Korean J Urol.
2008 May;49(5):418-423. 10.4111/kju.2008.49.5.418.
Initial Experience of Laparoscopic Simple Prostatectomy in Patients with Large Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. natisururo@yahoo.co.kr
- KMID: 1204522
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/kju.2008.49.5.418
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: Simple prostatectomy has been a mainstay of therapy for patients with large prostatic adenoma. We describe laparoscopic approach for resection of large prostatic adenoma as an alternative to open simple prostatectomy.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
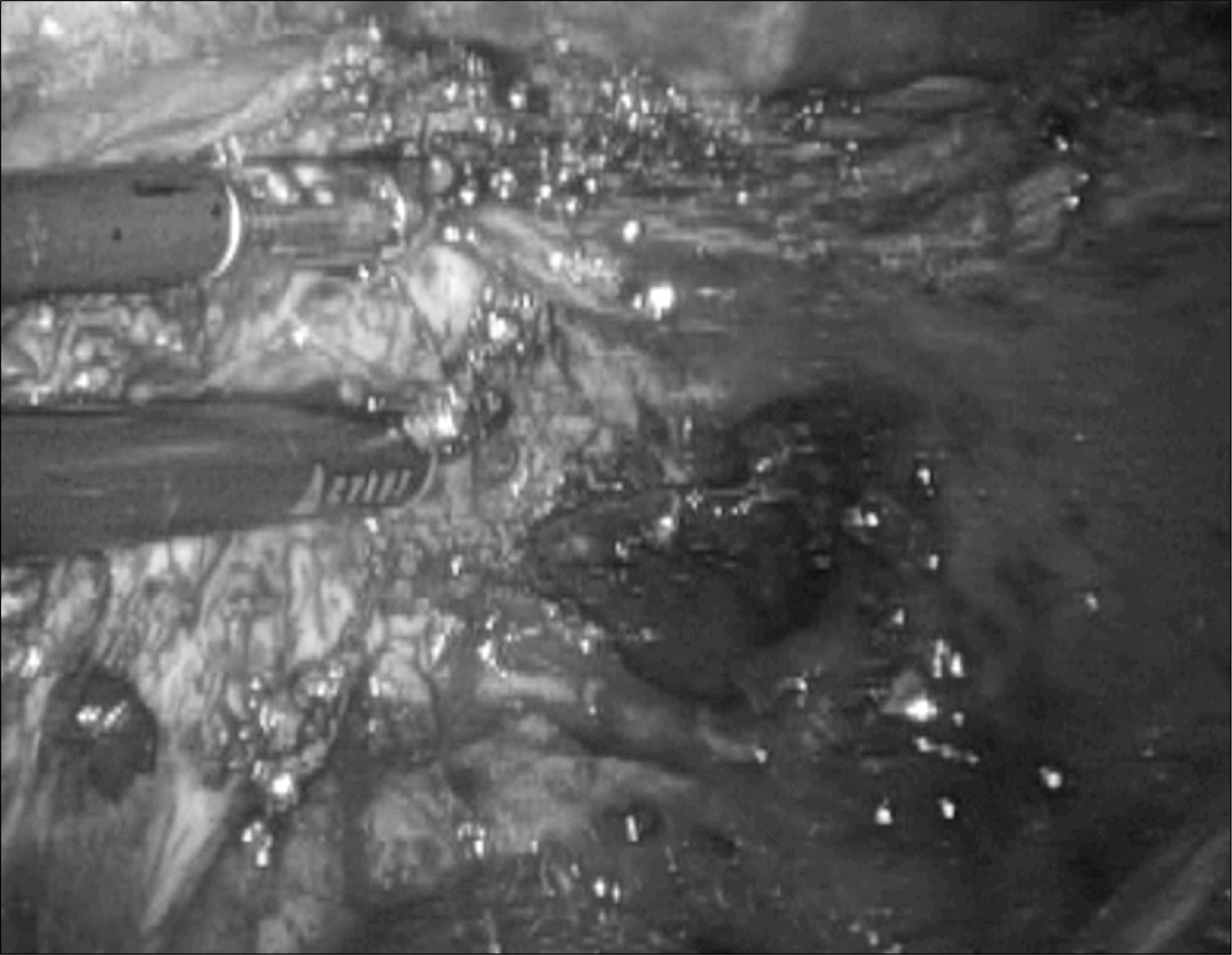
