Clin Orthop Surg.
2012 Mar;4(1):45-57. 10.4055/cios.2012.4.1.45.
Free Fat Graft for Congenital Hand Differences
- Affiliations
-
- 1Sapporo Hand Surgery and Congenital Hand Differences Center, Orthopaedic Hokushin-Higashi Hospital, Sapporo, Japan. hand@ogino1.com
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Yamagata University School of Medicine, Yamagata, Japan.
- 3Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Sapporo Medical University School of Medicine, Sapporo, Japan.
- KMID: 1245398
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2012.4.1.45
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Free fat graft has been used for the treatment of congenital hand differences. However, there have been a few reports about the outcome of that treatment. In this study, the outcome of free fat grafts for congenital hand and foot differences was investigated.
METHODS
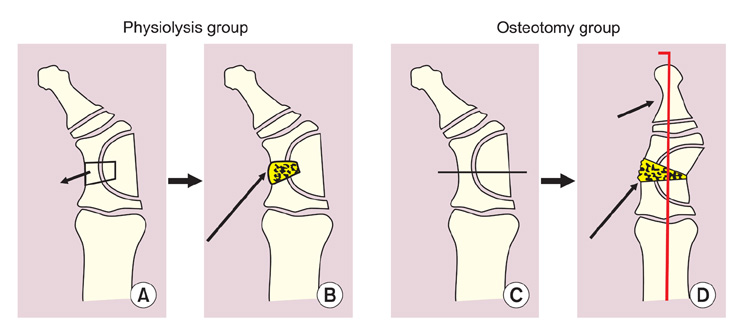
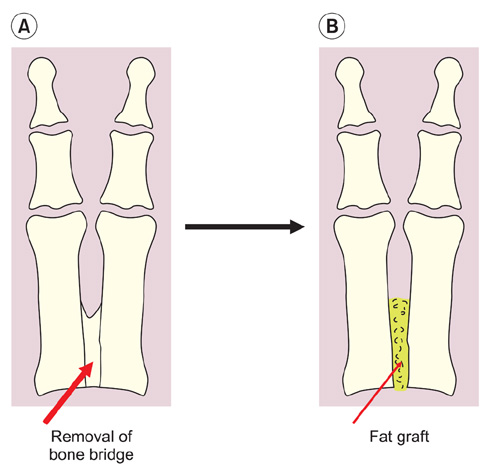
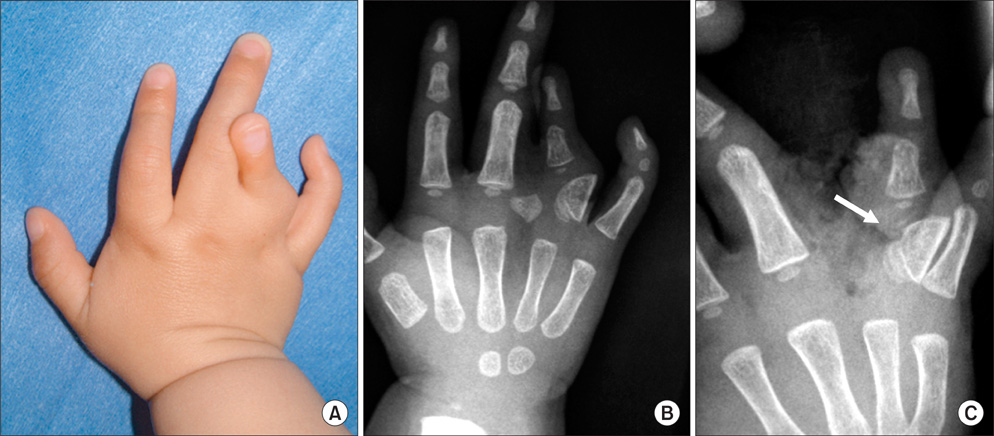
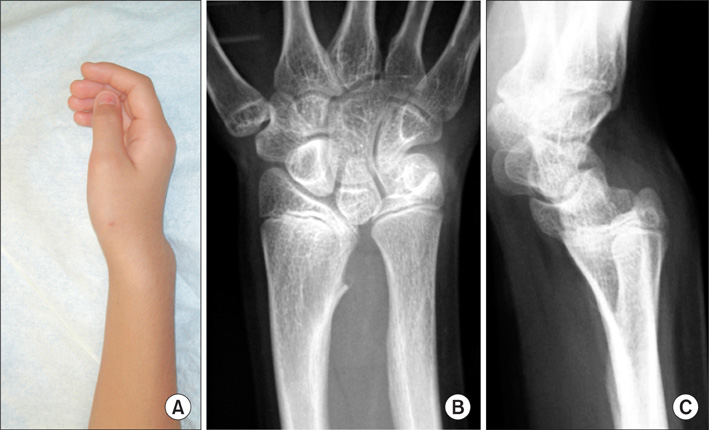
