Korean J Neurotrauma.
2012 Apr;8(1):48-50. 10.13004/kjnt.2012.8.1.48.
Skull Perforation and Depressed Fracture Following Skull Fixation for Stereotactic Surgery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Guri Hospital, College of Medicine, Hanyang University, Guri, Korea. kch5142@hanyang.ac.kr
- KMID: 1427683
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2012.8.1.48
Abstract
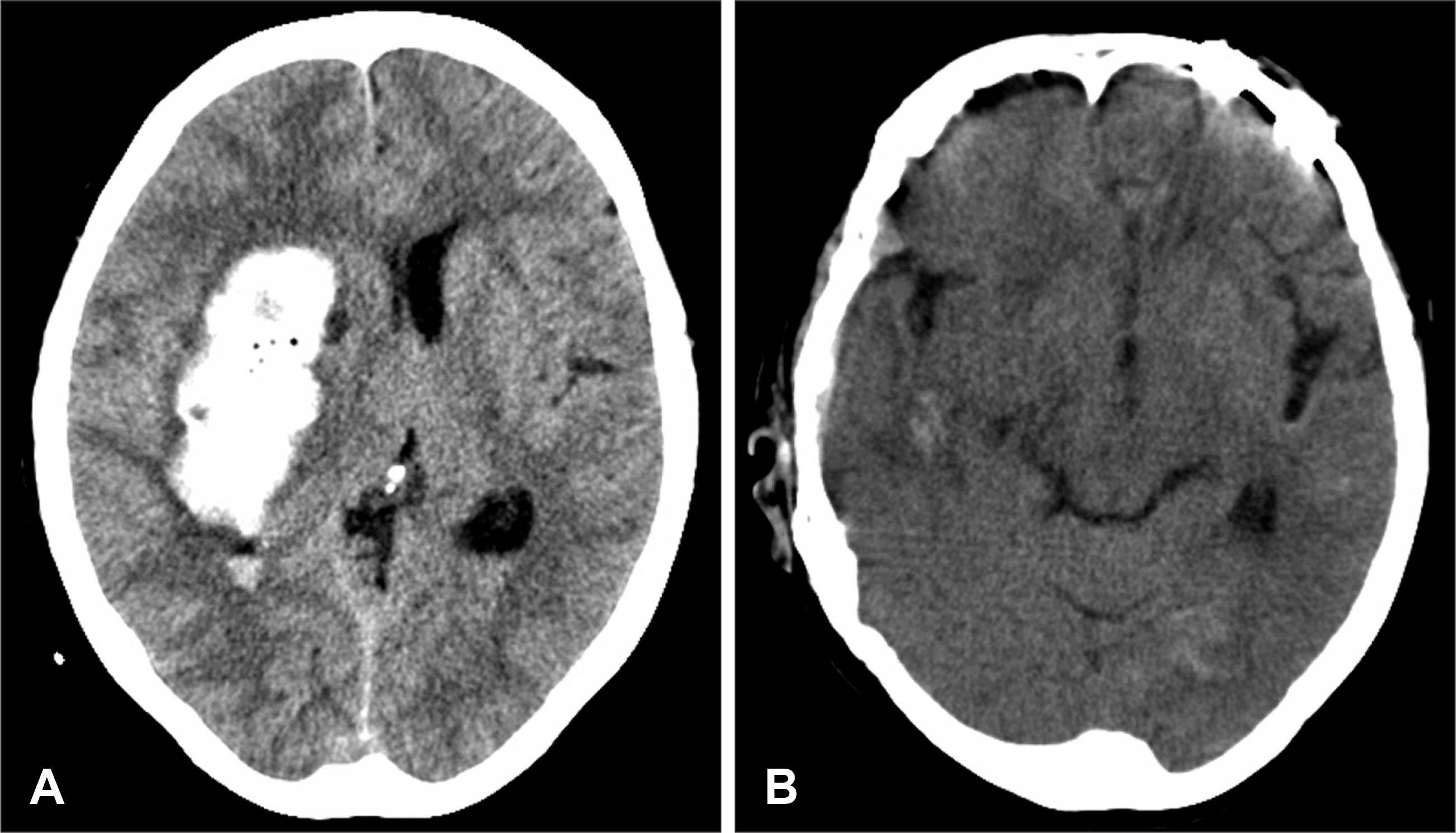
- We report an unusual case of skull perforation and depressed fracture with epidural hematoma in a 61-year-old woman who has been undertaken a skeletal fixation for stereotactic evacuation of intracerebral hematoma. Most neurosurgeons secure the patient's head in a skeletal fixation device with a three- or four-pronged pin-type headrest for stereotactic procedure or microsurgery. Although a variety of complications have been reported secondary to the use of head fixation devices, these potential complications of skull fixation have been infrequently described in the medical literatures. Consideration of calvarial thickness, tightening force, and adequate location of skull fixation may reduce the risk of skull perforation and depressed fracture.
