J Korean Fract Soc.
2012 Jan;25(1):20-25. 10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.1.20.
Comparative Analysis of Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis Using Periarticular Plate and Intramedullary Nailing in Distal Tibial Metaphyseal Fractures
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, College of Medicine, Chosun University Hospital, Gwangju, Korea. leejy88@chosun.ac.kr
- KMID: 1434106
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2012.25.1.20
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To compare results between minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis using a periarticular plate and intramedullary nailing in distal tibial metaphyseal fractures in two treatment groups.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
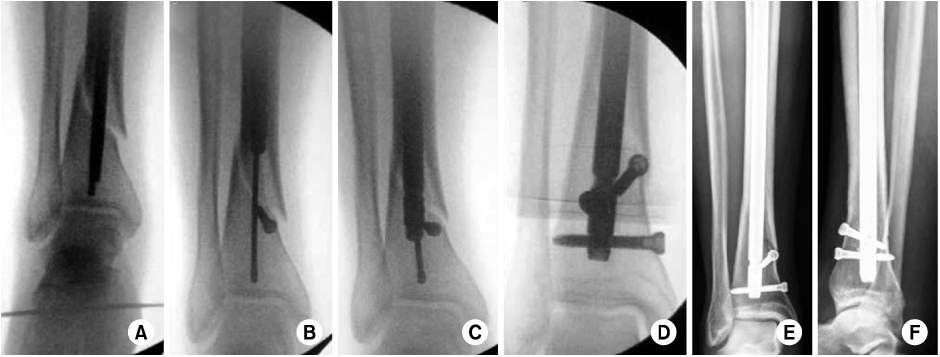
Sixty-one cases of distal tibial metaphyseal fractures from December 2008 to December 2009 were evaluated. The minimal follow-up period was 12 months. Thirty patients treated by minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis using a periarticular plate were Group A; 31 patients treated by intramedullary nailing were Group B. We compared and analyzed the results of each group by radiological and clinical assessments.
RESULTS
The mean bony union time was 16.4 weeks in Group A and 17.2 weeks in Group B. The mean operation time was 45 minutes in Group A and 48 minutes in Group B. The mean radiation exposure times were 4.2 minutes and 4.8 minutes, respectively. VAS scores were 0.7 points and 0.5 points in each respective group. In Group A, the VAS score was 1.7 points when we applied pressure on the skin around the plate. The mean Olerud and Molander Ankle Score was 87.4 points and 86.3 points, respectively. A superficial wound infection occurred in 1 case in each group, and angular deformities more than 5 degrees occurred in 2 Group B cases.
CONCLUSION
No significant differences in results were observed between the two groups. However, a higher incidence of angular deformity was seen in the intramedullary nailing group. Therefore, we must be careful during surgery.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
A Comparison of the Results between Intramedullary Nailing and Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis in Distal Tibia Fractures
Chul-Hyun Park, Chi-Bum Choi, Bum-Jin Shim, Dong-Chul Lee, Oog-Jin Shon
J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2014;49(4):285-293. doi: 10.4055/jkoa.2014.49.4.285.Comparative Analysis of Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis and Intramedullary Nailing in the Treatment of the Distal Tibia Fractures
Ho-Min Lee, Young-Sung Kim, Jong-Pil Kim, Phil-Hyun Chung, Suk Kang, Kaung Suk Jo
J Korean Fract Soc. 2018;31(3):94-101. doi: 10.12671/jkfs.2018.31.3.94.
Reference
-
1. Böstman O, Hänninen A. The fibular reciprocal fracture in tibial shaft fractures caused by indirect violence. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1982. 100:115–121.
Article2. Cheng W, Li Y, Manyi W. Comparison study of two surgical options for distal tibia fracture-minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis vs. open reduction and internal fixation. Int Orthop. 2011. 35:737–742.
Article3. Collinge C, Protzman R. Outcomes of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for metaphyseal distal tibia fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2010. 24:24–29.4. D'Aubigne RM, Maurer P, Zucman J, Masse Y. Blind intramedullary nailing for tibial fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1974. 105:267–275.5. Freedman EL, Johnson EE. Radiographic analysis of tibial fracture malalignment following intramedullary nailing. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995. 315:25–33.
Article6. Hazarika S, Chakravarthy J, Cooper J. Minimally invasive locking plate osteosynthesis for fractures of the distal tibia--results in 20 patients. Injury. 2006. 37:877–887.
Article7. Helfet DL, Suk M. Minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis of fractures of the distal tibia. Instr Course Lect. 2004. 53:471–475.
Article8. Im GI, Kim DY, Shin JH, Youn KS, Cho WH. Comparative analysis of interlocking nail and anatomical plate in the treatment of distal tibial fracture. J Korean Soc Fract. 1999. 12:632–637.
Article9. Janssen KW, Biert J, van Kampen A. Treatment of distal tibial fractures: plate versus nail: a retrospective outcome analysis of matched pairs of patients. Int Orthop. 2007. 31:709–714.
Article10. Kääb MJ, Frenk A, Schmeling A, Schaser K, Schütz M, Haas NP. Locked internal fixator: sensitivity of screw/plate stability to the correct insertion angle of the screw. J Orthop Trauma. 2004. 18:483–487.
Article11. Krackhardt T, Dilger J, Flesch I, Höntzsch D, Eingartner C, Weise K. Fractures of the distal tibia treated with closed reduction and minimally invasive plating. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2005. 125:87–94.
Article12. Lang GJ, Cohen BE, Bosse MJ, Kellam JF. Proximal third tibial shaft fractures. Should they be nailed? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995. 315:64–74.
Article13. Nork SE, Schwartz AK, Agel J, Holt SK, Schrick JL, Winquist RA. Intramedullary nailing of distal metaphyseal tibial fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005. 87:1213–1221.
Article14. Olerud C, Molander H. Bi- and trimalleolar ankle fractures operated with nonrigid internal fixation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986. 206:253–260.
Article15. Park KC, Park YS. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for distal tibial metaphyseal fracture. J Korean Fract Soc. 2005. 18:264–268.
Article16. Robinson CM, McLauchlan GJ, McLean IP, Court-Brown CM. Distal metaphyseal fractures of the tibia with minimal involvement of the ankle. Classification and treatment by locked intramedullary nailing. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1995. 77:781–787.
Article17. Teitz CC, Carter DR, Frankel VH. Problems associated with tibial fractures with intact fibulae. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1980. 62:770–776.
Article18. Vallier HA, Le TT, Bedi A. Radiographic and clinical comparisons of distal tibia shaft fractures (4 to 11 cm proximal to the plafond): plating versus intramedullary nailing. J Orthop Trauma. 2008. 22:307–311.
Article19. Wyrsch B, McFerran MA, McAndrew M, et al. Operative treatment of fractures of the tibial plafond. A randomized, prospective study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1996. 78:1646–1657.
Article20. Yang SW, Tzeng HM, Chou YJ, Teng HP, Liu HH, Wong CY. Treatment of distal tibial metaphyseal fractures: Plating versus shortened intramedullary nailing. Injury. 2006. 37:531–535.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparative Study of Intramedullary Nailing and Plate for Metaphyseal Fractures of the Distal Tibia
- Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis Using Periarticular Plate for Distal Tibial Fractures
- Comparison of Results of Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis according to Types of Locking Plate in Distal Femoral Fractures
- Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis for Periarticular Tibial Fractures
- Lateral Plate Fixation of Distal Tibial Metaphyseal Fracture Using Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis Technique