Yonsei Med J.
2007 Oct;48(5):795-801. 10.3349/ymj.2007.48.5.795.
Different Modulation of the Cortical Silent Period by Two Phases of Short Interval Intracortical Inhibition
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. yhsohn62@yuhs.ac
- 2Brain Korea 21 Project for Medical Science, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1122616
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2007.48.5.795
Abstract
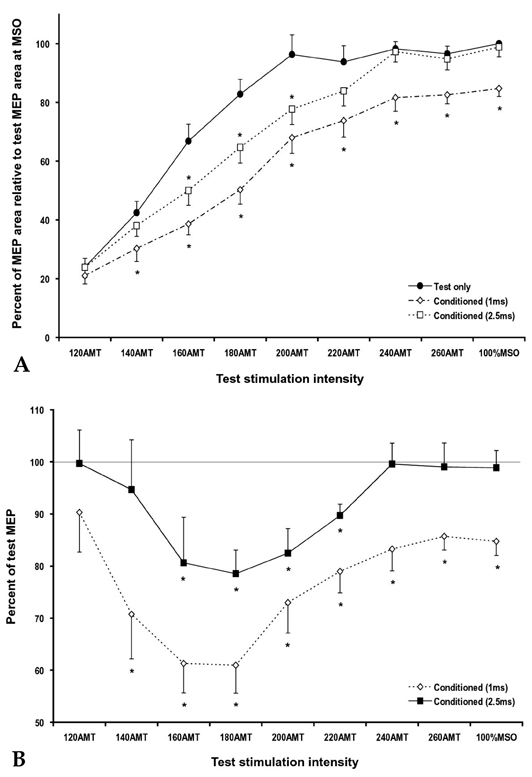
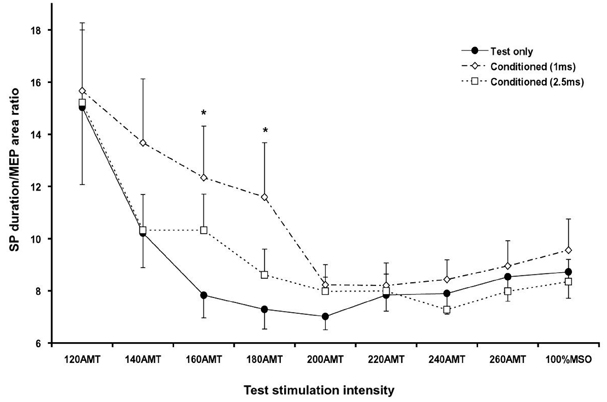
- PURPOSE: To investigate the influence of 2 phases of short interval intracortical inhibition (SICI) on the cortical silent period (SP). MATERIALS AND METHODS: Single- and paired-pulse transcranial magnetic stimulations (TMSs) at 1 and 2.5ms interstimulus intervals (ISIs) were applied to the left motor cortex in 12 healthy subjects while their right hand muscles were moderately activated. Conditioning stimulation intensity was 90% of the active motor threshold (AMT). Test stimulation intensities were 120, 140, 160, 180, 200, 220, 240, 260% of the AMT and at 100% of the maximal stimulator output, the order of which was arranged randomly. The rectified electromyography area of motor evoked potential (MEP) and duration of the SP were measured off-line using a computerized program. RESULTS: At high-test stimulation intensities, MEP areas were saturated in both single- and paired-pulse stimulations, except that saturated MEPs were smaller for the paired-pulse TMS at 1ms ISI than for the other conditions. As the test stimulation intensity increased, SP was progressively prolonged in both single- and paired-pulse stimulations but was shorter in paired-pulse than single-pulse TMS. Overall, the ratio of SP duration/MEP area was comparable between single- and paired-pulse TMS except for the paired-pulse TMS at 1 ms ISI with a test stimulation intensity at 140-180% of the AMT, in which the ratio was significantly higher than in the single pulse TMS. CONCLUSION: These results suggest that 2 phases of SICI modulate MEP saturation and SP duration differently and provide additional evidence supporting the view that 2 phases of SICI are mediated by different inhibitory mechanisms.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hallett M. Transcranial magnetic stimulation: a useful tool for clinical neurophysiology. Ann Neurol. 1996. 40:344–345.
Article2. Nakamura H, Kitagawa H, Kawaguchi Y, Tsuji H. Intracortical facilitation and inhibition after transcranial magnetic stimulation in conscious humans. J Physiol. 1997. 498:817–823.
Article3. Kujirai T, Caramia MD, Rothwell JC, Day BL, Thompson PD, Ferbert A, et al. Corticocortical inhibition in human motor cortex. J Physiol. 1993. 471:501–519.
Article4. Fuhr P, Agostino R, Hallett M. Spinal motor neuron excitability during the silent period after cortical stimulation. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1991. 81:257–262.