Figure
Reference
-
1). Anegawa S., Shigemori M., Yoshida M., Kojo N., Torigoe R., Shirou-zu T, et al. [Postoperative tension pneumocephalus—report of 3 cases]. No Shinkei Geka. 14:1017–1022. 1986.2). Baerts WD., de Lange JJ., Booij LH., Broere G. Complications of the Mayfield skull clamp. Anesthesiology. 61:460–461. 1984.
Article3). De Lange JJ., Baerts WD., Booij LH. Air embolism due to the Mayfield skull clamp. Acta Anaesthesiol Belg. 35:237–241. 1984.4). Erbayraktar S., Gökmen N., Acar U. Intracranial penetrating injury associated with an intraoperative epidural haematoma caused by a spring-laden pin of a multipoise headrest. Br J Neurosurg. 15:425–428. 2001.
Article5). Fernández-Portales I., Cabezudo JM., Lorenzana L., Gómez L., Por-ras L., Rodríguez JA. Traumatic aneurysm of the superficial temporal artery as a complication of pin-type head-holder device. Case report. Surg Neurol. 52:400–403. 1999.
Article6). Fukamachi A., Koizumi H., Nagaseki Y., Nukui H. Postoperative extradural hematomas: computed tomographic survey of 1105 intracranial operations. Neurosurgery. 19:589–593. 1986.
Article7). Grinberg F., Slaughter TF., McGrath BJ. Probable venous air embolism associated with removal of the Mayfield skull clamp. Anesth Analg. 80:1049–1050. 1995.
Article8). Heifetz MD. Use and misuse of instruments in Apuzzo MLJ (Ed): Brain surgery: complications avoidance and management. New York: Churchill Livingstone, pp71-90. 1993.9). Inagawa T., Takeda T., Taguchi H., Kamiya K., Yamada T. Traumatic middle meningeal arteriovenous fistula caused by three-point skull fixation. Case report. J Neurosurg. 60:853–855. 1984.10). Lee M., Rezai AR., Chou J. Depressed skull fractures in children secondary to skull clamp fixation devices. Pediatr Neurosurg. 21:174–177. discussion 178. 1994.
Article11). Medina M., Melcarne A., Musso C., Ettorre F. Acute brain swelling during removal of supratentorial cystic lesion caused by contralateral extradural hematoma: case report. Surg Neurol. 47:428–431. 1997.
Article12). Palmer JD., Sparrow OC., Iannotti F. Postoperative hematoma: a 5-year survey and identification of avoidable risk factors. Neurosurgery. 35:1061–1064. discussion 1064-1065. 1994.13). Sade B., Mohr G. Depressed skull fracture and epidural haematoma: an unusual post-operative complication of pin headrest in an adult. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 147:101–103. 2005.
Article14). Taira T., Tanikawa T. Breakage of Mayfield head rest. J Neurosurg. 77:160–161. 1992.
Article15). Tang CT., Hsieh CT., Chiang YH., Su YH. Epidural hematoma and depressed skull fracture resulted from pin headrest - a rare complication: case report. Cesk Slov Neurol N. 103:584–586. 2007.16). Yan HJ. Epidural hematoma following use of a three-point skull clamp. J Clin Neurosci. 14:691–693. 2007.
Article17). Ziadé N., Jougla E., Coste J. Population-level impact of osteoporotic fractures on mortality and trends over time: a nationwide analysis of vital statistics for France, 1968-2004. Am J Epidemiol. 172:942–951. 2010.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Spontaneous Elevation of Neonatal Depressed Skull Fracture
- Elevation of Depressed Skull Fracture with a Cup of Breast Pump and a Suction Generator: A Case Report in Technical Aspects
- Intrauterine Depressed Skull Fracture of the Newborn associated with Skull Capillary Hemangioma
- Clinical Comparison of the Predictive Value of the Simple Skull X-Ray and 3 Dimensional Computed Tomography for Skull Fractures of Children
- Delayed Intracerebral Hemorrhage from a Pseudoaneurysm Following a Depressed Skull Fracture