J Vet Sci.
2012 Jun;13(2):119-125. 10.4142/jvs.2012.13.2.119.
Production of a highly group-specific monoclonal antibody against zearalenone and its application in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- Affiliations
-
- 1Toxicology and Chemistry Division, Animal, Plant and Fisheries Quarantine and Inspection Agency, Anyang 430-824, Korea. kanghg67@korea.kr
- 2Analytical Toxicology Lab, College of Veterinary Medicine, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY 14850, USA.
- KMID: 1376185
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2012.13.2.119
Abstract
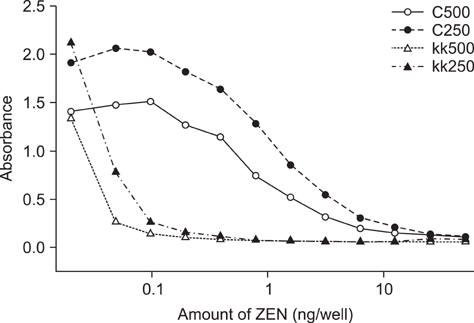
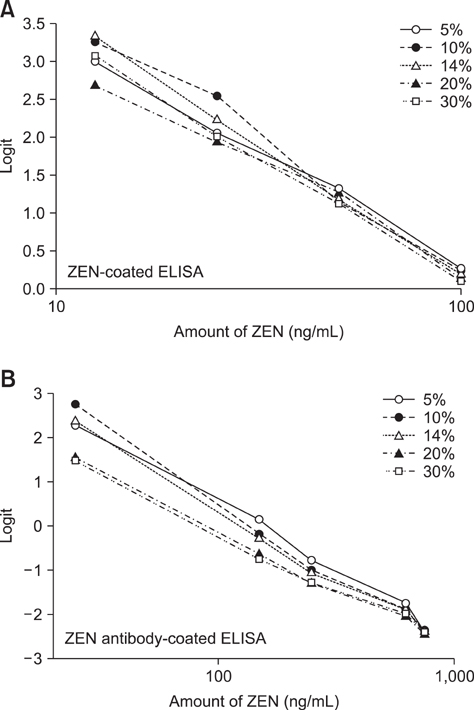
- A monoclonal antibody (mAb) against zearalenone (ZEN) was produced using ZEN-carboxymethoxylamine and -BSA conjugates. Antibody produced by one clone showing a very high binding ability was selected and found to have a higher affinity for ZEN compared to a commerciall ZEN antibody. We developed two direct competitive ELISA systems using the selected antibody (ZEN-coated and anti-ZEN antibody-coated ELISA). Quantitative ranges for the anti-ZEN antibody-coated ELISA and ZEN-coated ELISA were from 25 to 750 ppb and from 12.5 to 100 ppb, respectively. The detection limit of both methods as measured with standard solutions was 10 ppb. The intra-plate and inter-well variation of both ELISAs were less than 10%. The IC50 values for alpha-zearalenol, beta-zearalenol, alpha-zearalanol, and beta-zearalanol compared to ZEN were 108.1, 119.3, 114.1, and 130.3% for the ZEN-coated ELISA. These values were 100.7, 120.7, 121.6, and 151.6% for the anti-ZEN antibody-coated ELISA. According to the anti-ZEN antibody-coated ELISA, the average recovery rates of ZEN from spiked animal feed containing 150 to 600 ng/mL of ZEN ranged from 106.07 to 123.00% with 0.93 to 2.28% coefficients of variation. Our results demonstrate that the mAb developed in this study could be used to simultaneously screen for ZEN and its metabolites in feed.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bennett GA, Nelsen TC, Miller BM. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of zearalenone in corn, wheat, and pig feed: collaborative study. J AOAC Int. 1994. 77:1500–1509.
Article2. Burkin AA, Kononenko GP, Soboleva NA. Group-specific antibodies against zearalenone and its metabolites and synthetic analogs. Prikl Biokhim Mikrobiol. 2002. 38:194–202.3. Burmistrova NA, Goryacheva IY, Basova EY, Franki AS, Elewaut D, Van Beneden K, Deforce D, Van Peteghem C, De Saeger S. Application of a new anti-zearalenone monoclonal antibody in different immunoassay formats. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2009. 395:1301–1307.
