Korean J Phys Anthropol.
2013 Mar;26(1):55-59. 10.11637/kjpa.2013.26.1.55.
An Unusual Communication between the Radial and the Ulnar Nerves
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anatomy, Kwandong University College of Medicine, Korea. kslee@kwandong.ac.kr
- KMID: 1430200
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.11637/kjpa.2013.26.1.55
Abstract
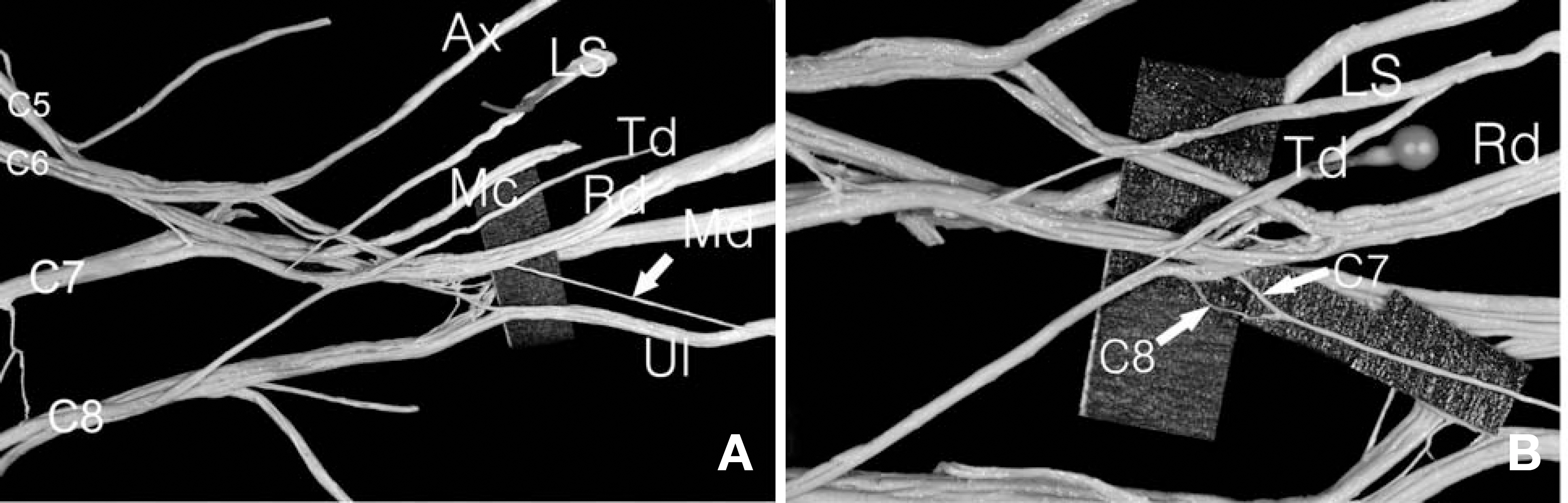
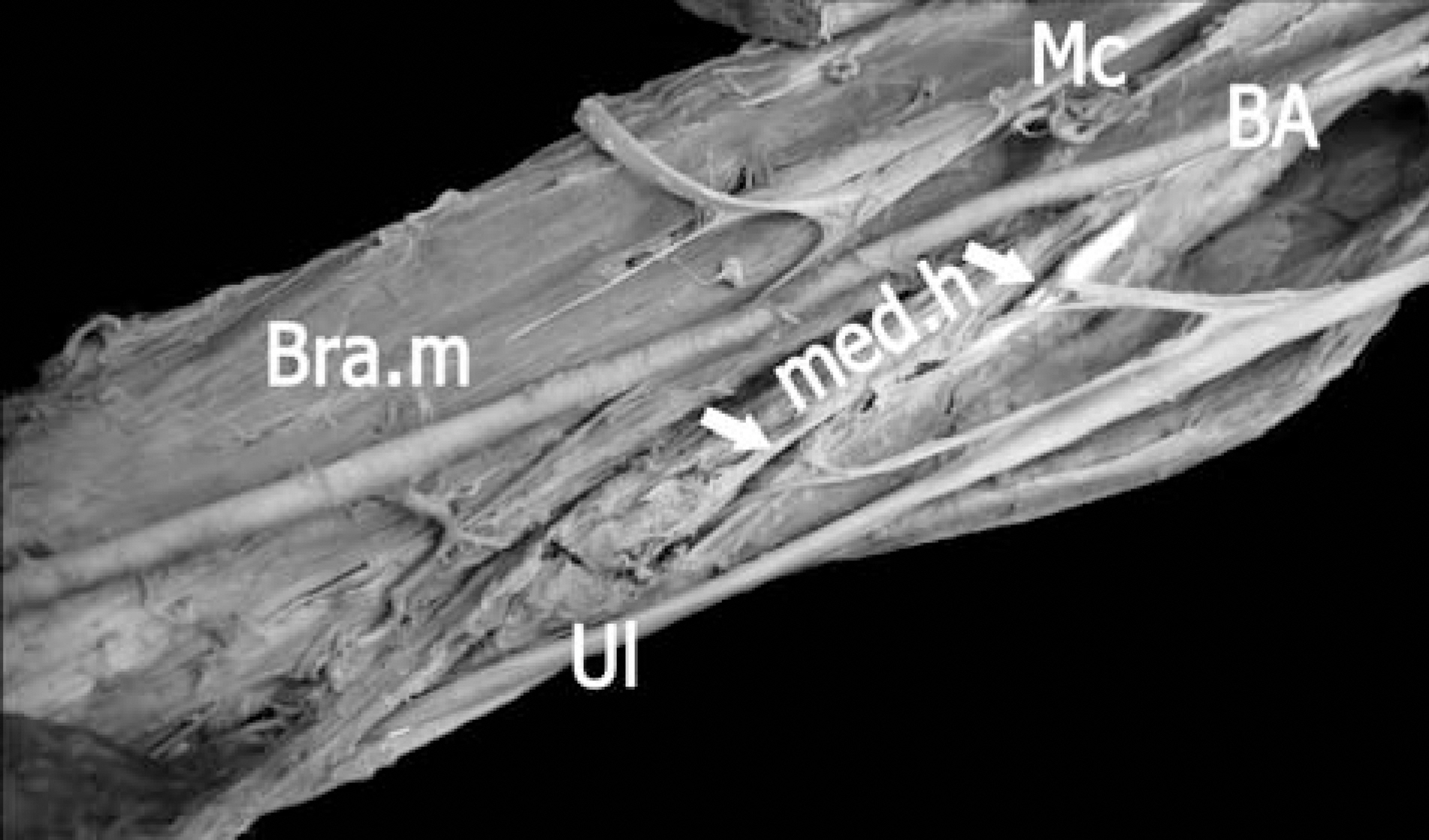
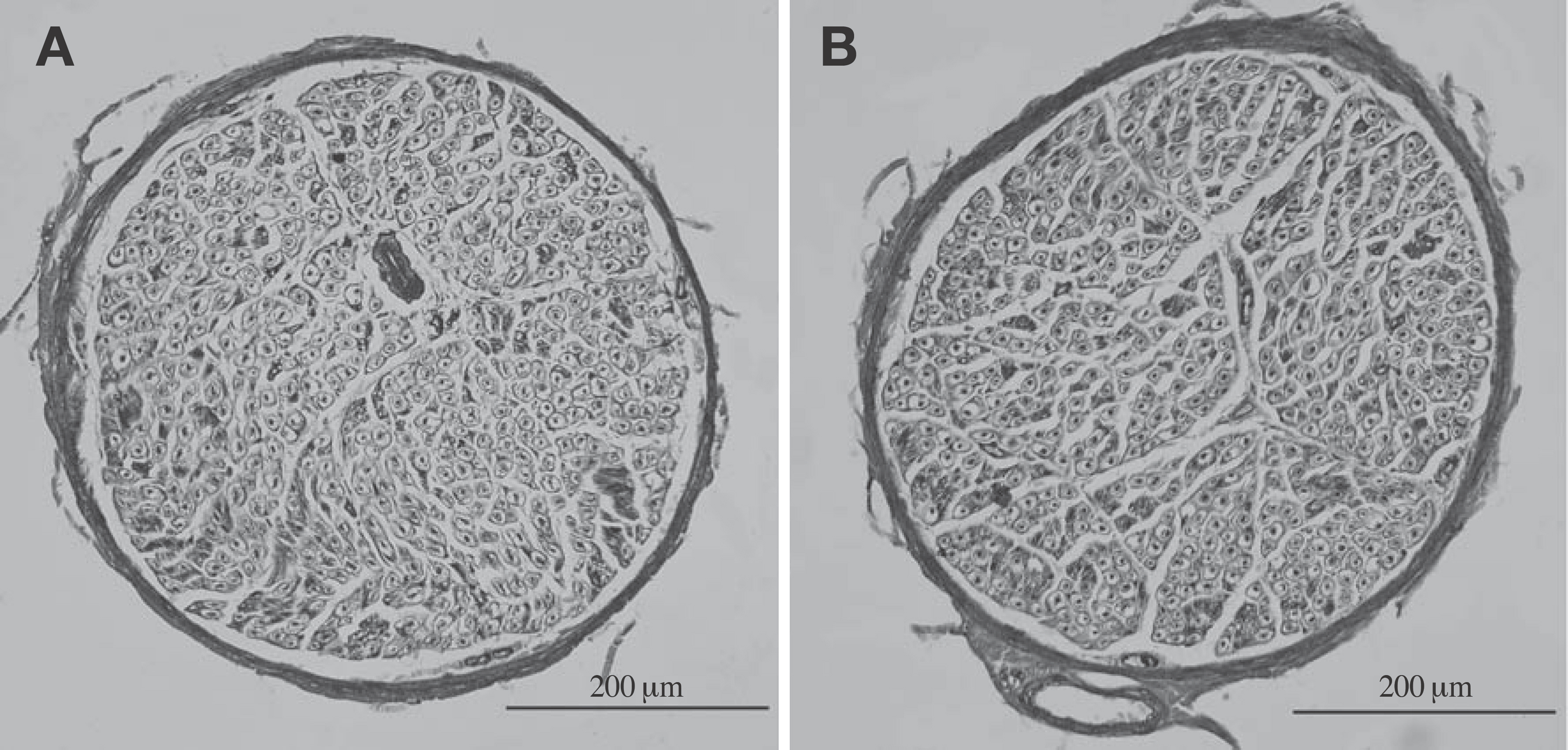
- This case report describes an unusual communicating branch from radial to ulnar nerves in the axilla region on the right side of the Korean cadaver of a 59-year-old male. The brachial plexus containing the communicating branch were extracted en bloc. The extracted specimens were immersed in Guanidine-HCl (0.2 M) for two weeks and then treated several times with an ultrasonic cleaner for an hour to soften the connective tissue around the nerve bundles. The spinal root origins of this communicating branch were found to be largely C7 and some C8. Unexpectedly, the branches of the ulnar nerve innervated the medial two-third of the medial head of the triceps brachii muscle on the right side in the same cadaver. Numbers of nerve fibers of the