Fourteen bones with longitudinal epiphyseal bracket, 3 wrists with Madelung deformity, and 5 cases of osseous syndactyly were treated with free fat graft with osteotomy, physiolysis, or separation of osseous syndactyly. Of the fourteen bones with longitudinal epiphyseal bracket, 9 were treated with open wedge osteotomy with free fat graft and 5 with physiolysis and free fat graft. The Madelung deformity was treated with physiolysis with free fat graft. For osseous syndactyly, syndactyly release with free fat graft was performed five times on four hands.
RESULTS
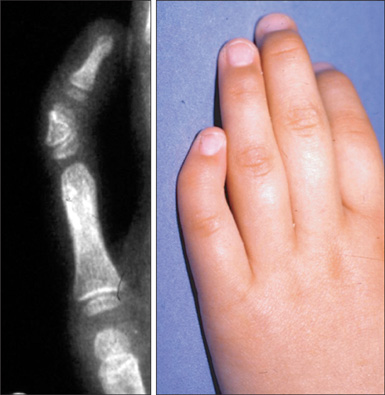
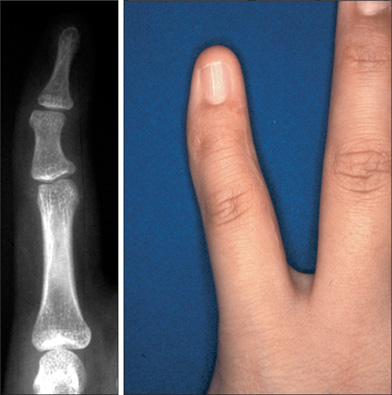
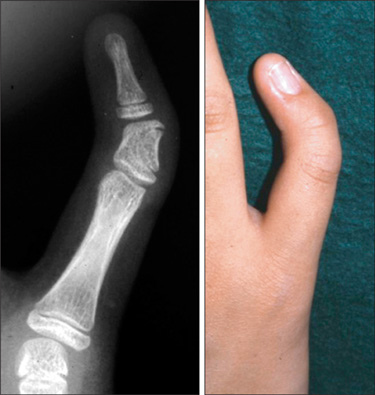
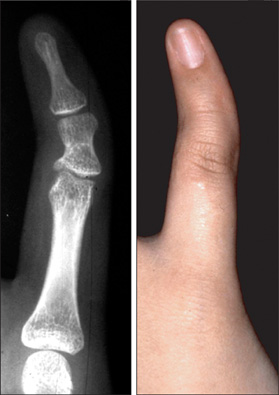
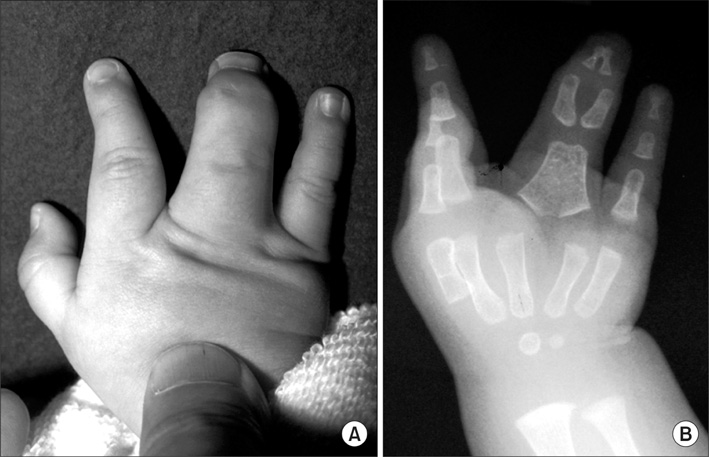
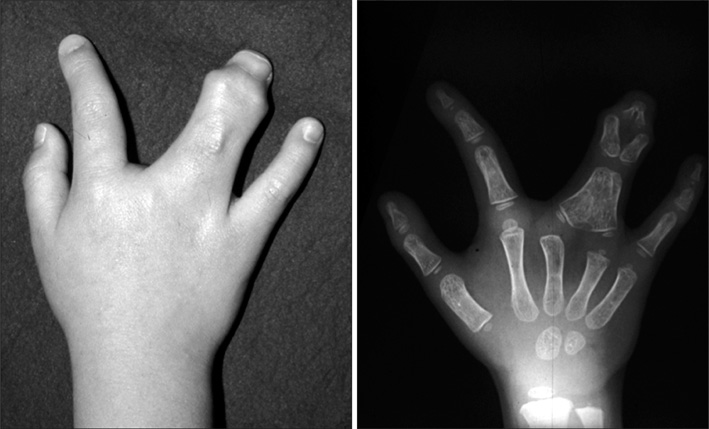
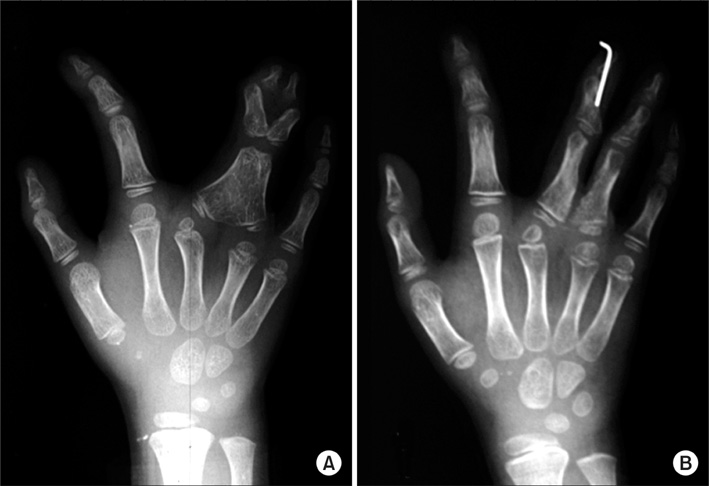
In the fourteen cases with longitudinal epiphyseal bracket, lateral deviation improved in all except two cases after surgery. The average lateral deviation angle changed from 32.5 degrees before surgery to 15.2 degrees after surgery. The average improvement of the lateral deviation angle was 12.2 degrees in the osteotomy group and 20.6 degrees in the physiolysis group. The mean ratio of improvement of the lateral deviation angle to the lateral deviation angle before surgery was 39.4% in the osteotomy group and 51.2% in the physiolysis group. The Madelung deformity improved after surgery in two cases but there was no improvement in one case. For these conditions, the results were not good enough when surgery was done after age 13 or at age four for severely hypoplastic brachymesophalangy. Of the 5 cases of osseous syndactyly, reunion of the separated bones occurred in one case. The grafted free fat should be deep enough to cover the osteotomy site of the bones to prevent reunion of the separated bones.
CONCLUSIONS
Physiolysis and free fat graft performed during the growth period can correct the deviation due to longitudinal epiphyseal bracket and Madelung deformity. Free fat graft is also useful to prevent reunion of the bones after separation of osseous syndcatyly, if the grafted fat is securely filled into the space between the separated bones.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Langenskiold A. The possibilities of eliminating premature partial closure of an epiphyseal plate caused by trauma or disease. Acta Orthop Scand. 1967. 38(1-4):267–279.
