Clin Orthop Surg.
2012 Sep;4(3):227-233. 10.4055/cios.2012.4.3.227.
Clinical Analysis of Femur Shaft Insufficiency Fractures
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Catholic University of Daegu School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. bong@cu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1392986
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2012.4.3.227
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
To characterize the recently issued femur shaft insufficiency fracture in terms of a patient's own epidemiological status.
METHODS
Fourteen patients were treated for insufficiency fracture from July 2002 to June 2008, excluding cases including the risk factors of insufficiency fracture. All patients were female, and their mean age was 75.6 years (range, 65 to 89 years). The mean follow-up period was 50.6 months (range, 14 to 86 months).
RESULTS
The mean body weight of the Koreans in the same age group was 58.1 +/- 9.7 kg, and the mean height was 155.5 +/- 8.8 cm. The mean body weight of our insufficiency fracture patients was 45.7 kg and it was statistically significantly lower than that of the Koreans in the same age group (p < 0.001). The mean height was 147.3 cm and it was significantly shorter than the mean height of the Koreans in the same age group (p = 0.002). In regard to menopausal time, the mean menopausal time of the Koreans was 48.0 +/- 4.2 years, it was 44 years in our study, as menopause occurred statistically significantly earlier (p = 0.017). The patients with insufficiency fracture showed statistically lower weight, shorter stature and an earlier menopausal period than that of the general population.
CONCLUSIONS
In early menopausal, underweight, and short patients prescribed osteoporosis medication for an extended period of time, if predromal symptom is present, it is necessary to suspect insufficiency fracture of the femur.
MeSH Terms
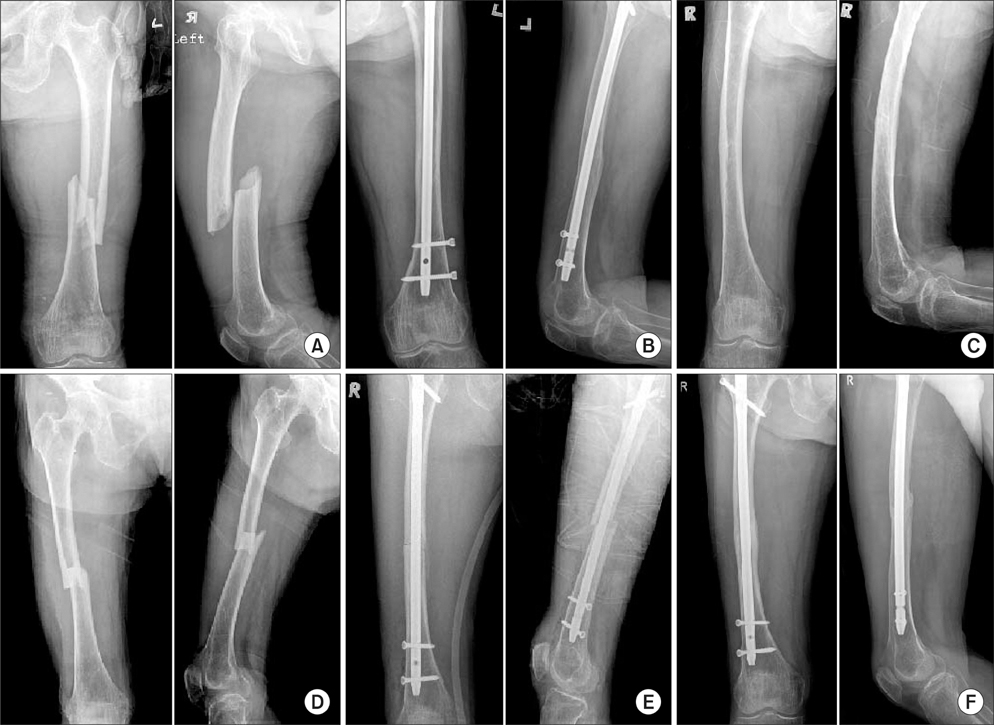
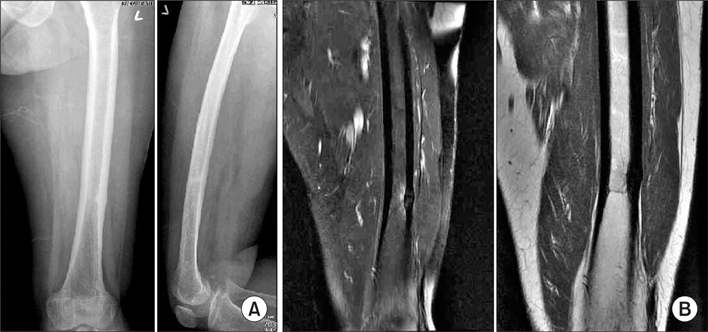
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lenart BA, Lorich DG, Lane JM. Atypical fractures of the femoral diaphysis in postmenopausal women taking alendronate. N Engl J Med. 2008. 358(12):1304–1306.
