Clin Orthop Surg.
2013 Mar;5(1):74-81. 10.4055/cios.2013.5.1.74.
Pulse Oximetry for the Diagnosis and Prediction for Surgical Exploration in the Pulseless Perfused Hand as a Result of Supracondylar Fractures of the Distal Humerus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, KK Women's and Children's Hospital, Singapore. drreuben@hotmail.com
- KMID: 1402329
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2013.5.1.74
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
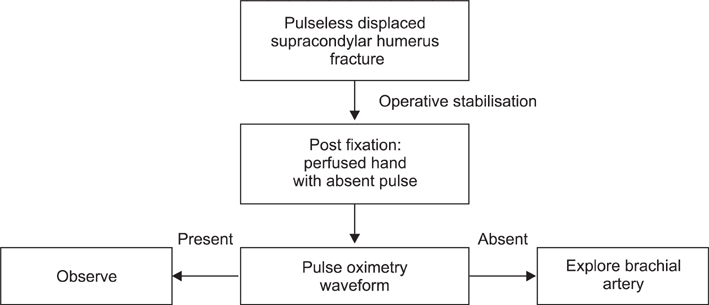
The management of the pulseless perfused hand in association with a supracondylar humerus fracture following operative stabilisation remains controversial. Previous authors have suggested the use of color-flow duplex monitoring, magnetic resonance angiography and segmental pressure monitoring as objective steps to ascertain blood flow following adequate internal fixation. We examine the use of the waveform of the pulse oximeter in objectively determining a perfused limb and in predicting the need for surgical exploration in patients who present with a pulseless perfused hand after operative stabilisation for supracondylar fracture of the humerus.
METHODS
A retrospective review of all supracondylar fractures over a 60 month duration (2005-2009) in our instituition was performed. Each electronic record was reviewed and limbs which had absent radial pulse following admission were identified. X-ray films of each of the patients were reviewed. A search using the Pubmed database was performed with the following keywords, supracondylar humerus fracture, pediatric, pulseless, vascular injury, arterial repair.
RESULTS
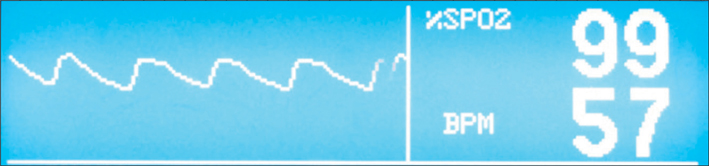
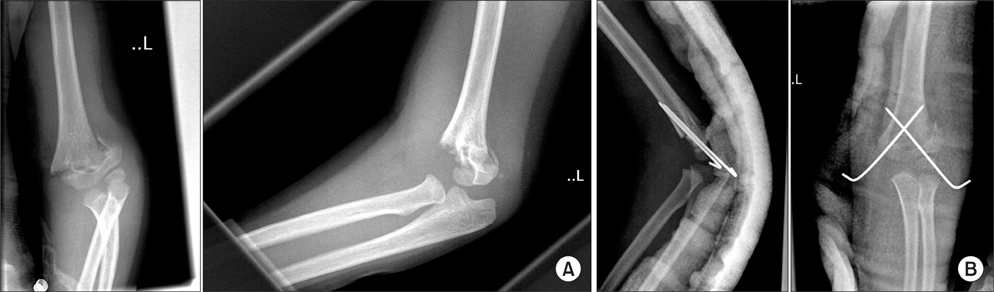
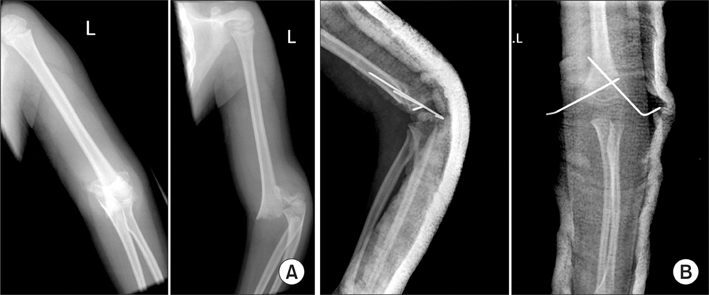
In this series of pulseless perfused hands following operative fixation of supracondylar fracture, a total of 26 patients were reviewed. All were Gartland grade III extension type fractures. Postoperative pulse oximeter waveforms were present in all but 4 patients. These patients subsequently had exploration of the brachial artery with significant findings. In the remaining 22 patients, waveforms were present and the child had return of the radial pulse soon after operative fixation without any further need for surgical exploration. At 24 months follow-up, all children were well with no neurovascular compromise.
