J Korean Med Sci.
2012 Jun;27(6):661-667. 10.3346/jkms.2012.27.6.661.
Treatment Response and Long Term Follow-up Results of Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine and Lung Institute, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ywkim@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1421619
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2012.27.6.661
Abstract
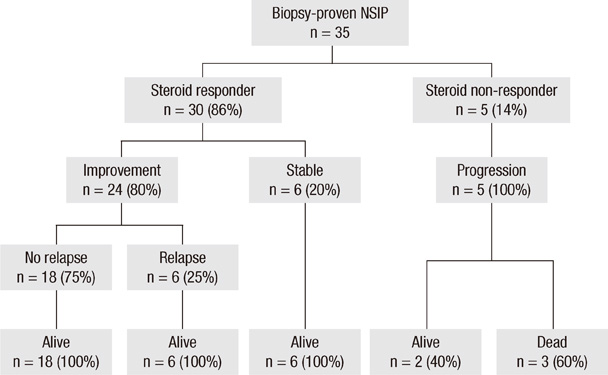
- The purpose of this study was to investigate the long-term clinical course of non-specific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP) and to determine which factors are associated with a response to steroid therapy and relapse. Thirty-five patients with pathologically proven NSIP were included. Clinical, radiological, and laboratory data were reviewed retrospectively. The male-to-female ratio was 7:28 (median age, 52 yr). Thirty (86%) patients responded to steroid therapy, and the median follow-up was 55.2 months (range, 15.9-102.0 months). Five patients (14%) showed sustained disease progression and three died despite treatment. In the five with sustained disease progression, NSIP was associated with various systemic conditions, and the seropositivity of fluorescent antinuclear antibody was significantly associated with a poor response to steroids (P = 0.028). The rate of relapse was 25%, but all relapsed patients improved after re-treatment. The initial dose of steroids was significantly low in the relapse group (P = 0.020). In conclusion, progression is associated with various systemic conditions in patients who show progression. A low dose of initial steroids is significantly associated with relapse.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Katzenstein AL, Fiorelli RF. Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia/fibrosis. Histologic features and clinical significance. Am J Surg Pathol. 1994. 18:136–147.2. Suffredini AF, Ognibene FP, Lack EE, Simmons JT, Brenner M, Gill VJ, Lane HC, Fauci AS, Parrillo JE, Masur H, et al. Nonspecific interstitial pneumonitis: a common cause of pulmonary disease in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1987. 107:7–13.3. Cottin V, Donsbeck AV, Revel D, Loire R, Cordier JF. Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia. Individualization of a clinicopathologic entity in a series of 12 patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998. 158:1286–1293.4. Fujita J, Yamadori I, Suemitsu I, Yoshinouchi T, Ohtsuki Y, Yamaji Y, Kamei T, Kobayashi M, Nakamura Y, Takahara J. Clinical features of non-specific interstitial pneumonia. Respir Med. 1999. 93:113–118.5. Douglas WW, Tazelaar HD, Hartman TE, Hartman RP, Decker PA, Schroeder DR, Ryu JH. Polymyositis-dermatomyositis-associated interstitial lung disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001. 164:1182–1185.6. Kim DS, Yoo B, Lee JS, Kim EK, Lim CM, Lee SD, Koh Y, Kim WS, Kim WD, Colby TV, et al. The major histopathologic pattern of pulmonary fibrosis in scleroderma is nonspecific interstitial pneumonia. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2002. 19:121–127.7. Yoshinouchi T, Ohtsuki Y, Fujita J, Yamadori I, Bandoh S, Ishida T, Ueda R. Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia pattern as pulmonary involvement of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int. 2005. 26:121–125.8. Nagai S, Kitaichi M, Itoh H, Nishimura K, Izumi T, Colby TV. Idiopathic nonspecific interstitial pneumonia/fibrosis: comparison with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and BOOP. Eur Respir J. 1998. 12:1010–1019.9. Travis WD, Matsui K, Moss J, Ferrans VJ. Idiopathic nonspecific interstitial pneumonia: prognostic significance of cellular and fibrosing patterns: survival comparison with usual interstitial pneumonia and desquamative interstitial pneumonia. Am J Surg Pathol. 2000. 24:19–33.10. Latsi PI, du Bois RM, Nicholson AG, Colby TV, Bisirtzoglou D, Nikolakopoulou A, Veeraraghavan S, Hansell DM, Wells AU. Fibrotic idiopathic interstitial pneumonia: the prognostic value of longitudinal functional trends. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003. 168:531–537.11. Flaherty KR, Toews GB, Travis WD, Colby TV, Kazerooni EA, Gross BH, Jain A, Strawderman RL 3rd, Paine R, Flint A, et al. Clinical significance of histological classification of idiopathic interstitial pneumonia. Eur Respir J. 2002. 