Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2013 Jun;17(3):229-235. 10.4196/kjpp.2013.17.3.229.
Electrophysiological and Histologic Evaluation of the Time Course of Retinal Degeneration in the rd10 Mouse Model of Retinitis Pigmentosa
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physiology, Chungbuk National University School of Medicine, Cheongju 361-763, Korea. ysgoo@chungbuk.ac.kr
- 2Department of Anatomy, Chungbuk National University School of Medicine, Cheongju 361-763, Korea.
- 3Department of Microbiology, Chungbuk National University School of Medicine, Cheongju 361-763, Korea.
- KMID: 1429303
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2013.17.3.229
Abstract
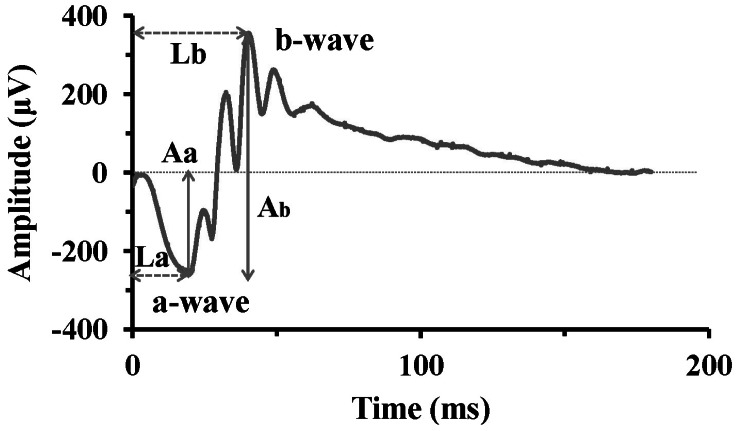
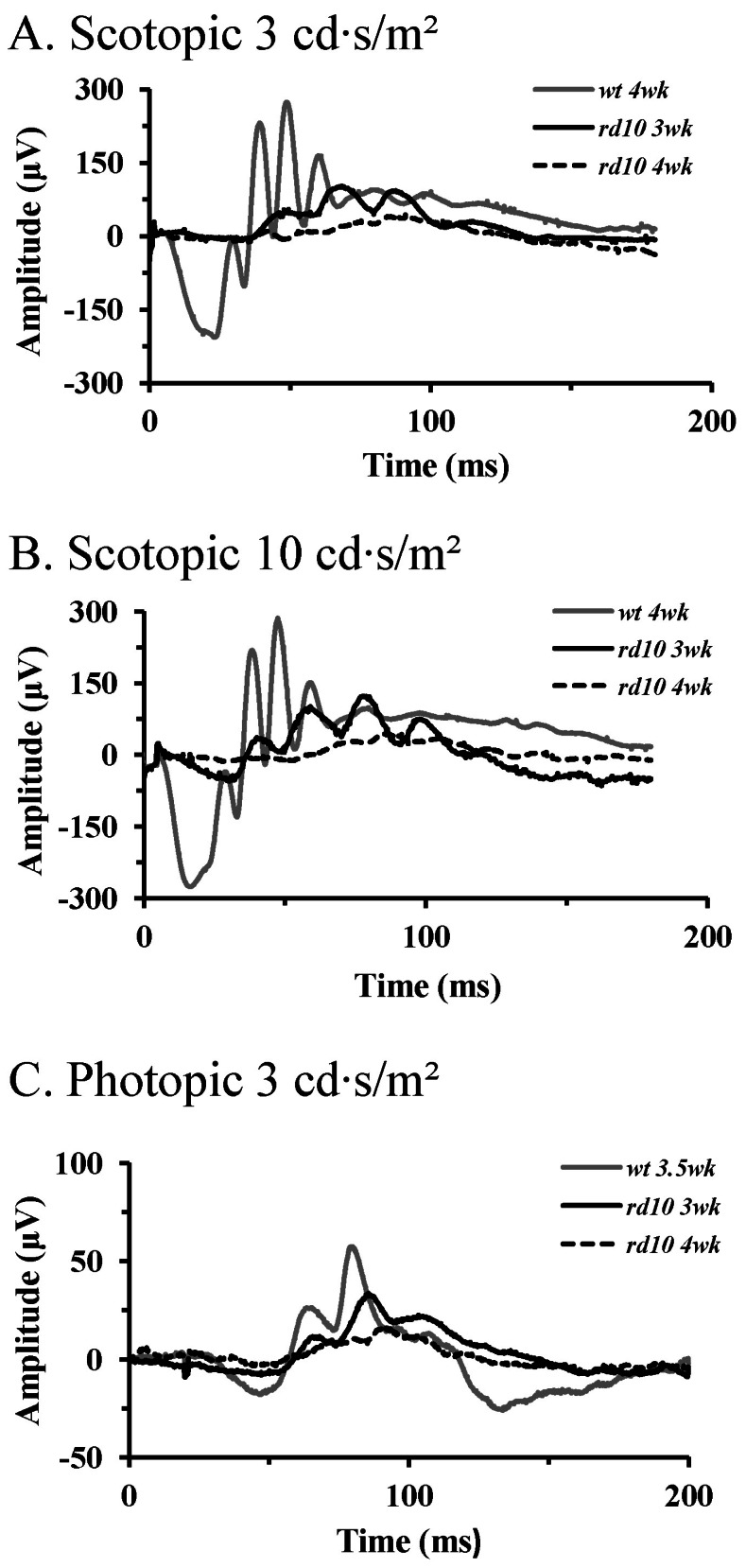
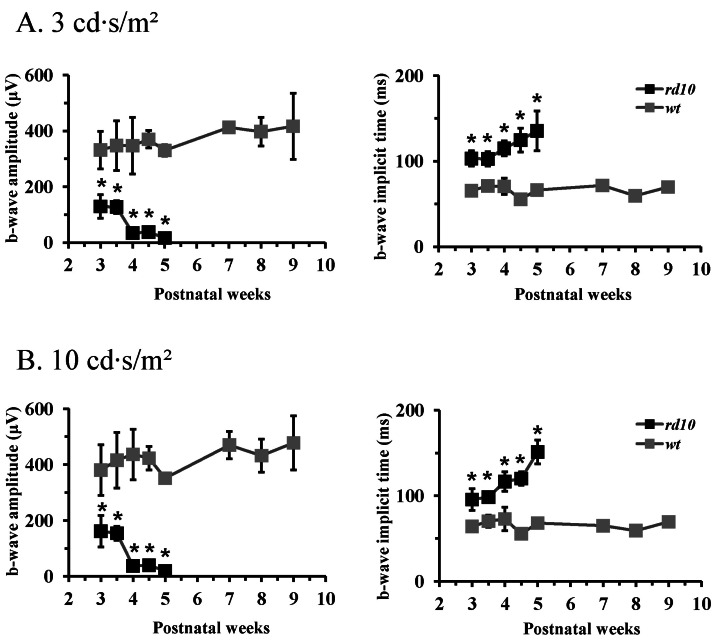
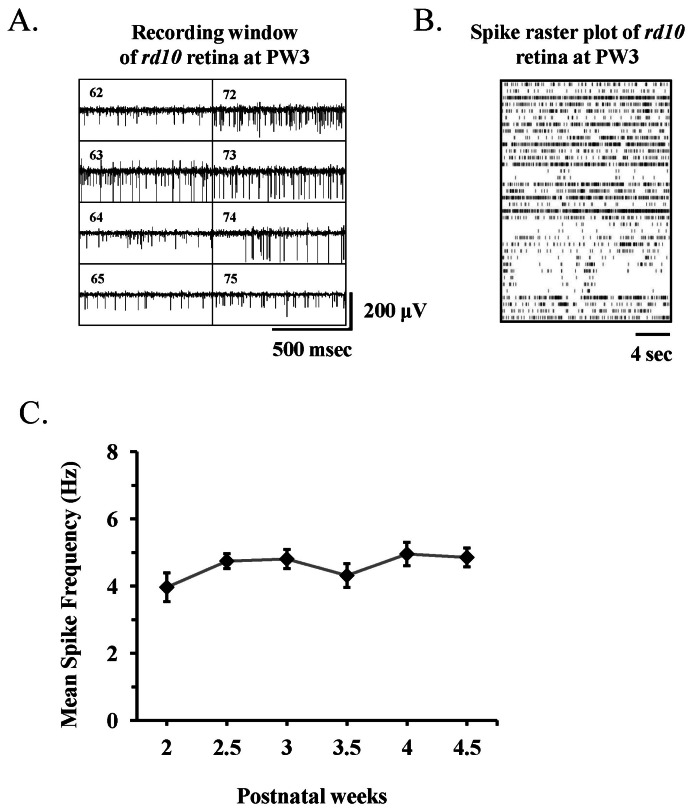
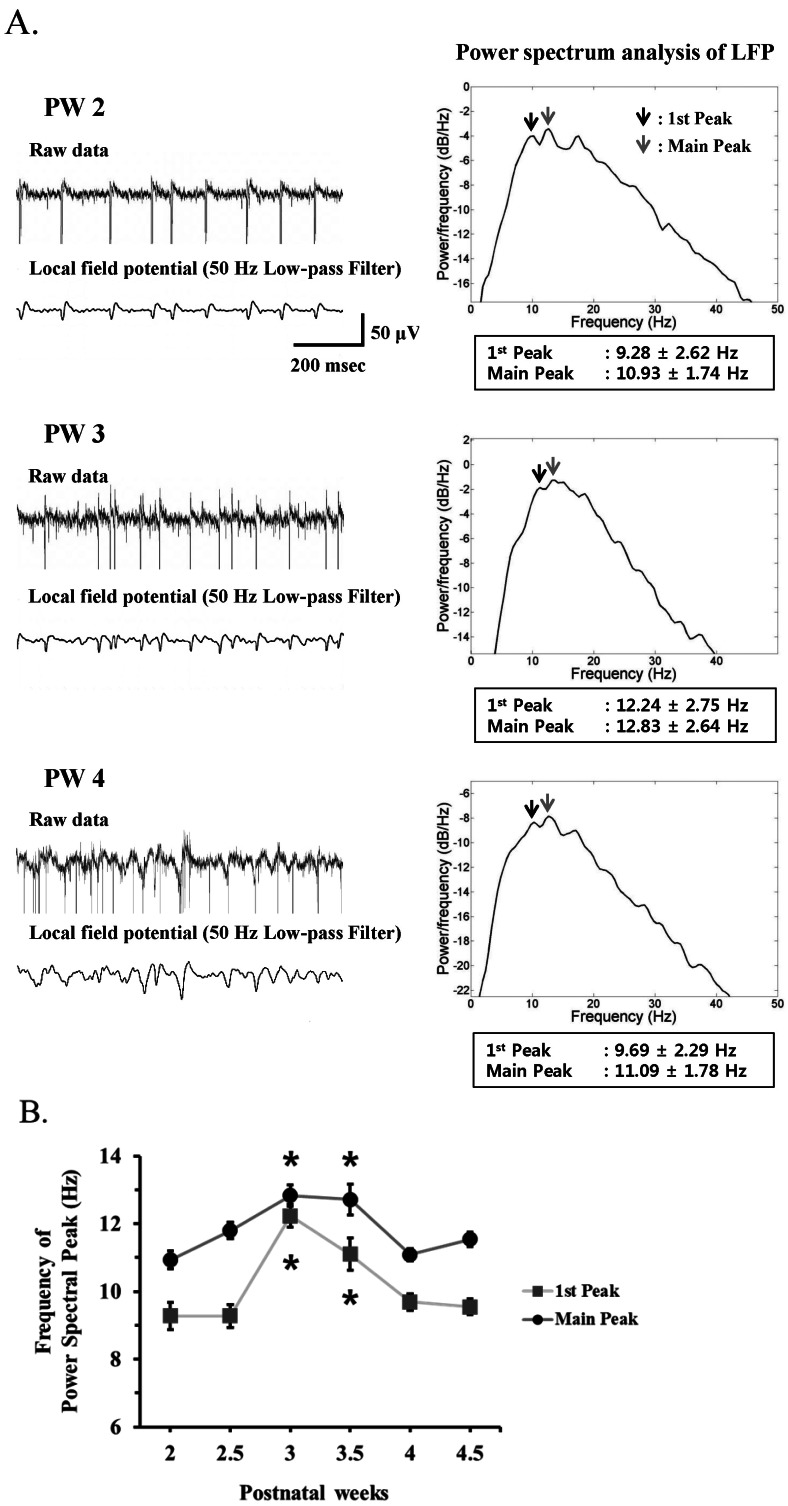
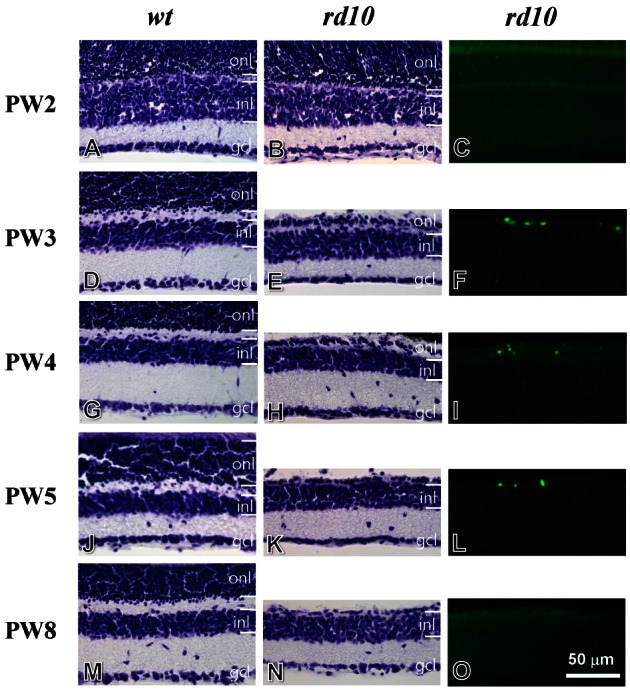
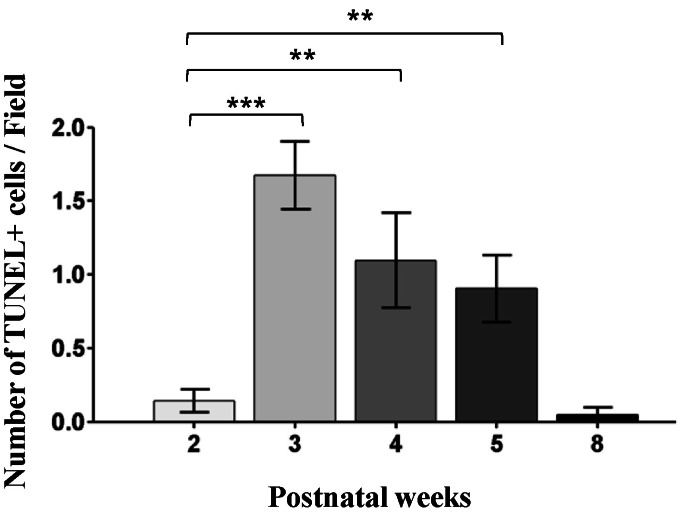