Article2. Goh SK, Yang KY, Koh JS, et al. Subtrochanteric insufficiency fractures in patients on alendronate therapy: a caution. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007. 89(3):349–353.3. Mashiba T, Hirano T, Turner CH, Forwood MR, Johnston CC, Burr DB. Suppressed bone turnover by bisphosphonates increases microdamage accumulation and reduces some biomechanical properties in dog rib. J Bone Miner Res. 2000. 15(4):613–620.
Article4. Neviaser AS, Lane JM, Lenart BA, Edobor-Osula F, Lorich DG. Low-energy femoral shaft fractures associated with alendronate use. J Orthop Trauma. 2008. 22(5):346–350.
Article5. Odvina CV, Zerwekh JE, Rao DS, Maalouf N, Gottschalk FA, Pak CY. Severely suppressed bone turnover: a potential complication of alendronate therapy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005. 90(3):1294–1301.
Article6. Schneider JP. Bisphosphonates and low-impact femoral fractures: current evidence on alendronate-fracture risk. Geriatrics. 2009. 64(1):18–23.7. Sayed-Noor AS, Sjoden GO. Case reports: two femoral insufficiency fractures after long-term alendronate therapy. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009. 467(7):1921–1926.
Article8. Black DM, Cummings SR, Karpf DB, et al. Randomised trial of effect of alendronate on risk of fracture in women with existing vertebral fractures: Fracture Intervention Trial Research Group. Lancet. 1996. 348(9041):1535–1541.
Article9. Black DM, Thompson DE, Bauer DC, et al. FIT Research Group. Fracture risk reduction with alendronate in women with osteoporosis: the Fracture Intervention Trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000. 85(11):4118–4124.
Article10. Fleisch H, Reszka A, Rodan G, Rogers M. Bilezikian JP, Raisz LG, Rodan GA, editors. Bisphosphonates: mechanisms of action. Principles of bone biology. 2002. 2nd ed. San Diego: Academic Press;1361–1385.11. Bone HG, Hosking D, Devogelaer JP, et al. Ten years' experience with alendronate for osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. N Engl J Med. 2004. 350(12):1189–1199.
Article12. Whyte MP, Wenkert D, Clements KL, McAlister WH, Mumm S. Bisphosphonate-induced osteopetrosis. N Engl J Med. 2003. 349(5):457–463.
Article13. Fleisch H. Bisphosphonates: mechanisms of action. Endocr Rev. 1998. 19(1):80–100.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ipsilateral Fractures of the Hip and Femoral Shaft
- Insufficiency Fracture of Proximal Femur Shaft without Bisphosphonate Therapy: Report of Three Cases
- Bilateral Femoral Neck Fractures in a Young Adult: A Case Report
- Repetitive Insufficiency Fractures of the Femoral Shaft: A Case Report
- Femur Neck Fracture during Closed Medullary Nailing of Femur Shaft Fracture: A Report of Two Cases