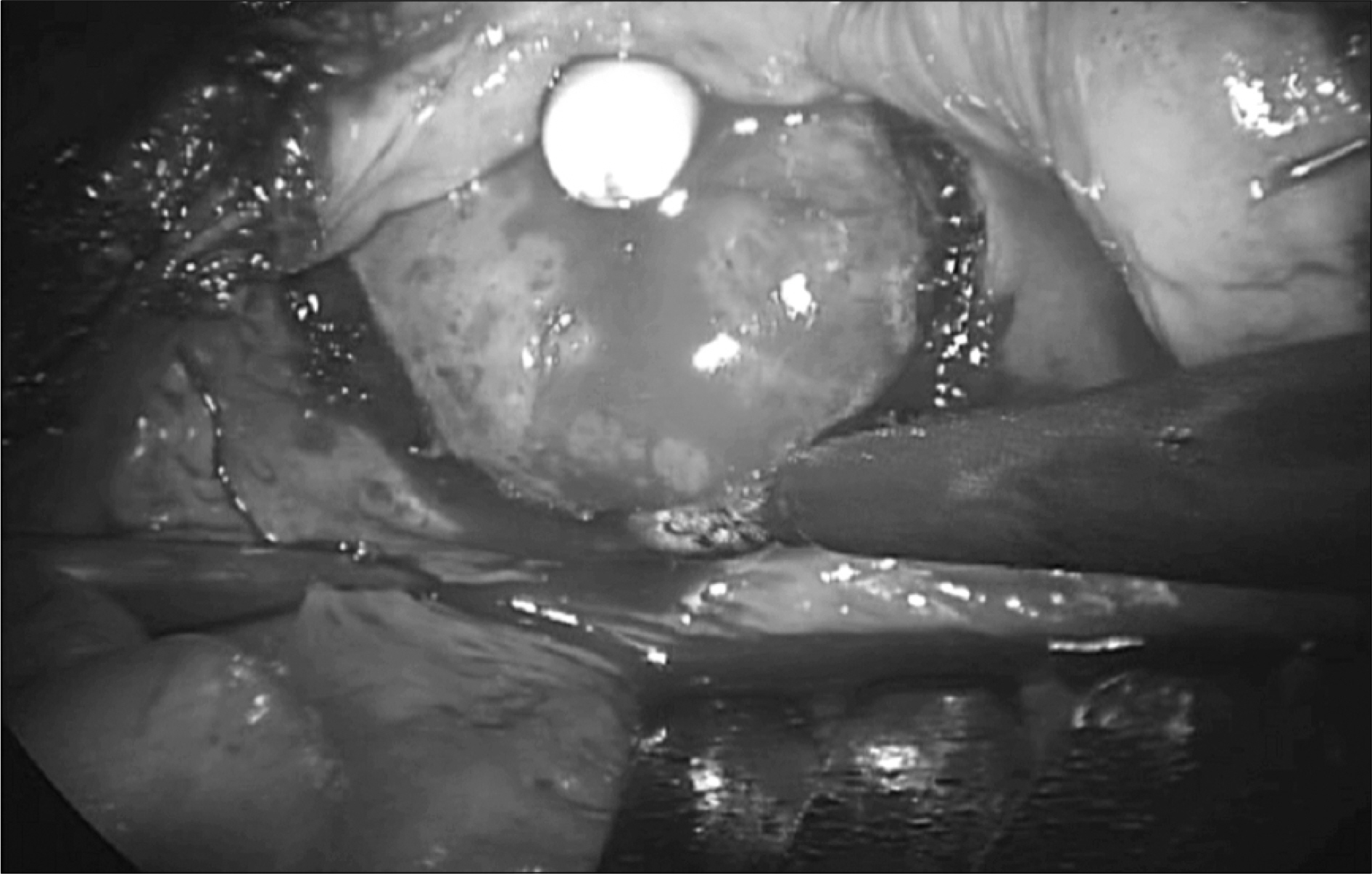
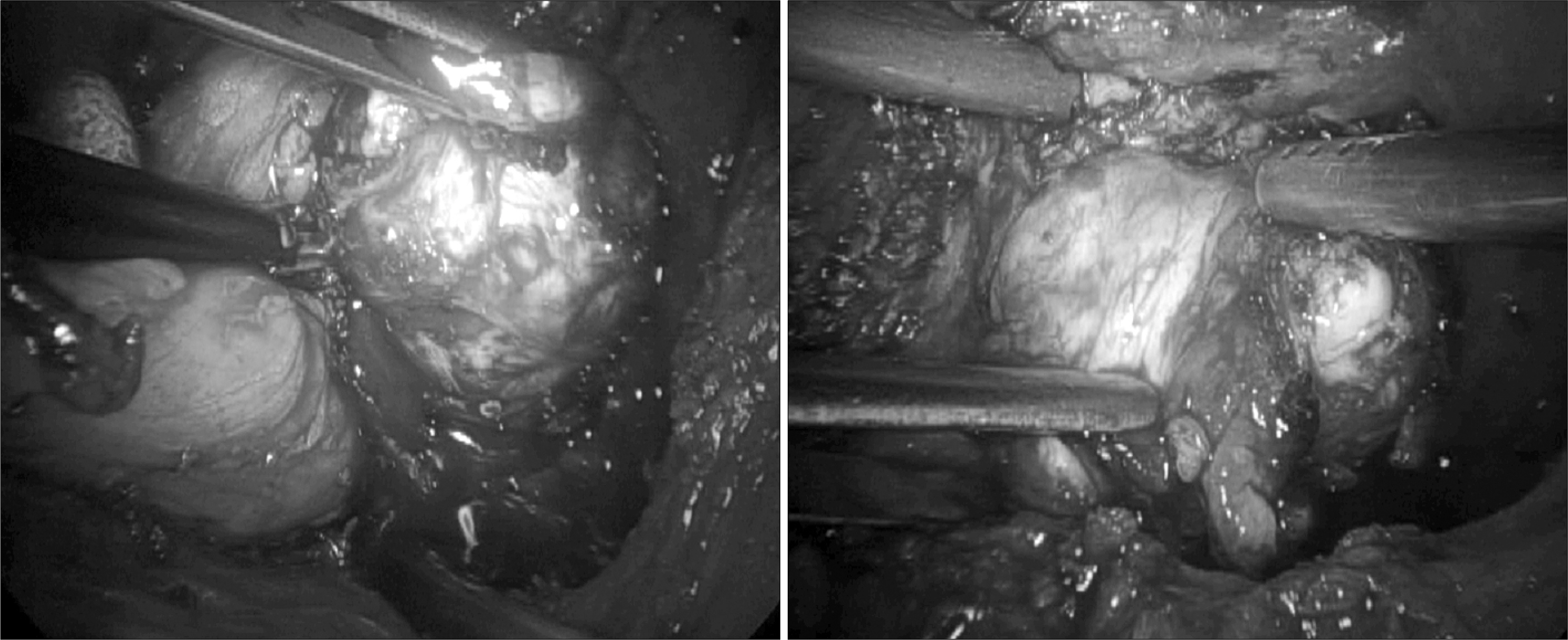
aterials and Methods: From July 2006 to May 2007 we performed Laparoscopic simple prostatectomy on 10 patients who were diagnosed with clinically benign prostate hyperplasia(maximal urine flow rate(MFR) < or=10ml/sec, International Prostate Symptom Score(IPSS) > or=12 scores, and prostate weight > or=75g). The steps of our extraperitoneal 5 port technique were longitudinal cystotomy, subcapsular plane development, enucleation of the obstructing prostatic adenoma, insertion of Spongospan into the prostatic fossa, traction of 22Fr balloon catheter and suture repair of cystotomy.
RESULTS
We successfully performed the operation in all cases without conversion. The mean patient age is 68.1 years old(60-73). The mean preoperative PSA, prostate volume were 8.8ng/ml(1.8-16.9), 97g(74.1- 120.6). The mean operating time and estimated blood loss were 204min (160-275) and 720ml(300-1,200). The resected mass weight was 45.5g (23-70). There were no major complications. The mean hospitalization stay and drain remove days were 11.3 days(9-14) and 5.6 days(4-8). The mean preoperative MFR, IPSS/quality of life(QoL) and were 2.8ml/sec(0-9.6), 25/5(14-35/4-6) and 270ml(250-310). At 3 months postoperatively, the mean MFR, IPSS/QoL and residual urine volume were 15.6ml/sec(12-23), 10/2.6(5-12/2-4) and 16.75(10-40).