communicating branch and the main distributing branch of the ulnar nerve to the triceps brachii muscle were 523 and 525, respectively. This result implies that nerve fibers moving from the radial to the ulnar nerves may innervate the original distributing territories of the radial nerve. Another possibility is that a part of radial muscular branch to the triceps beachii muscle may be fused to the ulnar nerve in their distributing territories.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Venieratos D, Anagnostopoulou S. Classification of communications between the musculocutaneous and median nerves. Clin Anat. 1998; 11:327–31.
Article2. Saeed M, Rufai AA. Median and musculocutaneous nerves: variant formation and distribution. Clin Anat. 2003; 16:453–7.
Article3. Shu HS, Chantelot C, Oberlin C, Alnot JY, Shao H. Martin-Gruber communicating branch: anatomical and histological study. Surg Radiol Anat. 1999; 21:115–8.
Article4. Meenakshi-Sundaram S, Sundar B, Arunkumar MJ. Marinacci communication: an electrophysiological study. Clin Neurophysiol. 2003; 114:2334–7.
Article5. Lee KS, Oh CS, Chung IH, Sunwoo IN. An anatomic study of the Martin-Gruber anastomosis: electrodiagnostic implication. Muscle Nerve. 2005; 31:95–7.6. Budak F, Gönenç Z. Innervation anomalies in upper and lower extremities. Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1999; 39:231–4.7. Bergman RA, Thompson SA, Afifi AK, Saadeh FA. Compendium of human anatomic variation. Baltimore: Urban & Schwarzenberg;1988. p. 142.8. Lee KS. Variation of the spinal nerve compositions of tho-racodorsal nerve. Clin Anat. 2007; 20:660–2.
Article9. Lindner HH. Clinical anatomy. International ed. London: Appleton & Lange;1989. p. 536.10. MaCluskey LF. Anomalous superficial radial sensory innervation of the ulnar dorsum of the hand: a cause of paradoxical presentation of ulnar sensory function. Muscle Nerve. 1996; 19:923–5.11. Kurivilla A, Laaksonen S, Falck B. Anomalous superficial radial nerve: a patient with probable autosomal dominant. Muscle Nerve. 2002; 26:716–9.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Distribution Patterns of the Cutaneous Nerves on Dorsum of the Hands in the Korean
- Ultrasonography for nerve compression syndromes of the upper extremity
- Peripheral Nerve Injuries of the Upper Extremity
- Clinical Experience of the Ilizarov Application for Correction of Ulnar Defect with a Dislocated Radial Head: 2 Cases report
- Neurologic Complications of Elbow Fractures in Children