Korean J Neurotrauma.
2012 Oct;8(2):128-133. 10.13004/kjnt.2012.8.2.128.
Comparison of Ventricular Type and Parenchymal Type Intracranial Pressure (ICP) Monitoring for the Severe Traumatic Brain Injury Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. ns9@naver.com
- KMID: 1427726
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2012.8.2.128
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
Intracranial pressure (ICP) is one of the critical parameter for the patients of severe traumatic brain injury (TBI) to determine the treatment modalities and predict clinical outcomes. Hence, the ICP monitoring with accuracy and safety is essential for the TBI patients. The purpose of this study is to compare its safety and clinical usefulness of intraventricular ICP monitoring method to the parenchymal type.
METHODS
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records and imaging data of 18 severe TBI patients. We used intraventricular ICP monitoring in 10 patients and parenchymal 8 patients. We compared the clinical findings of the two type ICP monitoring methods including procedure time, neurological status, outcome, complications and mortality.
RESULTS
The initial Glasgow Coma Scale of intraventricular ICP monitoring and parenchymal ICP monitoring patients were 5.8 (range: 4-7) and 6.5 (range: 3-7) respectively. The Glasgow Outcome Scale after 6 months was a little higher in intraventricular monitoring patients than parenchymal monitoring patients (2.8 vs. 2.0, p=0.25). We could not find any intraventricular catheter related complication in intraventricular ICP monitoring patients. There was no difference in mortality in both groups (p=0.56).
CONCLUSION
Our results suggest that intraventricular catheter insertion for ICP monitoring is relatively a safe procedure in the severe TBI patients. We could not demonstrate the significant benefit of intraventricular type ICP monitoring compared with parenchymal type ICP monitoring. Considering intraventricular type ICP monitoring have advantages of the accuracy and extraventricular drainage, intraventricular type ICP monitoring could be considered for severe TBI patients, regardless of hydrocephalus.
MeSH Terms
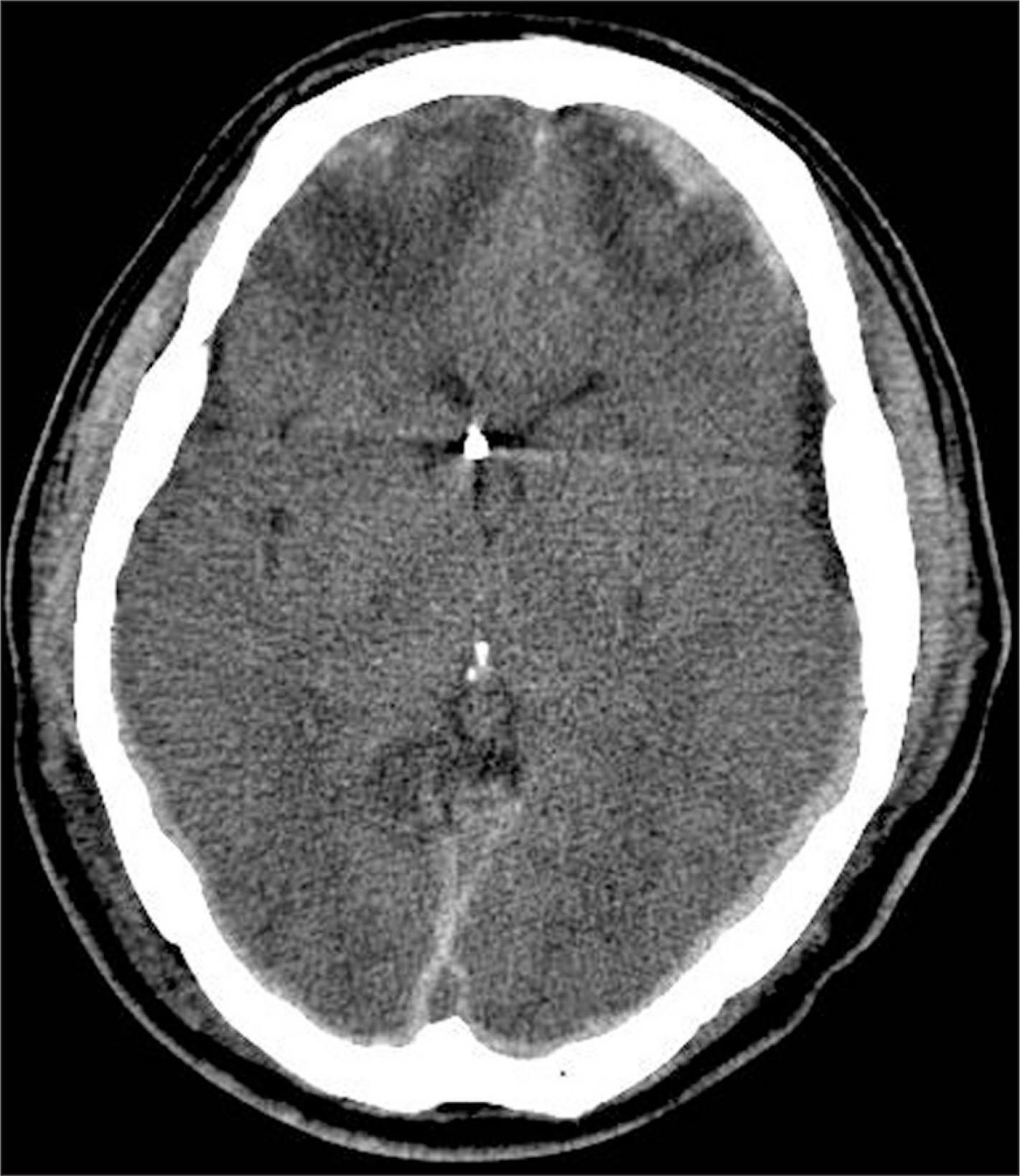
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Early Experience of Automated Intraventricular Type Intracranial Pressure Monitoring (LiquoGuard®) for Severe Traumatic Brain Injury Patients
Young Sub Kwon, Yun Ho Lee, Jin Mo Cho
Korean J Neurotrauma. 2016;12(1):28-33. doi: 10.13004/kjnt.2016.12.1.28.