CONCLUSIONS
Laparoscopic simple prostatectomy could be a useful method for the treatment of large benign prostate hyperplasia. However, more experiences and comparative studies are needed to document the safe and effect compared to open prostatectomy and transurethral resection of prostate.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Early Experience with Laparoscopic Retropubic Simple Prostatectomy in Patients with Voluminous Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
Han Ki Yun, Joon Beom Kwon, Sung Ryong Cho, Jae Soo Kim
Korean J Urol. 2010;51(5):323-329. doi: 10.4111/kju.2010.51.5.323.
Reference
-
1.Kuntz RM. Current role of lasers in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Eur Urol. 2006. 49:961–9.2.Blute ML., Tomera KM., Hellerstein DK., McKiel CF Jr., Lynch JH., Regan JB, et al. Transurethral microwave thermotherapy for management of benign prostatic hyperplasia results of the United States Prostatron Cooperative Study. J Urol. 1993. 150:1591–6.
Article3.Kaplan SA., Te AE. Transurethral electrovaporization of the prostate: a novel method for treating men with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Urology. 1995. 45:566–72.
Article4.Byun CY., Cho SR. Comparison between the early and late results of operative therapy and thermotherapy for the benign prostatic hyperplasia. Korean J Urol. 1995. 36:715–21.5.Yi JW., Kim JI., Jeon SH. Effectiveness and predictive value of responsiveness of the transurethral microwave thermotherapy in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Korean J Urol. 2005. 46:246–51.6.Olsson J., Nilsson A., Hahn RG. Symptoms of the transurethral resection syndrome using glycine as the irrigant. J Urol. 1995. 154:123–8.
Article7.AUA Practice Guideline Committee. AUA guideline on management of benign prostatic hyperplasia (2003). Chapter 1: diagnosis and treatment recommendations. J Urol. 2003. 170:530–47.8.Han M., Partin AW. Retropubic and suprapubic open prostatectomy. Wein AJ, Kavoussi LR, Novick AC, Partin AW, Peters CA, editors. editors.Campbell-Walsh urology. 9th ed.Philadelphia: Saunders;2007. 2845-53.
Article9.Rehman J., Khan SA., Sukkarieh T., Chughtai B., Waltzer WC. Extraperitoneal laparoscopic prostatectomy (adenomectomy) for obstructing benign prostatic hyperplasia: transvesical and transcapsular (Millin) techniques. J Endourol. 2005. 19:491–6.
Article10.Sotelo R., Spaliviero M., Garcia-Segui A., Hasan W., Novoa J., Desai MM, et al. Laparoscopic retropubic simple prostatectomy. J Urol. 2005. 173:757–60.
Article11.Baumert H., Ballaro A., Dugardin F., Kaisary AV. Laparoscopic versus open simple prostatectomy: a comparative study. J Urol. 2006. 175:1691–4.
Article12.van Velthoven R., Peltier A., Laguna MP., Piechaud T. Laparo-scopic extraperitoneal adenomectomy (Millin): pilot study on feasibility. Eur Urol. 2004. 45:103–9.
Article13.Mariano MB., Tefilli MV., Graziottin TM., Morales CM., Goldraich IH. Laparoscopic prostatectomy for benign prostatic hyperplasia--a six-year experience. Eur Urol. 2006. 49:127–31.14.Mebust MK., Holtgrewe HL., Cockett AT., Peters PC. Transurethral prostatectomy: immediate and postoperative complications. A cooperative study of 13 participating institutions evaluating 3,885 patients. J Urol. 1989. 141:243–7.15.Serretta V., Morgia G., Fondacaro L., Curto G., Lo bianco A., Pirritano D, et al. Open prostatectomy for benign prostatic enlargement in southern Europe in the late 1990s: a contemporary series of 1800 interventions. Urology. 2002. 60:623–7.
Article16.Rey D., Ducarme G., Hoepffner JL., Staerman F. Laparoscopic adenectomy: a novel technique for managing benign prostatic hyperplasia. BJU Int. 2005. 95:676–8.
Article17.Mariano MB., Graziottin TM., Tefilli MV. Laparoscopic prostatectomy with vascular control for benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Urol. 2002. 167:2528–9.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Laparoscopic Simple Prostatectomy
- Early Experience with Laparoscopic Retropubic Simple Prostatectomy in Patients with Voluminous Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
- Experience with Retropubic Prostatectomy in Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- Robotic Simple Prostatectomy: Why and How?
- Contact Laser Induced Prostatectomy: Preliminary Experience