Article4. Cervino C, Weber E, Knopp D, Niessner R. Comparison of hybridoma screening methods for the efficient detection of high-affinity hapten-specific monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 2008. 329:184–193.
Article5. Chun HS, Choi EH, Chang HJ, Choi SW, Eremin SA. A fluorescence polarization immunoassay for the detection of zearalenone in corn. Anal Chim Acta. 2009. 639:83–89.
Article6. Dong M, He XJ, Tulayakul P, Li JY, Dong KS, Manabe N, Nakayama H, Kumagai S. The toxic effects and fate of intravenously administered zearalenone in goats. Toxicon. 2010. 55:523–530.
Article7. Goyarts T, Dänicke S, Valenta H, Ueberschär KH. Carry-over of Fusarium toxins (deoxynivalenol and zearalenone) from naturally contaminated wheat to pigs. Food Addit Contam. 2007. 24:369–380.
Article8. Klaus GGB, Cross AM. The influence of epitope density on the immunological properties of hapten-protein conjugates. I. Characteristics of the immune response to hapten-coupled albumen with varying epitope density. Cell Immunol. 1974. 14:226–241.
Article9. Kuiper-Goodman T, Scott PM, Watanabe H. Risk assessment of the mycotoxin zearalenone. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 1987. 7:253–306.
Article10. Meng J, Zhang J, Zhang N, Shi J, Shao B. Determination of zearalenone and related mycotoxins in grain and its products by solid-phase extraction coupled with ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Se Pu. 2010. 28:601–607.
Article11. Nakagawa T, Blaser K, de Weck AL. Effect of epitope density on the induction of the IgE immune response in mice. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1980. 63:212–219.
Article12. Olsen M, Mirocha CJ, Abbas HK, Johansson B. Metabolism of high concentrations of dietary zearalenone by young male turkey poults. Poult Sci. 1986. 65:1905–1910.
Article13. Richard JL, Bennett GA, Ross PF, Nelson PE. Analysis of naturally occurring mycotoxins in feedstuffs and food. J Anim Sci. 1993. 71:2563–2574.
Article14. Schneider E, Usleber E, Märtlbauer E, Dietrich R, Terplan G. Multimycotoxin dipstick enzyme immunoassay applied to wheat. Food Addit Contam. 1995. 12:387–393.
Article15. Shim WB, Dzantiev BB, Eremin SA, Chung DH. One-step simultaneous immunochromatographic strip test for multianalysis of ochratoxin A and zearalenone. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2009. 19:83–92.16. Thongrussamee T, Kuzmina NS, Shim WB, Jiratpong T, Eremin SA, Intrasook J, Chung DH. Monoclonal-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of zearalenone in cereals. Food Addit Contam Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess. 2008. 25:997–1006.
Article17. Thouvenot D, Morfin RF. Radioimmunoassay for zearalenone and zearalanol in human serum: production, properties, and use of porcine antibodies. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983. 45:16–23.
Article18. Urraca JL, Benito-Peña E, Pérez-Conde C, Moreno-Bondi MC, Pestka JJ. Analysis of zearalenone in cereal and swine feed samples using an automated flow-through immunosensor. J Agric Food Chem. 2005. 53:3338–3344.
Article19. Wang YP, Ji R, Jiang T, Kang WJ. Development of ELISA-kit of quantitative analysis for zearalenone. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu. 2006. 35:221–224.20. Zinedine A, Soriano JM, Moltó JC, Mañes J. Review on the toxicity, occurrence, metabolism, detoxification, regulations and intake of zearalenone: an oestrogenic mycotoxin. Food Chem Toxicol. 2007. 45:1–18.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Application of aptamers for assessment of vaccine efficacy
- Production and Characterization of Monoclonal Antibodies Reactive to PPD of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
- Detection of anti-borrelia burgdorferi antibody by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in Korea
- Magnetic nanoparticle based purification and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using monoclonal antibody against enrofloxacin
- Comparison of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, indirect immunofluorescent antibody test and indirect immunoperoxidase antibody test in setecting antibodies to rickettsia tsutsugamushi