J Korean Soc Transplant.
2012 Mar;26(1):6-9. 10.4285/jkstn.2012.26.1.6.
The Diagnosis of Acute Antibody-Mediated Rejection in ABO-Incompatible Liver Transplants
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. geeo@skku.edu
- KMID: 1435076
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4285/jkstn.2012.26.1.6
Abstract
- Liver transplantation (LT) across the ABO-blood type barrier is prone to antibody-mediated rejection (AMR), which often leads to a deleterious clinical outcome. While it is of paramount importance to make an early diagnosis of AMR, the morphologic features of AMR in the liver are not specific, and the differential diagnosis is often difficult or even impossible on a morphologic basis alone. The clinical utility of C4d immunostaining is limited in the liver, unlike other organs, further complicating the situation. Therefore, the diagnosis of AMR in the liver requires integration of clinical, morphologic, immunopathologic, and serological evidence.
MeSH Terms
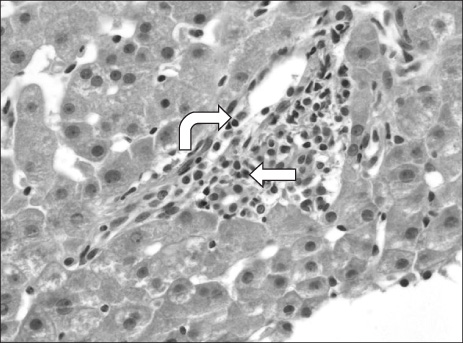
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
ABO-Incompatible Living Donor Liver Transplantation
Jong Man Kim
J Korean Soc Transplant. 2014;28(1):1-4. doi: 10.4285/jkstn.2014.28.1.1.
Reference
-
1. Egawa H, Teramukai S, Haga H, Tanabe M, Fukushima M, Shimazu M. Present status of ABO-incompatible living donor liver transplantation in Japan. Hepatology. 2008. 47:143–152.
Article2. Demetris AJ, Murase N, Nakamura K, Iwaki Y, Yagihashi A, Valdivia L, et al. Immunopathology of antibodies as effectors of orthotopic liver allograft rejection. Semin Liver Dis. 1992. 12:51–59.
Article3. Tanabe M, Kawachi S, Obara H, Shinoda M, Hibi T, Kitagawa Y, et al. Current progress in ABO-incompatible liver transplantation. Eur J Clin Invest. 2010. 40:943–949.
Article4. Mathew JM, Ruiz P. Ruiz P, editor. Immunopathology of organ transplantation. Transplantation pathology. 2009. 1st ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press;1–16.
Article5. Gierej B, Górnicka B, Wasiutyński A. Role of C3d and C4d complement fragments in the diagnostics of acute allograft rejection after transplantations. Ann Transplant. 2009. 14:61–70.6. Takemoto SK, Zeevi A, Feng S, Colvin RB, Jordan S, Kobashigawa J, et al. National conference to assess antibody-mediated rejection in solid organ transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2004. 4:1033–1041.
Article7. Collins AB, Schneeberger EE, Pascual MA, Saidman SL, Williams WW, Tolkoff-Rubin N, et al. Complement activation in acute humoral renal allograft rejection: diagnostic significance of C4d deposits in peritubular capillaries. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999. 10:2208–2214.8. Behr TM, Feucht HE, Richter K, Reiter C, Spes CH, Pongratz D, et al. Detection of humoral rejection in human cardiac allografts by assessing the capillary deposition of complement fragment C4d in endomyocardial biopsies. J Heart Lung Transplant. 1999. 18:904–912.
Article9. Troxell ML, Higgins JP, Kambham N. Evaluation of C4d staining in liver and small intestine allografts. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2006. 130:1489–1496.
Article10. Sakashita H, Haga H, Ashihara E, Wen MC, Tsuji H, Miyagawa-Hayashino A, et al. Significance of C4d staining in ABO-identical/compatible liver transplantation. Mod Pathol. 2007. 20:676–684.
Article11. Demetris AJ, Jaffe R, Tzakis A, Ramsey G, Todo S, Belle S, et al. Antibody-mediated rejection of human orthotopic liver allografts. A study of liver transplantation across ABO blood group barriers. Am J Pathol. 1988. 132:489–502.12. Demetris AJ, Minervini M, Nalesnik M, Ochoa E, Randhawa P, Sasatomi E, et al. Ruiz P, editor. Histopathology of liver transplantation. Transplantation pathology. 2009. 1st ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press;111–184.
Article13. Haga H, Egawa H, Shirase T, Miyagawa A, Sakurai T, Minamiguchi S, et al. Periportal edema and necrosis as diagnostic histological features of early humoral rejection in ABO-incompatible liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2004. 10:16–27.
Article14. Sanchez-Urdazpal L, Batts KP, Gores GJ, Moore SB, Sterioff S, Wiesner RH, et al. Increased bile duct complications in liver transplantation across the ABO barrier. Ann Surg. 1993. 218:152–158.
Article15. Sebagh M, Farges O, Kalil A, Samuel D, Bismuth H, Reynes M. Sclerosing cholangitis following human orthotopic liver transplantation. Am J Surg Pathol. 1995. 19:81–90.
Article16. Bellamy CO. Complement C4d immunohistochemistry in the assessment of liver allograft biopsy samples: applications and pitfalls. Liver Transpl. 2011. 17:747–750.
Article17. Ali S, Ormsby A, Shah V, Segovia MC, Kantz KL, Skorupski S, et al. Significance of complement split product C4d in ABO-compatible liver allograft: diagnosing utility in acute antibody mediated rejection. Transpl Immunol. 2012. 26:62–69.
Article18. Neuman UP, Neuhaus P. C4d immunostaining in acute humoral rejection after ABO blood group-incompatible liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2006. 12:356–357.
Article19. Haas M. The significance of C4d staining with minimal histologic abnormalities. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2010. 15:21–27.
Article20. Haga H, Egawa H, Fujimoto Y, Ueda M, Miyagawa-Hayashino A, Sakurai T, et al. Acute humoral rejection and C4d immunostaining in ABO blood type-incompatible liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2006. 12:457–464.
Article21. Morioka D, Togo S, Kumamoto T, Takeda K, Matsuo K, Inayama Y, et al. Six consecutive cases of successful adult ABO-incompatible living donor liver transplantation: a proposal for grading the severity of antibody-mediated rejection. Transplantation. 2008. 85:171–178.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- ABO-Incompatible Living Donor Liver Transplantation
- ABO Blood Type Incompatible Liver Transplantation in a Child
- Immunologic strategies and outcomes in ABO-incompatible living donor liver transplantation
- Donor Specific Antibody Negative Antibody-Mediated Rejection after ABO Incompatible Liver Transplantation
- Overcoming high pre-transplant isoagglutinin titers using high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin, salvage plasmapheresis, and booster rituximab without splenectomy in ABO-incompatible living donor liver transplantation: a case report