- Among several animal models of retinitis pigmentosa (RP), the more recently developed rd10 mouse with later onset and slower rate of retinal degeneration than rd1 mouse is a more suitable model for testing therapeutic modalities. We therefore investigated the time course of retinal degeneration in rd10 mice before adopting this model in our interventional studies. Electroretinogram (ERG) recordings were carried out in postnatal weeks (PW) 3~5 rd10 (n=23) and wild-type (wt) mice (n=26). We compared the amplitude and implicit time of the b-wave of ERG records from wt and rd10 mice. Our results showed that b-wave amplitudes in rd10 mice were significantly lower and the implicit time of b-waves in rd10 mice were also significantly slower than that in wt mice (20~160 microV vs. 350~480 microV; 55~75 ms vs. 100~150 ms: p<0.001) through PW3 to PW5. The most drastic changes in ERG amplitudes and latencies were observed during PW3 to PW4. In multichannel recording of rd10 retina in PW2 to PW4.5, we found no significant difference in mean spike frequency, but the frequency of power spectral peak of local field potential at PW3 and PW3.5 is significantly different among other age groups (p<0.05). Histologic examination of rd10 retinae showed significant decrease in thickness of the outer nuclear layer at PW3. TUNEL positive cells were most frequently observed at PW3. From these data, we confirm that in the rd10 mouse, the most precipitous retinal degeneration occurs between PW3~PW4 and that photoreceptor degeneration is complete by PW5.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
2. Pagon RA, Daiger SP. Retinitis pigmentosa Overview. GeneReviews. Seattle: University of Washington;2000.3. Chang B, Hawes NL, Hurd RE, Davisson MT, Nusinowitz S, Heckenlively JR. Retinal degeneration mutants in the mouse. Vision Res. 2002; 42:517–525. PMID: 11853768.