Article5. Fisher RJ, Nakamura Y, Bestmann S, Rothwell JC, Bostock H. Two phases of intracortical inhibition revealed by transcranial magnetic threshold tracking. Exp Brain Res. 2002. 143:240–248.
Article6. Roshan L, Paradiso GO, Chen R. Two phases of short-interval intracortical inhibition. Exp Brain Res. 2003. 151:330–337.
Article7. Shimizu T, Oliveri M, Filippi MM, Palmieri MG, Pasqualetti P, Rossini PM. Effect of paired transcranial magnetic stimulation on the cortical silent period. Brain Res. 1999. 834:74–82.
Article8. Trompetto C, Buccolieri A, Marinelli L, Abbruzzese G. Differential modulation of motor evoked potential and silent period by activation of intracortical inhibitory circuits. Clin Neurophysiol. 2001. 112:1822–1827.
Article9. Inghilleri M, Berardelli A, Cruccu G, Manfredi M. Silent period evoked by transcranial stimulation of the human cortex and cervicomedullary junction. J Physiol. 1993. 466:521–534.10. Orth M, Rothwell JC. The cortical silent period: intrinsic variability and relation to the waveform of the transcranial magnetic stimulation pulse. Clin Neurophysiol. 2004. 115:1076–1082.
Article11. Kaelin-Lang A, Cohen LG. Enhancing the quality of studies using transcranial magnetic and electrical stimulation with a new computer-controlled system. J Neurosci Methods. 2000. 102:81–89.
Article12. Pfadt A, Wheeler DJ. Using statistical process control to make data-based clinical decisions. J Appl Behav Anal. 1995. 28:349–370.
Article13. Garvey MA, Ziemann U, Becker DA, Barker CA, Bartko JJ. New graphical method to measure silent periods evoked by transcranial magnetic stimulation. Clin Neurophysiol. 2001. 112:1451–1460.
Article14. Nilsson J, Panizza M, Arieti P. Computer-aided determination of the silent period. J Clin Neurophysiol. 1997. 14:136–143.
Article15. Magistris MR, Rösler KM, Truffert A, Myers JP. Transcranial stimulation excites virtually all motor neurons supplying the target muscle. A demonstration and a method improving the study of motor evoked potentials. Brain. 1998. 121:437–450.
Article16. Tergau F, Wanschura V, Canelo M, Wischer S, Wassermann EM, Ziemann U, et al. Complete suppression of voluntary motor drive during the silent period after transcranial magnetic stimulation. Exp Brain Res. 1999. 124:447–454.
Article17. Chen R, Lozano AM, Ashby P. Mechanism of the silent period following transcranial magnetic stimulation. Evidence from epidural recordings. Exp Brain Res. 1999. 128:539–542.
Article18. Schulze-Bonhage A, Knott H, Ferbert A. Effects of carbamazepine on cortical excitatory and inhibitory phenomena: a study with paired transcranial magnetic stimulation. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1996. 99:267–273.
Article19. Ziemann U, Lönnecker S, Steinhoff BJ, Paulus W. Effects of antiepileptic drugs on motor cortex excitability in humans: a transcranial magnetic stimulation study. Ann Neurol. 1996. 40:367–378.
Article20. Ziemann U, Lönnecker S, Steinhoff BJ, Paulus W. The effect of lorazepam on the motor cortical excitability in man. Exp Brain Res. 1996. 109:127–135.
Article21. Ziemann U, Bruns D, Paulus W. Enhancement of human motor cortex inhibition by the dopamine receptor agonist pergolide: evidence from transcranial magnetic stimulation. Neurosci Lett. 1996. 208:187–190.
Article22. Ghosh S, Porter R. Corticocortical synaptic influences on morphologically identified pyramidal neurones in the motor cortex of the monkey. J Physiol. 1988. 400:617–629.
Article23. Phillips CG, Porter R. Corticospinal neurones. Their role in movement. Monogr Physiol Soc. 1977. 34:v–xii. 1–450.24. Ilić TV, Meintzschel F, Cleff U, Ruge D, Kessler KR, Ziemann U. Short-interval paired-pulse inhibition and facilitation of human motor cortex: the dimension of stimulus intensity. J Physiol. 2002. 545:153–167.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Zonisamide Changes Unilateral Cortical Excitability in Focal Epilepsy Patients
- Effects of Repetitive High Frequency Motor Cortex Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation and Cortical Disinhibition in Diabetic Patients with Neuropathic Pain: A Case Control Study
- Increased Cortical Excitability in Female Migraineurs: A Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Study Conducted in the Preovulatory Phase
- Intracortical Bone Metastasis Mimicking Intracortical Osteoid Osteoma: A Case Report
- The Effect of Lorazepam on the Silent Period of the Motor Evoked Potential