Article2. Langenskiold A. An operation for partial closure of an epiphysial plate in children, and its experimental basis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1975. 57(3):325–330.3. Light TR, Ogden JA. The longitudinal epiphyseal bracket: implications for surgical correction. J Pediatr Orthop. 1981. 1(3):299–305.
Article4. Vickers D. Clinodactyly of the little finger: a simple operative technique for reversal of the growth abnormality. J Hand Surg Br. 1987. 12(3):335–342.
Article5. Vickers D, Nielsen G. Madelung deformity: surgical prophylaxis (physiolysis) during the late growth period by resection of the dyschondrosteosis lesion. J Hand Surg Br. 1992. 17(4):401–407.
Article6. Zhang G, Kato H, Yamazaki H. Physiolysis for correction of the delta phalanx in clinodactyly of the bilateral little fingers. Hand Surg. 2005. 10(2-3):297–302.
Article7. Bednar MS, Bindra RR, Light TR. Epiphyseal bar resection and fat interposition for clinodactyly. J Hand Surg Am. 2010. 35(5):834–837.
Article8. Kato H, Ogino T, Minami A, Sugimoto Y, Nakatsuchi Y. Delta pahalnax: roetntgenographic findings and surgical treatment. J Jpn Soc Surg Hand. 1990. 6(6):1031–1041.9. Ishigaki D, Ogino T, Takahara M, Kikuchi N, Watanabe T. Pysiolysis and free fat graft for congenital growth plate disorders. J Jpn Soc Surg Hand. 2007. 24(3):306–311.10. Jonew GB. Delta phalanx. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1964. 46(2):226–228.11. Carstam N, Theander G. Surgical treatment of clinodactyly caused by longitudinally bracketed diaphysis ("delta phalanx"). Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg. 1975. 9(3):199–202.
Article12. Swanson AB, Swanson GD, Tada K. A classification for congenital limb malformation. J Hand Surg Am. 1983. 8(5 Pt 2):693–702.
Article13. Jaeger M, Refior HJ. The congenital triangular deformity of the tubular bones of hand and foot. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1971. 81:139–150.
Article14. Congenital Committee of the Japanese Society for Surgery of the Hand. A manual for classification of congenital hand deformities. J Jpn Soc Surg Hand. 2000. 17(3):353–365.15. Smith RJ. Osteotomy for "delta-phalanx" deformity. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1977. (123):91–94.
Article16. White GM, Weiland AJ. Madelung's deformity: treatment by osteotomy of the radius and Lauenstein procedure. J Hand Surg Am. 1987. 12(2):202–204.
Article17. Sakuma T, Ogino T, Minami A, Fukuda K, Muramatsu I. Clinical features of Madelung's deformity and functional results after surgery. J Jpn Soc Surg Hand. 1987. 4(2):586–592.18. Watson HK, Pitts EC, Herber S. Madelung's deformity: a surgical technique. J Hand Surg Br. 1993. 18(5):601–605.19. Langenskiold A, Kiviluoto O. Prevention of epidural scar formation after operations on the lumbar spine by means of free fat transplants: a preliminary report. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1976. (115):92–95.20. Kanaya F, Ibaraki K. Mobilization of a congenital proximal radioulnar synostosis with use of a free vascularized fascio-fat graft. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998. 80(8):1186–1192.
Article21. Ueba Y, Nishijima N, Takada H. Congenital synostosis of the fourth and fifth metacarpal. Seikei Geka. 1983. 34(12):1810–1812.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Congenital hand differences: a comprehensive literature review
- Congenital Pseudarthrosisof the Tibia: Treated with Free Vascularized Fibular Graft
- Management of the Posttraumatic Neuralgia of the Peripheral Nerve by External Neurolysis
- Cauda Equina Syndrome after Laminectomy of Lumbar Spine with Application of Autogenous Free Fat Graft: A Case Report
- Correction of the Tear Trough Using Orbital Fat Graft from the Lower Lid