Article4. Chang B, Hawes NL, Pardue MT, German AM, Hurd RE, Davisson MT, Nusinowitz S, Rengarajan K, Boyd AP, Sidney SS, Phillips MJ, Stewart RE, Chaudhury R, Nickerson JM, Heckenlively JR, Boatright JH. Two mouse retinal degenerations caused by missense mutations in the beta-subunit of rod cGMP phosphodiesterase gene. Vision Res. 2007; 47:624–633. PMID: 17267005.5. Baehr W, Frederick JM. Naturally occurring animal models with outer retina phenotypes. Vision Res. 2009; 49:2636–2652. PMID: 19375447.
Article6. Goo YS, Ye JH, Lee S, Nam Y, Ryu SB, Kim KH. Retinal ganglion cell responses to voltage and current stimulation in wild-type and rd1 mouse retinas. J Neural Eng. 2011; 8:035003. PMID: 21593549.7. Ryu SB, Ye JH, Goo YS, Kim CH, Kim KH. Decoding of temporal visual information from electrically evoked retinal ganglion cell activities in photoreceptor-degenerated retinas. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011; 52:6271–6278. PMID: 21680865.
Article8. Ryu SB, Ye JH, Goo YS, Kim CH, Kim KH. Temporal response properties of retinal ganglion cells in rd1 mice evoked by amplitude-modulated electrical pulse trains. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010; 51:6762–6769. PMID: 20671284.9. Slatter DH. Fundamentals of veterinary ophthalmology. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Saunders;2001. p. 419–456.10. Armington JC, Bloom MB. Relations between the amplitudes of spontaneous saccades and visual responses. J Opt Soc Am. 1974; 64:1263–1271. PMID: 4424715.
Article11. Penn RD, Hagins WA. Signal transmission along retinal rods and the origin of the electroretinographic a-wave. Nature. 1969; 223:201–204. PMID: 4307228.
Article12. Miller RF, Dowling JE. Intracellular responses of the Müller (glial) cells of mudpuppy retina: their relation to b-wave of the electroretinogram. J Neurophysiol. 1970; 33:323–341. PMID: 5439340.
Article13. Stockton RA, Slaughter MM. B-wave of the electroretinogram. A reflection of ON bipolar cell activity. J Gen Physiol. 1989; 93:101–122. PMID: 2915211.