19:275–283.12. Riha RL, Duhig EE, Clarke BE, Steele RH, Slaughter RE, Zimmerman PV. Survival of patients with biopsy-proven usual interstitial pneumonia and nonspecific interstitial pneumonia. Eur Respir J. 2002. 19:1114–1118.13. Park IN, Jegal Y, Kim DS, Do KH, Yoo B, Shim TS, Lim CM, Lee SD, Koh Y, Kim WS, et al. Clinical course and lung function change of idiopathic nonspecific interstitial pneumonia. Eur Respir J. 2009. 33:68–76.14. Shimizu S, Yoshinouchi T, Ohtsuki Y, Fujita J, Sugiura Y, Banno S, Yamadori I, Eimoto T, Ueda R. The appearance of S-100 protein-positive dendritic cells and the distribution of lymphocyte subsets in idiopathic nonspecific interstitial pneumonia. Respir Med. 2002. 96:770–776.15. Park JH, Kim DS, Park IN, Jang SJ, Kitaichi M, Nicholson AG, Colby TV. Prognosis of fibrotic interstitial pneumonia: idiopathic versus collagen vascular disease-related subtypes. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007. 175:705–711.16. Travis WD, Hunninghake G, King TE Jr, Lynch DA, Colby TV, Galvin JR, Brown KK, Chung MP, Cordier JF, du Bois RM, et al. Idiopathic nonspecific interstitial pneumonia: report of an American Thoracic Society project. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008. 177:1338–1347.17. Bjoraker JA, Ryu JH, Edwin MK, Myers JL, Tazelaar HD, Schroeder DR, Offord KP. Prognostic significance of histopathologic subsets in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998. 157:199–203.18. Daniil ZD, Gilchrist FC, Nicholson AG, Hansell DM, Harris J, Colby TV, du Bois RM. A histologic pattern of nonspecific interstitial pneumonia is associated with a better prognosis than usual interstitial pneumonia in patients with cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999. 160:899–905.19. Nicholson AG, Colby TV, du Bois RM, Hansell DM, Wells AU. The prognostic significance of the histologic pattern of interstitial pneumonia in patients presenting with the clinical entity of cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000. 162:2213–2217.20. Romagnoli M, Nannini C, Piciucchi S, Girelli F, Gurioli C, Casoni G, Ravaglia C, Tomassetti S, Gurioli Ch, Gavelli G, et al. Idiopathic nonspecific interstitial pneumonia: an interstitial lung disease associated with autoimmune disorders? Eur Respir J. 2011. 38:384–391.21. Kinder BW, Collard HR, Koth L, Daikh DI, Wolters PJ, Elicker B, Jones KD, King TE Jr. Idiopathic nonspecific interstitial pneumonia: lung manifestation of undifferentiated connective tissue disease? Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007. 176:691–697.22. Felicio CH, Parra ER, Capelozzi VL. Idiopathic and collagen vascular disease nonspecific interstitial pneumonia: clinical significance of remodeling process. Lung. 2007. 185:39–46.23. Schneider F, Hwang DM, Gibson K, Yousem SA. Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia: a study of 6 patients with progressive disease. Am J Surg Pathol. 2012. 36:89–93.24. Meduri GU, Chinn AJ, Leeper KV, Wunderink RG, Tolley E, Winer-Muram HT, Khare V, Eltorky M. Corticosteroid rescue treatment of progressive fibroproliferation in late ARDS. Patterns of response and predictors of outcome. Chest. 1994. 105:1516–1527.25. Nakamura Y, Chida K, Suda T, Hayakawa H, Iwata M, Imokawa S, Tsuchiya T, Ida M, Gemma H, Yasuda K, et al. Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia in collagen vascular diseases: comparison of the clinical characteristics and prognostic significance with usual interstitial pneumonia. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2003. 20:235–241.26. Daimon T, Johkoh T, Honda O, Sumikawa H, Ichikado K, Kondoh Y, Taniguchi H, Fujimoto K, Yanagawa M, Inoue A, et al. Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia associated with collagen vascular disease: analysis of CT features to distinguish the various types. Intern Med. 2009. 48:753–761.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias: Radiologic Findings
- A Case of Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia with Clinical Course of Rapid Aggravation
- A Case of Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia in a Patient with Ulcerative Colitis
- Clinical Year in Review of Interstitial Lung Diseases: Focused on Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonia
- Korean Guidelines for Diagnosis and Management of Idiopathic Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia