Ann Lab Med.
2012 Jul;32(4):289-293. 10.3343/alm.2012.32.4.289.
MYC Rearrangement Involving a Novel Non-immunoglobulin Chromosomal Locus in Precursor B-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine and Genetics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. heejinkim@skku.edu
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, Chonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju, Korea.
- KMID: 1380089
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2012.32.4.289
Abstract
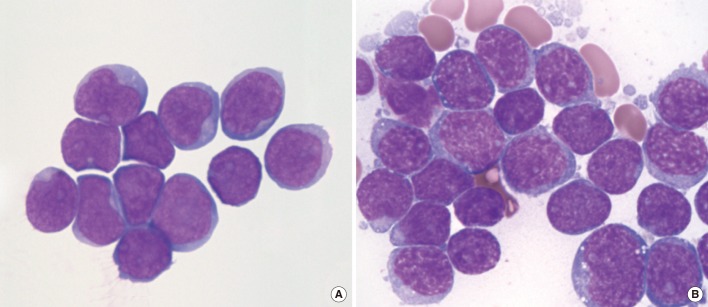
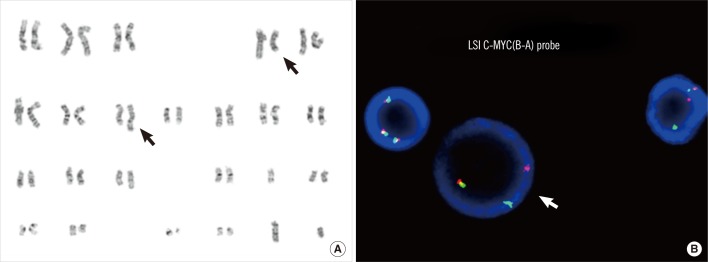
- MYC rearrangement, a characteristic cytogenetic abnormality of Burkitt lymphoma and several subsets of other mature B-cell neoplasms, typically involves an immunoglobulin gene partner. Herein, we describe a case of precursor B-cell lymphoblastic leukemia harboring a MYC rearrangement with a novel non-immunoglobulin partner locus. The patient was a 4-yr-old Korean boy with ALL of the precursor B-cell immunophenotype. At the time of the second relapse, cytogenetic analyses revealed t(4;8)(q31.1;q24.1) as a clonal evolution. The MYC rearrangement was confirmed by FISH analysis. He died 3 months after the second relapse without achieving complete remission. To our knowledge, this is the first report of a case of MYC rearrangement with a non-immunoglobulin partner in precursor B-cell lymphoblastic leukemia.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Bone Marrow Cells/pathology
Child, Preschool
Chromosomes, Human, Pair 4
Chromosomes, Human, Pair 8
Genetic Loci
Humans
Immunoglobulins/genetics
Karyotyping
Male
Precursor B-Cell Lymphoblastic Leukemia-Lymphoma/*genetics/metabolism/pathology
Proto-Oncogene Proteins c-myc/*genetics
Recurrence
Translocation, Genetic
Figure
Reference
-
1. Boerma EG, Siebert R, Kluin PM, Baudis M. Translocations involving 8q24 in Burkitt lymphoma and other malignant lymphomas: a historical review of cytogenetics in the light of todays knowledge. Leukemia. 2009; 23:225–234. PMID: 18923440.
Article2. De Jong D, Voetdijk BM, Beverstock GC, van Ommen GJ, Willemze R, Kluin PM. Activation of the c-myc oncogene in a precursor-B-cell blast crisis of follicular lymphoma, presenting as composite lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 1988; 318:1373–1378. PMID: 3285208.3. Gupta AA, Grant R, Shago M, Abdelhaleem M. Occurrence of t(8;22) (q24.1;q11.2) involving the MYC locus in a case of pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia with a precursor B cell immunophenotype. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2004; 26:532–534. PMID: 15284595.4. Hassan R, Felisbino F, Stefanoff CG, Pires V, Klumb CE, Dobbin J, et al. Burkitt lymphoma/leukaemia transformed from a precursor B cell: clinical and molecular aspects. Eur J Haematol. 2008; 80:265–270. PMID: 18005389.
Article5. Kaneko Y, Rowley JD, Check I, Variakojis D, Moohr JW. The 14q+ chromosome in pre-B-ALL. Blood. 1980; 56:782–785. PMID: 6968599.
Article6. Komrokji R, Lancet J, Felgar R, Wang N, Bennett JM. Burkitt's leukemia with precursor B-cell immunophenotype and atypical morphology (atypical Burkitt's leukemia/lymphoma): case report and review of literature. Leuk Res. 2003; 27:561–566. PMID: 12648517.