Reference
-
1). Aufdenblatten CA., Altermatt S. Intraventricular catheter placement by electromagnetic navigation safely applied in a paediatric major head injury patient. Childs Nerv Syst. 24:1047–1050. 2008.
Article2). Brain Trauma Foundation; American Association of Neurological Surgeons; Congress of Neurological Surgeons; J; Joint Section on Neurotrauma and Critical Care, AANS/CNS. Bratton SL., Chestnut RM, et al. Guidelines for the management of severe traumatic brain injury. VII. Intracranial pressure monitoring technology. J Neurotrauma. 24(Suppl 1):S45–S54. 2007.3). Brain Trauma Foundation; American Association of Neurological Surgeons; Congress of Neurological Surgeons; J; Joint Section on Neurotrauma and Critical Care, AANS/CNS. Bratton SL., Chestnut RM, et al. Guidelines for the management of severe traumatic brain injury. VIII. Intracranial pressure thresholds. J Neurotrauma. 24(Suppl 1):S55–S58. 2007.4). Brazinova A., Mauritz W., Leitgeb J., Wilbacher I., Majdan M., Jan-ciak I, et al. Outcomes of patients with severe traumatic brain injury who have Glasgow Coma Scale scores of 3 or 4 and are over 65 years old.: 1549-1555. 2010.5). Eide PK. Comparison of simultaneous continuous intracranial pressure (ICP) signals from a Codman and a Camino ICP sensor. Med Eng Phys. 28:542–549. 2006.
Article6). Eide PK., Bakken A. The baseline pressure of intracranial pressure (ICP) sensors can be altered by electrostatic discharges. Biomed Eng Online. 10:75. 2011.
Article7). Exo J., Kochanek PM., Adelson PD., Greene S., Clark RS., Bayir H, et al. Intracranial pressure-monitoring systems in children with traumatic brain injury: combining therapeutic and diagnostic tools. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 12:560–565. 2011.
Article8). Fakhry SM., Trask AL., Waller MA., Watts DD. IRTC Neurotrauma Task Force. Management of brain-injured patients by an evidence-based medicine protocol improves outcomes and decreases hospital charges. J Trauma. 56:492–499. discussion 499-500. 2004.
Article9). Gelabert-González M., Ginesta-Galan V., Sernamito-García R., Allut AG., Bandin-Diéguez J., Rumbo RM. The Camino intracranial pressure device in clinical practice. Assessment in a 1000 cases. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 148:435–441. 2006.
Article10). Haddad SH., Arabi YM. Critical care management of severe traumatic brain injury in adults. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med. 20:12. 2012.
Article11). Kasotakis G., Michailidou M., Bramos A., Chang Y., Velmahos G., Alam H, et al. Intraparenchymal vs extracranial ventricular drain intracranial pressure monitors in traumatic brain injury: less is more? J Am Coll Surg. 214:950–957. 2012.
Article12). Lescot T., Reina V., Le Manach Y., Boroli F., Chauvet D., Boch AL, et al. In vivo accuracy of two intraparenchymal intracranial pressure monitors. Intensive Care Med. 37:875–879. 2011.
Article13). Li LM., Timofeev I., Czosnyka M., Hutchinson PJ. Review article: the surgical approach to the management of increased intracranial pressure after traumatic brain injury. Anesth Analg. 111:736–748. 2010.14). Münch E., Weigel R., Schmiedek P., Schürer L. The Camino intracranial pressure device in clinical practice: reliability, handling characteristics and complications. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 140:1113–1119. discussion 1119-1120. 1998.
Article15). Piper I., Barnes A., Smith D., Dunn L. The Camino intracranial pressure sensor: is it optimal technology? An internal audit with a review of current intracranial pressure monitoring technologies. Neurosurgery. 49:1158–1164. discussion 1164-1165. 2001.
Article16). Raboel PH., Bartek J Jr., Andresen M., Bellander BM., Romner B. Intracranial pressure monitoring: invasive versus non-invasive methods-A review. Crit Care Res Pract. 2012:950393. 2012.
Article17). Shafi S., Diaz-Arrastia R., Madden C., Gentilello L. Intracranial pressure monitoring in brain-injured patients is associated with worsening of survival. J Trauma. 64:335–340. 2008.
Article18). Stein SC., Georgoff P., Meghan S., Mirza KL., El Falaky OM. Relationship of aggressive monitoring and treatment to improved outcomes in severe traumatic brain injury. J Neurosurg. 112:1105–1112. 2010.
Article19). Vender J., Waller J., Dhandapani K., McDonnell D. An evaluation and comparison of intraventricular, intraparenchymal, and fluid-coupled techniques for intracranial pressure monitoring in patients with severe traumatic brain injury. J Clin Monit Comput. 25:231–236. 2011.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Early Experience of Automated Intraventricular Type Intracranial Pressure Monitoring (LiquoGuard®) for Severe Traumatic Brain Injury Patients
- Intracranial Pressure Monitoring for Acute Brain Injured Patients: When, How, What Should We Monitor
- Assessment of increased intracranial pressure in patients with brain injury
- Current Status of Intracranial Pressure Monitoring in Patients with Severe Traumatic Brain Injury in Korea : A Post Hoc Analysis of Korea Neurotrauma Databank Project with a Nationwide Survey
- Serial Brain CT Scans in Severe Head Injury without Intracranial Pressure Monitoring