Korean J Radiol.
2012 Aug;13(4):492-495. 10.3348/kjr.2012.13.4.492.
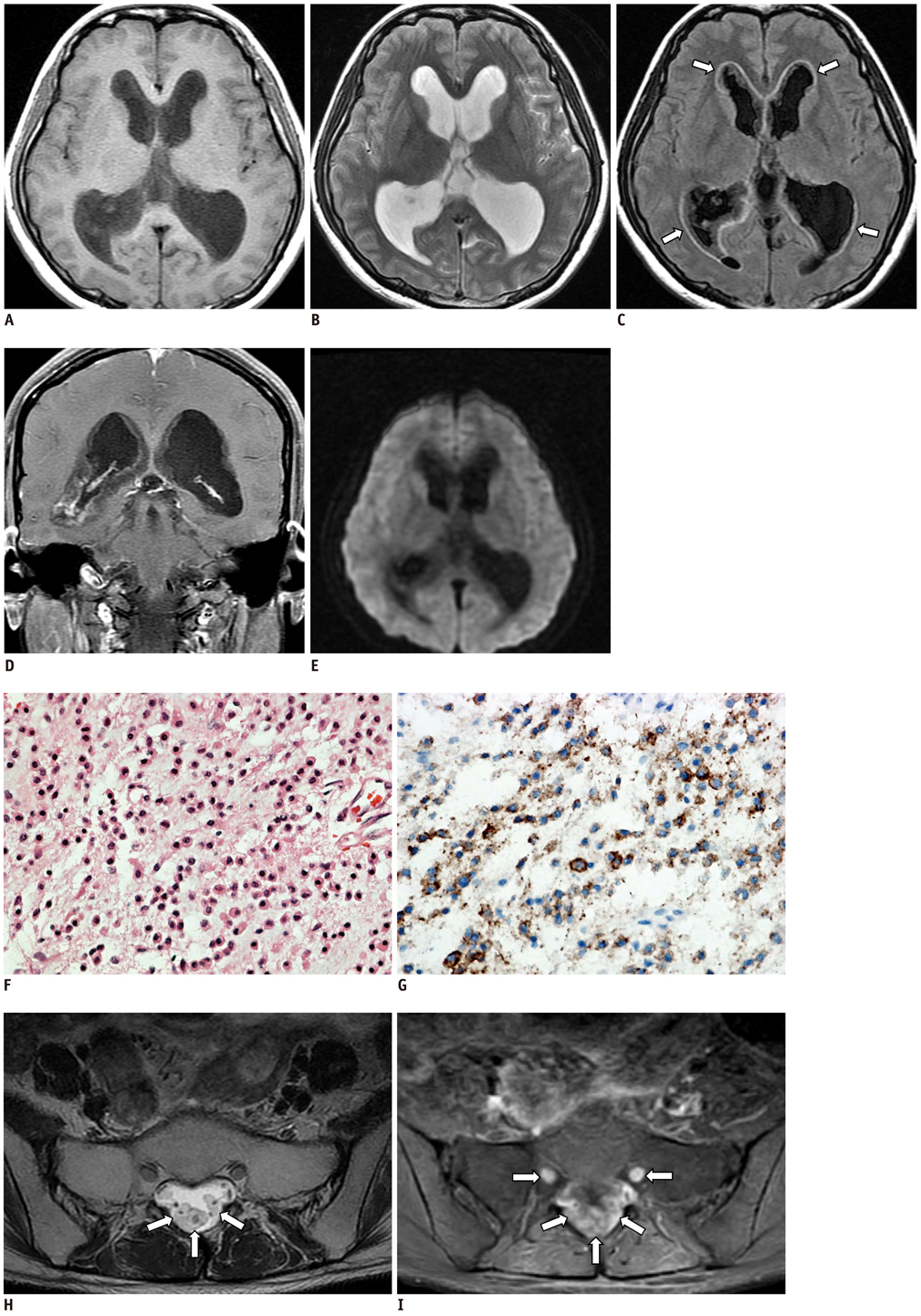
Diffuse Ependymal Dysembryoplastic Neuroepithelial Tumor Causing Spinal Drop Metastases: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Chonnam National University Medical School, Chonnam National University Hospital, Gwangju 501-757, Korea. radyoon@jnu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, Hwasun 519-809, Korea.
- KMID: 1383862
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2012.13.4.492
Abstract
- Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumors (DNETs) arise mostly in the supratentorial cerebral cortex. A very rare case of intraventricular DNET with diffuse ependymal involvement, which causes spinal drop metastasis, is presented.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Daumas-Duport C, Scheithauer BW, Chodkiewicz JP, Laws ER Jr, Vedrenne C. Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor: a surgically curable tumor of young patients with intractable partial seizures. Report of thirty-nine cases. Neurosurgery. 1988. 23:545–556.2. Cervera-Pierot P, Varlet P, Chodkiewicz JP, Daumas-Duport C. Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumors located in the caudate nucleus area: report of four cases. Neurosurgery. 1997. 40:1065–1069. discussion 1069-1070.3. Guesmi H, Houtteville JP, Courthéoux P, Derlon JM, Chapon F. [Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumors. Report of 8 cases including two with unusual localization]. Neurochirurgie. 1999. 45:190–200.4. Fujimoto K, Ohnishi H, Tsujimoto M, Hoshida T, Nakazato Y. Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor of the cerebellum and brainstem. Case report. J Neurosurg. 2000. 93:487–489.5. Cataltepe O, Marshall P, Smith TW. Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor located in pericallosal and intraventricular area in a child. Case report. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2009. 3:456–460.6. Ongürü O, Deveci S, Sirin S, Timurkaynak E, Günhan O. Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor in the left lateral ventricle. Minim Invasive Neurosurg. 2003. 46:306–309.7. Harter DH, Omeis I, Forman S, Braun A. Endoscopic resection of an intraventricular dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor of the septum pellucidum. Pediatr Neurosurg. 2006. 42:105–107.8. Altinörs N, Calisaneller T, Gülsşen S, Ozen O, Ongürü O. Intraventricular dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor: case report. Neurosurgery. 2007. 61:E1332–E1333. discussion E1333.9. Bilginer B, Söylemezoğlu F, Cila A, Akalan N. Intraventricular dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor-like neoplasm with disseminated spinal tumor. Turk Neurosurg. 2009. 19:69–72.10. Campos AR, Clusmann H, von Lehe M, Niehusmann P, Becker AJ, Schramm J, et al. Simple and complex dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumors (DNT) variants: clinical profile, MRI, and histopathology. Neuroradiology. 2009. 51:433–443.11. Stanescu Cosson R, Varlet P, Beuvon F, Daumas Duport C, Devaux B, Chassoux F, et al. Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumors: CT, MR findings and imaging follow-up: a study of 53 cases. J Neuroradiol. 2001. 28:230–240.12. Parmar HA, Hawkins C, Ozelame R, Chuang S, Rutka J, Blaser S. Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery ring sign as a marker of dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumors. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2007. 31:348–353.