Yonsei Med J.
2006 Apr;47(2):191-195. 10.3349/ymj.2006.47.2.191.
Liquid Heparin Anticoagulant Produces More Negative Bias in the Determination of Ionized Magnesium than Ionized Calcium
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Yongdong Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Yongdong Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jeongho@yumc.yonsei.ac.kr
- KMID: 1110741
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2006.47.2.191
Abstract
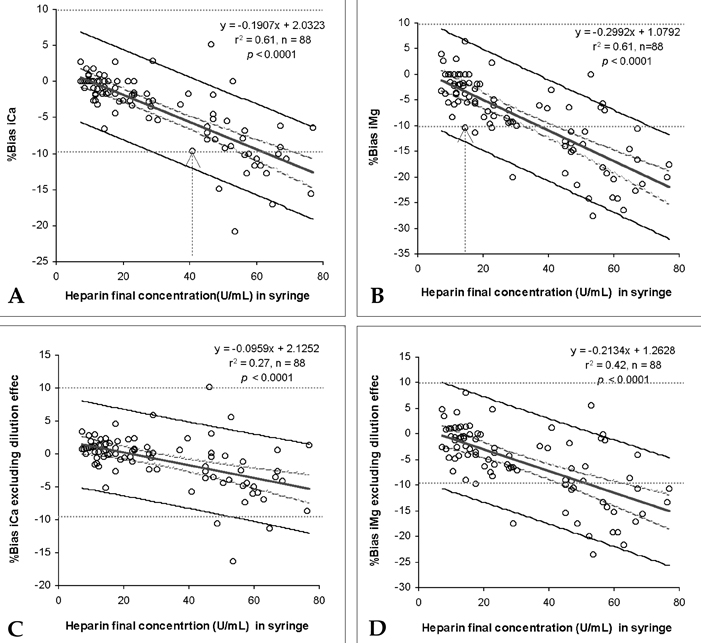
- The ionized calcium level in blood is known to be falsely decreased when self-prepared liquid heparin anticoagulant is used, due to dilution and binding effects. The effect of liquid heparin on the determination of ionized magnesium is not as well understood. We compared the effect of liquid sodium heparin on the determination of ionized calcium and magnesium in 44 clinical samples using two types of user-prepared heparin syringes which differed in the amount of residual heparin from the BD Preset(TM) reference syringe. With the type 1 syringe, the liquid heparin was expelled once or twice such that some heparin could be left in the dead space at the syringe hub, while the liquid sodium heparin was thoroughly expelled from the type 2 syringe. The ionized magnesium levels obtained with the type 1 syringe were significantly lower than the reference value (by 0.068 mmol/L) (p < 0.0001), while the value obtained with the type 2 syringe differed less from the reference, by only 0.014 mmol/L (p < 0.0001). The heparin binding effect resulted in more negative bias in ionized magnesium (-0.026 +/- 0.032 mmol/L) than in ionized calcium (-0.009 +/- 0.042 mmol/L, p < 0.0001). In conclusion, we recommend using lyophilized, calcium-balanced, heparinized syringes for the determination of ionized magnesium and ionized calcium due to the increased negative bias in ionized magnesium determinations. When user-prepared syringes are used, the thorough evacuation of heparin solution should be strictly prescribed.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sachs C, Rabouine P, Chaneac M, Kindermans C, Dechaux M. In vitro evaluation of a heparinized blood sampler for ionized calcium measurement. Ann Clin Biochem. 1991. 28:240–244.2. National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. NCCLS Document C31-A. Ionized calcium determinations: precollection variables, specimen choice, collection, and handling; proposed guideline. 2001. Villonova, PA: NCCLS.3. Ritter C, Ghahramani M, Marsoner HJ. More on the measurement of ionized magnesium in whole blood. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1996. 224:275–280.4. Toffaletti JG, Wildermann RF. The effects of heparin anticoagulants and fill volume in blood gas syringes on ionized calcium and magnesium measurements. Clin Chim Acta. 2001. 304:147–151.5. