J Korean Med Sci.
2012 Jun;27(6):707-710. 10.3346/jkms.2012.27.6.707.
Amnesia and Pain Relief after Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation in a Cancer Pain Patient: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. mhsjshcat@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 1421628
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2012.27.6.707
Abstract
- The mechanism of chronic pain is very complicated. Memory, pain, and opioid dependence appear to share common mechanism, including synaptic plasticity, and anatomical structures. A 48-yr-old woman with severe pain caused by bone metastasis of breast cancer received epidural block. After local anesthetics were injected, she had a seizure and then went into cardiac arrest. Following cardiopulmonary resuscitation, her cardiac rhythm returned to normal, but her memory had disappeared. Also, her excruciating pain and opioid dependence had disappeared. This complication, although uncommon, gives us a lot to think about a role of memory for chronic pain and opioid dependence.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Amnesia/*diagnosis
Anesthesia, Local/adverse effects
Bone Neoplasms/drug therapy/radiotherapy/secondary
Breast Neoplasms/drug therapy/pathology/radiotherapy
*Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation
Electroencephalography
Female
Heart Arrest/etiology
Humans
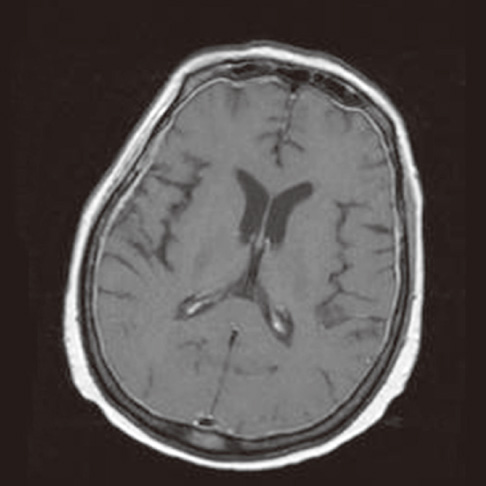
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Mepivacaine/adverse effects
Middle Aged
*Pain Management
Seizures/etiology
Tomography, X-Ray Computed
Mepivacaine
Figure
Reference
-
1. Price DD. Psychological and neural mechanisms of the affective dimension of pain. Science. 2000. 288:1769–1772.2. Hyman SE. Addiction: a disease of learning and memory. Am J Psychiatry. 2005. 162:1414–1422.3. Choi DS, Choi DY, Whittington RA, Nedeljković SS. Sudden amnesia resulting in pain relief: the relationship between memory and pain. Pain. 2007. 132:206–210.4. Mesulam M. Longo DL, Fauci AS, Kasper DL, Hauser SL, Jameson JL, Loscalzo J, editors. Aphasia, momory loss, and other focal cerebral disorders. Harrison's principles of internal medicine. 2011. 18th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill;202–212.5. Squire LR, Zola SM. Ischemic brain damage and memory impairment: a commentary. Hippocampus. 1996. 6:546–552.6. Bass E. Cardiopulmonary arrest. Pathophysiology and neurologic complications. Ann Intern Med. 1985. 103:920–927.7. Fleiss B, Coleman HA, Castillo-Melendez M, Ireland Z, Walker DW, Parkington HC. Effects of birth asphyxia on neonatal hippocampal structure and function in the spiny mouse. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2011. 29:757–766.8. De Reuck J, Vanwalleghem I, Hemelsoet D, De Weweire M, Strijckmans K, Lemahieu I. Positron emission tomographic study of post-ischaemic-hypoxic amnesia. Eur Neurol. 2003. 49:131–136.9. O'Reilly SM, Grubb NR, O'Carroll RE. In-hospital cardiac arrest leads to chronic memory impairment. Resuscitation. 2003. 58:73–79.10. Butler CR, Zeman AZ. Recent insights into the impairment of memory in epilepsy: transient epileptic amnesia, accelerated long-term forgetting and remote memory impairment. Brain. 2008. 131:2243–2263.11. Zhou C, Lippman JJ, Sun H, Jensen FE. Hypoxia-induced neonatal seizures diminish silent synapses and long-term potentiation in hippocampal CA1 neurons. J Neurosci. 2011. 31:18211–18222.12. Niv D, Devor M. Chronic pain as a disease in its own right. Pain Pract. 2004. 4:179–181.13. Katz J, Melzack R. Pain 'memories' in phantom limbs: review and clinical observations. Pain. 1990. 43:319–336.14. Flor H. Painful memories. Can we train chronic pain patients to 'forget' their pain? EMBO Rep. 2002. 3:288–291.15. Lorenz J, Hauck M. Fishman SM, Ballantyne JC, Rathmell JP, editors. Supraspinal mechanisms of pain and nociception. Bonica's management of pain. 2010. 4th ed. Baltimore: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;61–73.16. Zola-Morgan S, Squire LR, Amaral DG. Human amnesia and the medial temporal region: enduring memory impairment following a bilateral lesion limited to field CA1 of the hippocampus. J Neurosci. 1986. 6:2950–2967.17. Vogt BA. Pain and emotion interactions in subregions of the cingulate gyrus. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2005. 6:533–544.18. Nielsen FA, Balslev D, Hansen LK. Mining the posterior cingulate: segregation between memory and pain components. Neuroimage. 2005. 27:520–532.19. Nestler EJ. Common molecular and cellular substrates of addiction and memory. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2002. 78:637–647.20. von der Goltz C, Kiefer F. Learning and memory in the aetiopathogenesis of addiction: future implications for therapy? Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2009. 259:S183–S187.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Percutaneous cardiopulmonary support for the management of recurrent cardiac arrest during scoliosis correction surgery in the prone position: A case report
- Cardiac arrest due to coronary spasms in a patient in a lateral decubitus position and contralateral thoracotomy state during Ivor Lewis esophagogastrectomy: A case report
- Liver Laceration with Hemoperitoneum after Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation
- Experience of Transient Global Amnesia after General Anesthesia : A case report
- Left Ventricular Rupture during Closed-chest Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation after Pneumonectomy: A case report