J Korean Fract Soc.
2013 Jul;26(3):191-198. 10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.3.191.
Arthroscopic Assisted Intra-Articular Reduction and Internal Fixation of Tibia Plateau Fracture
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, School of Medicine, Chosun University, Gwangju, Korea. leekci@chosun.ac.kr
- KMID: 1431663
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.3.191
Abstract
- PURPOSE
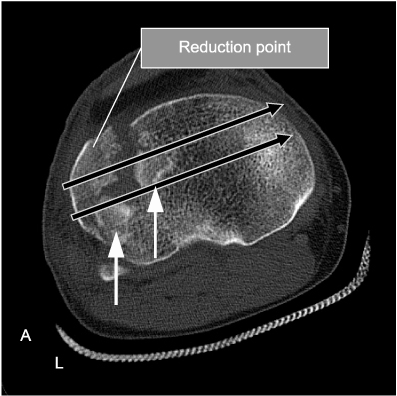
We evaluated the results of arthroscopic intra-articular reduction and internal fixation of tibial plateau fractures without cortical window along with any additional bone grafts.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
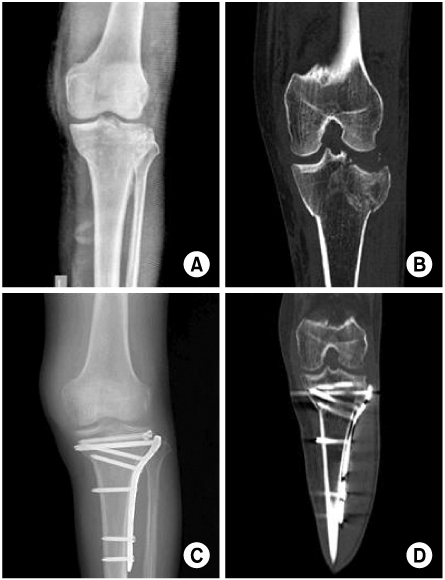
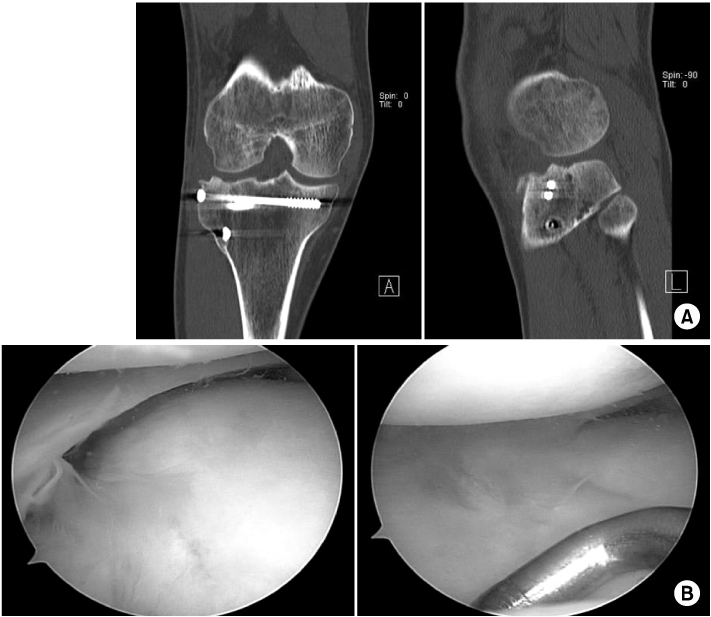
From March 2006 to March 2009, twelve patients with arthroscopic intra-articular reduction and internal fixation of tibial plateau fractures over 5 mm in depression and displacement on the articular surface in computed tomography (CT) were enrolled in this study. We reduced or removed the depressed fracture fragment using freer without making a cortical window. Then, we accomplished internal fixation by a cannulated screw. All cases have not received bone graft. Both the postoperative clinical and radiological results were evaluated by the Rasmussen system.
RESULTS
The fractures were healed completely in an average of 9 (range from 7 to 12) weeks. According to Rasmussen classification, we obtained satisfactory clinical results as excellent in 8 cases, good in 3 cases, and fair in 1 case; and radiological results were excellent in 7 cases and good in 5 cases.
CONCLUSION
We consider that arthroscopic intra-articular reduction and internal fixation of tibial plateau fractures without cortical window and any additional bone grafts is are a useful methods for attaining satisfactory results.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Current Concepts in Management of Tibia Plateau Fracture
Sang Hak Lee, Kang-Il Kim
J Korean Fract Soc. 2014;27(3):245-260. doi: 10.12671/jkfs.2014.27.3.245.
Reference
-
1. Asik M, Cetik O, Talu U, Sozen YV. Arthroscopy-assisted operative management of tibial plateau fractures. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2002; 10:364–370.
Article2. Bernfeld B, Kligman M, Roffman M. Arthroscopic assistance for unselected tibial plateau fractures. Arthroscopy. 1996; 12:598–602.
Article3. Buchko GM, Johnson DH. Arthroscopy assisted operative management of tibial plateau fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996; (332):29–36.
Article4. Caspari RB, Hutton PM, Whipple TL, Meyers JF. The role of arthroscopy in the management of tibial plateau fractures. Arthroscopy. 1985; 1:76–82.
Article5. Chan YS, Chiu CH, Lo YP, et al. Arthroscopy-assisted surgery for tibial plateau fractures: 2- to 10-year follow-up results. Arthroscopy. 2008; 24:760–768.
