Yonsei Med J.
2007 Oct;48(5):891-893. 10.3349/ymj.2007.48.5.891.
Femoral Neuropathy in a Patient with Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Ministry of Health, Ankara Education and Research Hospital, 2nd Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Ankara, Turkey. hakangenc06@hotmail.com
- KMID: 1122633
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2007.48.5.891
Abstract
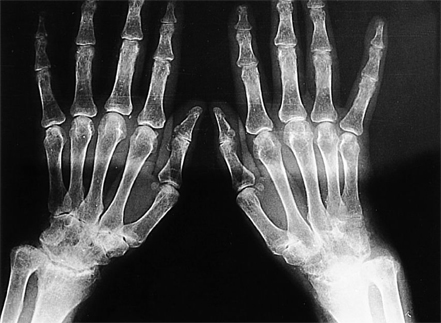
- Femoral mononeuropathy (FMN) as an extraarticular finding of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a phenomenon which has not been reported previously. We report a 53-year-old female patient with RA, presenting FMN findings during the course of the disease. On examination, right quadriceps and iliopsoas muscles showed grade 3 weakness on the Medical Research Council (MRC) scale. Sensory examination revealed sensory loss in the right medial leg and thigh. Patellar tendon reflex was absent in the right side. A diagnosis of a partial right femoral neuropathy was confirmed using nerve conduction study and electromyography. The probable mechanism of FMN was thought to be vasculitis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Harris ED. Clinical Features of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Kelley's Textbook of Rheumatology. 2001. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders Company;967–1000.2. O'Dell J. Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatology Secrets. 1997. Philadelphia: Hanley and Belfus, Inc.;100–109.3. Weber RJ. Johnson EW, Pease WS, editors. Nerve conduction studies. Practical Electromyography. 1997. 3rd ed. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins;131–195.4. OH SJ. Clinical Electromyography: Nerve conduction studies. 1993. 2nd ed. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins;496–575.5. Fealy S, Paletta GA. Femoral nerve palsy secondary to traumatic iliacus muscle hematoma: course after nonoperative management. J Trauma. 1999. 47:1150–1152.
Article6. Katirji MB, Lanska DJ. Femoral mononeuropathy after radical prostatectomy. Urology. 1990. 36:539–540.
Article7. Corbu C, Campodonico F, Traverso P, Carmignani G. Femoral nerve palsy caused by a self-retaining polyretractor during major pelvic surgery. Urol Int. 2002. 68:66–68.
Article8. Hakim MA, Katirji MB. Femoral mononeuropathy induced by the lithotomy position: A report of 5 cases with a review of literature. Muscle Nerve. 1993. 16:891–895.
Article9. Debiais F, Bataille B, Debiais P, Azais I, Bontoux D, Alcalay M. Femoral neuropathy secondary to ossification of the ligamentum flavum. J Rheumatol. 2000. 27:1313–1314.10. Cohen S, Zada Y. Postpartum femoral neuropathy. Anaesthesia. 2001. 56:500–501.
Article11. Dar AQ, Robinson A, Lyons G. Postpartum femoral neuropathy: more common than you think. Anaesthesia. 1999. 54:512.
Article12. Matteson EL, Cohen MD, Conn DL. Klippel JH, Dieppe PA, editors. Rheumatoid arthritis: Clinical features-systemic involvement. Rheumatology. 1994. St. Louis: Mosby;Section 5.1-5.8.13. Chalk CH, Dyck PJ, Conn DL. Dyck PJ, Thomas PK, editors. Vasculitic Neuropathy. Peripheral Neuropathy. 1993. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders Company;1424–1436.14. Katirji B. Electrodiagnostic approach to the patient with suspected mononeuropathy of the lower extremity. Neurol Clin. 2002. 20:479–501. vii.
Article15. Muellner T, Ganko A, Bugge W, Engebretsen L. Isolated femoral mononeuropathy in the athlete. Anatomic considerations and report of two cases. Am J Sports Med. 2001. 29:814–817.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Peripheral Neuropathy in a Patient with Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated with Leflunomide
- Attritional Rupture of Ulnar Nerve in a Patient with Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis
- Clinical significance of rheumatoid factor in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
- Seropositive rheumatoid arthritis in a female patient with sensory neuropathy