Article14. Xu X, Karwoski CJ. Current source density analysis of retinal field potentials. II. Pharmacological analysis of the b-wave and M-wave. J Neurophysiol. 1994; 72:96–105. PMID: 7965036.
Article15. Shiells RA, Falk G. Contribution of rod, on-bipolar, and horizontal cell light responses to the ERG of dogfish retina. Vis Neurosci. 1999; 16:503–511. PMID: 10349971.
Article16. Robson JG, Frishman LJ. Response linearity and kinetics of the cat retina: the bipolar cell component of the dark-adapted electroretinogram. Vis Neurosci. 1995; 12:837–850. PMID: 8924408.
Article17. Pugh EN Jr, Falsini B, Lyurbarsky A. The origin of the major rod- and cone-driven components of the rodent electroretinogram and the effects of age and light-rearing history on the magnitude of these components. Photostasis and Related Phenomena. New York: Plenum Press;1998. p. 128.18. Stett A, Barth W, Haemmerle H, Weiss S, Zrenner E. Electrical multisite stimulation of the isolated chicken retina. Vision Res. 2000; 40:1785–1795. PMID: 10814763.
Article19. Hayes MH. Statistical digital signal processing and modeling. New York: John Wiley & Sons;1996.20. LaVail MM, Matthes MT, Yasumura D, Steinberg RH. Variability in rate of cone degeneration in the retinal degeneration (rd/rd) mouse. Exp Eye Res. 1997; 65:45–50. PMID: 9237863.21. Strettoi E, Porciatti V, Falsini B, Pignatelli V, Rossi C. Morphological and functional abnormalities in the inner retina of the rd/rd mouse. J Neurosci. 2002; 22:5492–5504. PMID: 12097501.
Article22. Strettoi E, Pignatelli V, Rossi C, Porciatti V, Falsini B. Remodeling of second-order neurons in the retina of rd/rd mutant mice. Vision Res. 2003; 43:867–877. PMID: 12668056.
Article23. Lin B, Masland RH, Strettoi E. Remodeling of cone photoreceptor cells after rod degeneration in rd mice. Exp Eye Res. 2009; 88:589–599. PMID: 19087876.
Article24. Chen M, Wang K, Lin B. Development and degeneration of cone bipolar cells are independent of cone photoreceptors in a mouse model of retinitis pigmentosa. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e44036. PMID: 22952865.
Article25. Gargini C, Terzibasi E, Mazzoni F, Strettoi E. Retinal organization in the retinal degeneration 10 (rd10) mutant mouse: a morphological and ERG study. J Comp Neurol. 2007; 500:222–238. PMID: 17111372.
Article26. Lyubarsky AL, Daniele LL, Pugh EN Jr. From candelas to photoisomerizations in the mouse eye by rhodopsin bleaching in situ and the light-rearing dependence of the major components of the mouse ERG. Vision Res. 2004; 44:3235–3251. PMID: 15535992.
Article27. Barhoum R, Martínez-Navarrete G, Corrochano S, Germain F, Fernandez-Sanchez L, de la Rosa EJ, de la Villa P, Cuenca N. Functional and structural modifications during retinal degeneration in the rd10 mouse. Neuroscience. 2008; 155:698–713. PMID: 18639614.
Article28. Ye JH, Goo YS. The slow wave component of retinal activity in rd/rd mice recorded with a multi-electrode array. Physiol Meas. 2007; 28:1079–1088. PMID: 17827655.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Strategies for Mutation Discovery in Retinitis Pigmentosa: Transition to the Next Generation
- A Case of Unilateral Retinitis Pigmentosa
- Advancements in Retinal Prosthesis Systems: A Review of the Literature
- Electrophysiologic Finding of Retinitis Pigmentosa Inversus and Differential Diagnosis from Peripapillary Choroidal Dystrophy
- A Case of Pigmented Paravenous Retino-Choroidal Atrophy and Retinitis Pigmentosa