Yonsei Med J.
2012 Mar;53(2):337-345. 10.3349/ymj.2012.53.2.337.
How Many Valid Measurements Are Necessary to Assess Liver Fibrosis Using FibroScan(R) in Patients with Chronic Viral Hepatitis? An Analysis of Subjects with at Least 10 Valid Measurements
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. dyk1025@yuhs.ac
- 2Institute of Gastroenterology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Biostatistics, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Pathology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Liver Cirrhosis Clinical Research Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Brain Korea 21 Project for Medical Science, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1120200
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2012.53.2.337
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Using FibroScan(R) to obtain a reliable liver stiffness measurement (LSM) may require more than 10 valid measurements (VMs), according to the manufacturer's recommendations. However, this requirement lacks scientific evidence in support thereof. We investigated the minimal number of VMs required to assess liver fibrosis without significant loss of accuracy in patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB) and C (CHC) and predictors of discordance between LSM and liver biopsy (LB).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Between January 2005 and December 2009, we prospectively enrolled 182 patients with CHB and 68 patients with CHC who were to undergo LB and LSM before starting antiviral treatment. Only LSMs with at least 10 VMs were considered reliable. The Batts and Ludwig scoring system was used for histologic assessment.
RESULTS
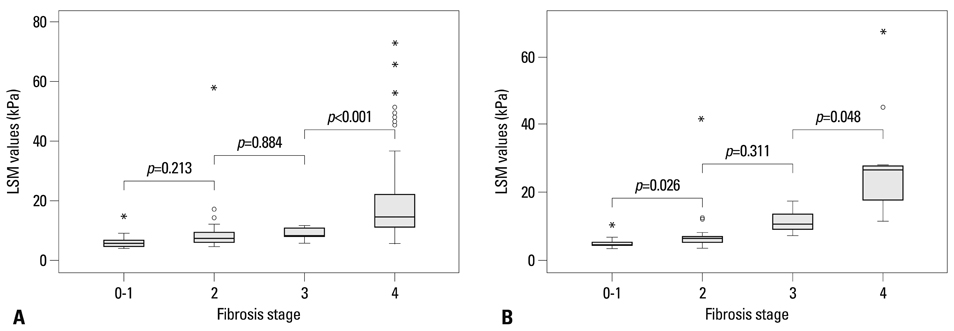
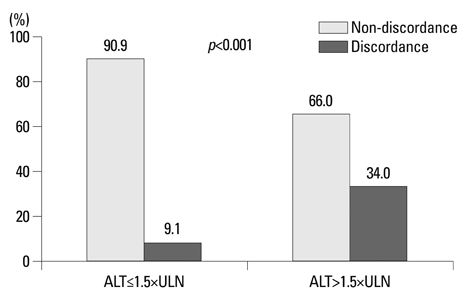
The mean age and body mass index were 46.0 years and 23.4 kg/m2 in patients with CHB and 49.7 years and 23.1 kg/m2 in those with CHC, respectively. The median elasticity scores from the first 3, first 5, and all VMs taken significantly predicted fibrosis stages > or =F2 and F4 (all p<0.05) without significant differences (all p>0.05 by DeLong's method). Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) was the only predictor of discordance in fibrosis stage as estimated by the median elasticity score from the first 3 VMs and by LB in patients with CHB, whereas no significant predictor was identified in those with CHC.
CONCLUSION
After comparison of patients who had more than 10 valid measurements for LSM, three VMs may be enough to assess liver fibrosis using LSM without significant loss of accuracy in patients with CHC and patients with CHB. However, ALT should be considered when interpreting LSM for patients with CHB.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Can We Accurately Assess Liver Fibrosis with Fibroscan® Using Fewer Valid Measurements?
Omid Pournik, Seyed Moayed Alavian, Saeid Eslami
Yonsei Med J. 2013;54(2):541-542. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2013.54.2.541.
Reference
-
1. Castéra L, Vergniol J, Foucher J, Le Bail B, Chanteloup E, Haaser M, et al. Prospective comparison of transient elastography, Fibrotest, APRI, and liver biopsy for the assessment of fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology. 2005. 128:343–350.
Article2. Ziol M, Handra-Luca A, Kettaneh A, Christidis C, Mal F, Kazemi F, et al. Noninvasive assessment of liver fibrosis by measurement of stiffness in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2005. 41:48–54.
Article3. Marcellin P, Ziol M, Bedossa P, Douvin C, Poupon R, de Lédinghen V, et al. Non-invasive assessment of liver fibrosis by stiffness measurement in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Liver Int. 2009. 29:242–247.
Article4. Kim SU, Kim do Y, Park JY, Lee JH, Ahn SH, Kim JK, et al. How can we enhance the performance of liver stiffness measurement using FibroScan in diagnosing liver cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B? J Clin Gastroenterol. 2010. 44:66–71.
Article5. Fraquelli M, Rigamonti C, Casazza G, Conte D, Donato MF, Ronchi G, et al. Reproducibility of transient elastography in the evaluation of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic liver disease. Gut. 2007. 56:968–973.
Article6. Roulot D, Czernichow S, Le Clésiau H, Costes JL, Vergnaud AC, Beaugrand M. Liver stiffness values in apparently healthy subjects: influence of gender and metabolic syndrome. J Hepatol. 2008. 48:606–613.