CONCLUSIONS
The presence of a waveform on a pulse oximeter is a sensitive and easily available modality in determining vascular perfusion as compared to other more complex investigations. The high sensitivity of this test will allow surgeons to objectively determine the requirement for surgical exploration of the brachial artery.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Green NE. Green NE, Swiontkowski MF, editors. Fractures and dislocations about the elbow. Skeletal trauma in children. 2002. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Saunders;257–321.2. Garbuz DS, Leitch K, Wright JG. The treatment of supracondylar fractures in children with an absent radial pulse. J Pediatr Orthop. 1996. 16(5):594–596.3. Shuck JM, Omer GE Jr, Lewis CE Jr. Arterial obstruction due to intimal disruption in extremity fractures. J Trauma. 1972. 12(6):481–489.4. Sabharwal S, Tredwell SJ, Beauchamp RD, et al. Management of pulseless pink hand in pediatric supracondylar fractures of humerus. J Pediatr Orthop. 1997. 17(3):303–310.5. Schoenecker PL, Delgado E, Rotman M, Sicard GA, Capelli AM. Pulseless arm in association with totally displaced supracondylar fracture. J Orthop Trauma. 1996. 10(6):410–415.6. Copley LA, Dormans JP, Davidson RS. Vascular injuries and their sequelae in pediatric supracondylar humeral fractures: toward a goal of prevention. J Pediatr Orthop. 1996. 16(1):99–103.7. White L, Mehlman CT, Crawford AH. Perfused, pulseless, and puzzling: a systematic review of vascular injuries in pediatric supracondylar humerus fractures and results of a POSNA questionnaire. J Pediatr Orthop. 2010. 30(4):328–335.8. Reigstad O, Thorkildsen R, Grimsgaard C, Reigstad A, Rokkum M. Supracondylar fractures with circulatory failure after reduction, pinning, and entrapment of the brachial artery: excellent results more than 1 year after open exploration and revascularization. J Orthop Trauma. 2011. 25(1):26–30.9. Blakey CM, Biant LC, Birch R. Ischaemia and the pink, pulseless hand complicating supracondylar fractures of the humerus in childhood: long-term follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2009. 91(11):1487–1492.10. Beaty JH, Kasser JR . Beaty JH, Kasser JR, editors. Supracondylar fractures of the distal humerus. Rockwood and Wilkins' fractures in children. 2005. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;577–624.11. Shaw BA, Kasser JR, Emans JB, Rand FF. Management of vascular injuries in displaced supracondylar humerus fractures without arteriography. J Orthop Trauma. 1990. 4(1):25–29.12. Fry WR, Smith RS, Sayers DV, et al. The success of duplex ultrasonographic scanning in diagnosis of extremity vascular proximity trauma. Arch Surg. 1993. 128(12):1368–1372.13. Malviya A, Simmons D, Vallamshetla R, Bache CE. Pink pulseless hand following supra-condylar fractures: an audit of British practice. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2006. 15(1):62–64.14. Noaman HH. Microsurgical reconstruction of brachial artery injuries in displaced supracondylar fracture humerus in children. Microsurgery. 2006. 26(7):498–505.15. Korompilias AV, Lykissas MG, Mitsionis GI, Kontogeorgakos VA, Manoudis G, Beris AE. Treatment of pink pulseless hand following supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children. Int Orthop. 2009. 33(1):237–241.16. Ramesh P, Avadhani A, Shetty AP, Dheenadhayalan J, Rajasekaran S. Management of acute 'pink pulseless' hand in pediatric supracondylar fractures of the humerus. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2011. 20(3):124–128.17. McMinn RM. Last's anatomy: regional and applied. 1994. 9th ed. New York: Churchill Livingstone;78–96.18. Mangat KS, Martin AG, Bache CE. The 'pulseless pink' hand after supracondylar fracture of the humerus in children: the predictive value of nerve palsy. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2009. 91(11):1521–1525.19. Luria S, Sucar A, Eylon S, et al. Vascular complications of supracondylar humeral fractures in children. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2007. 16(2):133–143.20. Shaker IJ, White JJ, Signer RD, Golladay ES, Haller JA Jr. Special problems of vascular injuries in children. J Trauma. 1976. 16(11):863–867.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- An Experimental Study and Clinical Investigation on Rotational Deformity in Supracondylar Fracture of the Humerus in Children
- Flexion-type Humerus Supracondylar Fractures in Children
- Treatment of Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children by Open Reduction
- Radiologic Study of Torsion Type of Supracondylar Fracture of Humerus in Children
- Ulnar nerve palsy After Percutaneous Pinning in Childrens Supracondylar fracture