suppl):289–98.
Article5.Kato M., Nakamura H., Konishi S, et al. Effect of preserving paraspinal muscles on postoperative axial pain in the selective cervical laminoplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008. 33:E455–9.
Article6.Wang SJ., Jiang SD., Jiang LS., Dai LY. Axial pain after posterior cervical spine surgery: a systematic review. Eur Spine J. 2011. 20:185–94.
Article7.Law MD Jr., Bernhardt M., White AA 3rd. Evaluation and management of cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Instr Course Lect. 1995. 44:99–110.
Article8.Shiozaki T., Otsuka H., Nakata Y, et al. Spinal cord shift on magnetic resonance imaging at 24 hours after cervical laminoplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009. 34:274–9.
Article9.Okada M., Minamide A., Endo T, et al. A prospective randomized study of clinical outcomes in patients with cervical compressive myelopathy treated with open-door or French-door laminoplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009. 34:1119–26.
Article10.Hirabayashi S., Yamada H., Motosuneya T, et al. Com-parison of enlargement of the spinal canal after cervical laminoplasty: open-door type and double-door type. Eur Spine J. 2010. 19:1690–4.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Original Surgical Treatment and Long-term Follow-up for Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy Causing a Compressive Cervical Myelopathy: Review of the Literature
- Expansive Laminoplasty for Cervical Compression Myelopathy
- The Technique of Enlargement of Cervical Canal in Treatment of Cervical OPLL
- Changes in Cervical Spine Range of Motion after Laminoplasty in Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy
- Comparison of Clinical Results according to the Complications after or during Open Door Laminoplasty Surgery for Cervical Myelopathy