Article7. Lucidarme D, Foucher J, Le Bail B, Vergniol J, Castera L, Duburque C, et al. Factors of accuracy of transient elastography (fibroscan) for the diagnosis of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2009. 49:1083–1089.
Article8. Kim SU, Seo YS, Cheong JY, Kim MY, Kim JK, Um SH, et al. Factors that affect the diagnostic accuracy of liver fibrosis measurement by Fibroscan in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2010. 32:498–505.
Article9. Kettaneh A, Marcellin P, Douvin C, Poupon R, Ziol M, Beaugrand M, et al. Features associated with success rate and performance of FibroScan measurements for the diagnosis of cirrhosis in HCV patients: a prospective study of 935 patients. J Hepatol. 2007. 46:628–634.
Article10. Myers RP, Crotty P, Pomier-Layrargues G, Ma M, Urbanski SJ, Elkashab M. Prevalence, risk factors and causes of discordance in fibrosis staging by transient elastography and liver biopsy. Liver Int. 2010. 30:1471–1480.
Article11. Kim SU, Kim do Y, Lee CK, Park JY, Kim SH, Kim HM, et al. Ascitic fluid infection in patients with hepatitis B virus-related liver cirrhosis: culture-negative neutrocytic ascites versus spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010. 25:122–128.
Article12. Bedossa P, Dargére D, Paradis V. Sampling variability of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2003. 38:1449–1457.
Article13. Lebray P, Varnous S, Charlotte F, Varaut A, Poynard T, Ratziu V. Liver stiffness is an unreliable marker of liver fibrosis in patients with cardiac insufficiency. Hepatology. 2008. 48:2089.
Article14. Sandrin L, Fourquet B, Hasquenoph JM, Yon S, Fournier C, Mal F, et al. Transient elastography: a new noninvasive method for assessment of hepatic fibrosis. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2003. 29:1705–1713.
Article15. Batts KP, Ludwig J. Chronic hepatitis. An update on terminology and reporting. Am J Surg Pathol. 1995. 19:1409–1417.16. Brunt EM, Janney CG, Di Bisceglie AM, Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Bacon BR. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a proposal for grading and staging the histological lesions. Am J Gastroenterol. 1999. 94:2467–2474.
Article17. Talwalkar JA, Kurtz DM, Schoenleber SJ, West CP, Montori VM. Ultrasound-based transient elastography for the detection of hepatic fibrosis: systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007. 5:1214–1220.
Article18. Friedrich-Rust M, Ong MF, Martens S, Sarrazin C, Bojunga J, Zeuzem S, et al. Performance of transient elastography for the staging of liver fibrosis: a meta-analysis. Gastroenterology. 2008. 134:960–974.
Article19. Stebbing J, Farouk L, Panos G, Anderson M, Jiao LR, Mandalia S, et al. A meta-analysis of transient elastography for the detection of hepatic fibrosis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2010. 44:214–219.
Article20. Chan HL, Wong GL, Choi PC, Chan AW, Chim AM, Yiu KK, et al. Alanine aminotransferase-based algorithms of liver stiffness measurement by transient elastography (Fibroscan) for liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B. J Viral Hepat. 2009. 16:36–44.
Article21. Wang JH, Changchien CS, Hung CH, Eng HL, Tung WC, Kee KM, et al. FibroScan and ultrasonography in the prediction of hepatic fibrosis in patients with chronic viral hepatitis. J Gastroenterol. 2009. 44:439–446.
Article22. Takeda T, Yasuda T, Nakayama Y, Nakaya M, Kimura M, Yamashita M, et al. Usefulness of noninvasive transient elastography for assessment of liver fibrosis stage in chronic hepatitis C. World J Gastroenterol. 2006. 12:7768–7773.
Article23. Nitta Y, Kawabe N, Hashimoto S, Harata M, Komura N, Kobayashi K, et al. Liver stiffness measured by transient elastography correlates with fibrosis area in liver biopsy in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatol Res. 2009. 39:675–684.
Article24. DeLong ER, DeLong DM, Clarke-Pearson DL. Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: a nonparametric approach. Biometrics. 1988. 44:837–845.
Article25. Yuen MF, Yuan HJ, Hui CK, Wong DK, Wong WM, Chan AO, et al. A large population study of spontaneous HBeAg seroconversion and acute exacerbation of chronic hepatitis B infection: implications for antiviral therapy. Gut. 2003. 52:416–419.
Article26. Poynard T, Halfon P, Castera L, Munteanu M, Imbert-Bismut F, Ratziu V, et al. Standardization of ROC curve areas for diagnostic evaluation of liver fibrosis markers based on prevalences of fibrosis stages. Clin Chem. 2007. 53:1615–1622.
Article27. Liaw YF. Hepatitis flares and hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion: implication in anti-hepatitis B virus therapy. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2003. 18:246–252.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Can We Accurately Assess Liver Fibrosis with Fibroscan(R) Using Fewer Valid Measurements?
- Liver Stiffness Measurement for the Diagnosis of Hepatic Fibrosis in Patients with Chronic Viral Hepatitis
- Prediction of fibrosis progression in chronic viral hepatitis
- Comparison of Transient Elastography and Hepatic Fibrosis Assessed by Histology in Chronic Liver Disease
- Clinical applications of transient elastography