Article7. Loh ML, Samson Y, Motte E, Moreau LA, Dalton V, Waters S, et al. Translocation (2;8)(p12;q24) associated with a cryptic t(12;21)(p13;q22) TEL/AML1 gene rearrangement in a child with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2000; 122:79–82. PMID: 11106815.
Article8. Mufti GJ, Hamblin TJ, Oscier DG, Johnson S. Common ALL with pre-B-cell features showing (8;14) and (14;18) chromosome translocations. Blood. 1983; 62:1142–1146. PMID: 6605167.
Article9. Navid F, Mosijczuk AD, Head DR, Borowitz MJ, Carroll AJ, Brandt JM, et al. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia with the (8;14)(q24;q32) translocation and FAB L3 morphology associated with a B-precursor immunophenotype: the Pediatric Oncology Group experience. Leukemia. 1999; 13:135–141. PMID: 10049049.
Article10. Au WY, Horsman DE, Gascoyne RD, Viswanatha DS, Klasa RJ, Connors JM. The spectrum of lymphoma with 8q24 aberrations: a clinical, pathological and cytogenetic study of 87 consecutive cases. Leuk Lymphoma. 2004; 45:519–528. PMID: 15160914.
Article11. Young KH, Xie Q, Zhou G, Eickhoff JC, Sanger WG, Aoun P, et al. Transformation of follicular lymphoma to precursor B-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma with c-myc gene rearrangement as a critical event. Am J Clin Pathol. 2008; 129:157–166. PMID: 18089500.12. O'Neil J, Look AT. Mechanisms of transcription factor deregulation in lymphoid cell transformation. Oncogene. 2007; 26:6838–6849. PMID: 17934490.13. Mikhail FM, Serry KA, Hatem N, Mourad ZI, Farawela HM, El Kaffash DM, et al. A new translocation that rearranges the AML1 gene in a patient with T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2002; 135:96–100. PMID: 12072207.
Article14. Nguyen TT, Ma LN, Slovak ML, Bangs CD, Cherry AM, Arber DA. Identification of novel Runx1 (AML1) translocation partner genes SH3D19, YTHDf2, and ZNF687 in acute myeloid leukemia. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2006; 45:918–932. PMID: 16858696.15. Van Limbergen H, Poppe B, Michaux L, Herens C, Brown J, Noens L, et al. Identification of cytogenetic subclasses and recurring chromosomal aberrations in AML and MDS with complex karyotypes using M-FISH. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2002; 33:60–72. PMID: 11746988.
Article16. Veldman T, Vignon C, Schrock E, Rowley JD, Ried T. Hidden chromosome abnormalities in haematological malignancies detected by multicolour spectral karyotyping. Nat Genet. 1997; 15:406–410. PMID: 9090389.
Article17. Lin SE, Oyama T, Nagase T, Harigaya K, Kitagawa M. Identification of new human mastermind proteins defines a family that consists of positive regulators for notch signaling. J Biol Chem. 2002; 277:50612–50620. PMID: 12386158.
Article18. Preudhomme C, Dervite I, Wattel E, Vanrumbeke M, Flactif M, Lai JL, et al. Clinical significance of p53 mutations in newly diagnosed Burkitt's lymphoma and acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a report of 48 cases. J Clin Oncol. 1995; 13:812–820. PMID: 7707106.
Article19. Rowh MA, DeMicco A, Horowitz JE, Yin B, Yang-Iott KS, Fusello AM, et al. Tp53 deletion in B lineage cells predisposes mice to lymphomas with oncogenic translocations. Oncogene. 2011; 30:4757–4764. PMID: 21625223.
Article20. Ahmed D, Ahmed TA, Ahmed S, Tipu HN, Wiqar MA. CD5-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2008; 18:310–311. PMID: 18541090.21. Peterson MR, Noskoviak KJ, Newbury R. CD5-positive B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr Dev Pathol. 2007; 10:41–45. PMID: 17378623.
Article22. Subirá D, Roman A, Jiménez-Garófano C, Prieto E, Martínez-Delgado B, Aceituno E, et al. Brief report. CD19/CD5 acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1998; 31:551–552. PMID: 9835918.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Precursor B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Two Patients with a History of Cytotoxic Therapy
- A Case of CD7+, CD4-, CD8-, CD3-acute T cell lymphoblastic leukemia
- Mixed-phenotypic acute leukemia: cytochemically myeloid and phenotypically early T-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- A Case of Pediatric Precursor B-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Associated with Translocations (14;18)(q32;q21) and (8;9)(q24;p13)
- A Case of Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia with Trisomy 5 as a Sole Chromosomal Anomaly: A Prognostic Significance