Article6. Delamarter R, Hohl M. The cast brace and tibial plateau fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989; (242):26–31.
Article7. Fowble CD, Zimmer JW, Schepsis AA. The role of arthroscopy in the assessment and treatment of tibial plateau fractures. Arthroscopy. 1993; 9:584–590.
Article8. Gausewitz S, Hohl M. The significance of early motion in the treatment of tibial plateau fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986; (202):135–138.
Article9. Guanche CA, Markman AW. Arthroscopic management of tibial plateau fractures. Arthroscopy. 1993; 9:467–471.
Article10. Holzach P, Matter P, Minter J. Arthroscopically assisted treatment of lateral tibial plateau fractures in skiers: use of a cannulated reduction system. J Orthop Trauma. 1994; 8:273–281.
Article11. Honkonen SE. Indications for surgical treatment of tibial condyle fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994; (302):199–205.
Article12. Honkonen SE. Degenerative arthritis after tibial plateau fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 1995; 9:273–277.
Article13. Jennings JE. Arthroscopic management of tibial plateau fractures. Arthroscopy. 1985; 1:160–168.
Article14. Keogh P, Kelly C, Cashman WF, McGuinness AJ, O'Rourke SK. Percutaneous screw fixation of tibial plateau fractures. Injury. 1992; 23:387–389.
Article15. Lansinger O, Bergman B, Körner L, Andersson GB. Tibial condylar fractures. A twenty-year follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1986; 68:13–19.
Article16. Lee KW, Lee HH, Yang DH, Choy WS. Arthroscopic reduction and internal fixation of intra-articular fractures of lateral tibial plateau. J Korean Arthrosc Soc. 2006; 10:53–60.17. Lemon RA, Bartlett DH. Arthroscopic assisted internal fixation of certain fractures about the knee. J Trauma. 1985; 25:355–358.
Article18. Lubowitz JH, Elson WS, Guttmann D. Part I: arthroscopic management of tibial plateau fractures. Arthroscopy. 2004; 20:1063–1070.
Article19. Marsh JL, Smith ST, Do TT. External fixation and limited internal fixation for complex fractures of the tibial plateau. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995; 77:661–673.
Article20. McCarthy JJ, Parker RD. Arthroscopic reduction and internal fixation of a displaced intraarticular lateral femoral condyle fracture of the knee. Arthroscopy. 1996; 12:224–227.
Article21. McLennan JG. The role of arthroscopic surgery in the treatment of fractures of the intercondylar eminence of the tibia. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1982; 64:477–480.
Article22. Moore TM, Patzakis MJ, Harvey JP. Tibial plateau fractures: definition, demographics, treatment rationale, and long-term results of closed traction management or operative reduction. J Orthop Trauma. 1987; 1:97–119.23. O'Dwyer KJ, Bobic VR. Arthroscopic management of tibial plateau fractures. Injury. 1992; 23:261–264.24. O'Keeffe RM Jr, Riemer BL, Butterfield SL. Harvesting of autogenous cancellous bone graft from the proximal tibial metaphysis. A review of 230 cases. J Orthop Trauma. 1991; 5:469–474.25. Park IH, Lee KB, Park MR, Lee JY, Rhee DY. Arthroscopic management of the tibial condylar fracture. J Korean Soc Fract. 1990; 25:1323–1332.26. Perez Carro L. Arthroscopic management of tibial plateau fractures: special techniques. Arthroscopy. 1997; 13:265–267.
Article27. Rasmussen PS. Tibial condylar fractures. Impairment of knee joint stability as an indication for surgical treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1973; 55:1331–1350.28. Roerdink WH, Oskam J, Vierhout PA. Arthroscopically assisted osteosynthesis of tibial plateau fractures in patients older than 55 years. Arthroscopy. 2001; 17:826–831.
Article29. Schatzker J, McBroom R, Bruce D. The tibial plateau fracture. The Toronto experience 1968--1975. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1979; (138):94–104.30. Scheerlinck T, Ng CS, Handelberg F, Casteleyn PP. Medium-term results of percutaneous, arthroscopically-assisted osteosynthesis of fractures of the tibial plateau. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1998; 80:959–964.
Article31. Tscherne H, Lobenhoffer P. Tibial plateau fractures. Management and expected results. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993; (292):87–100.32. Volpin G, Dowd GS, Stein H, Bentley G. Degenerative arthritis after intra-articular fractures of the knee. Long-term results. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1990; 72:634–638.
Article33. Waddell JP, Johnston DW, Neidre A. Fractures of the tibial plateau: a review of ninety-five patients and comparison of treatment methods. J Trauma. 1981; 21:376–381.
Article34. Watson JT. High-energy fractures of the tibial plateau. Orthop Clin North Am. 1994; 25:723–752.
Article35. Young MJ, Barrack RL. Complications of internal fixation of tibial plateau fractures. Orthop Rev. 1994; 23:149–154.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Arthroscopically Assisted Reduction and Internal Fixation of Intra-Articular Fractures of Tibial Plateau
- Arthroscopically-Assisted Reduction and Internal Fixation of Intra-Articular Fractures of the Lateral Tibial Plateau
- Arthroscopic and Conventional Treatment of Lateral Tibial Plateau Fractures
- Treatment of Fracture of the Tibial Intercondylar Eminence with Arthroscopic Pull-Out Suture
- Surgical Treatment of Tibial Plateau Fracture: Validity of Arthroscopy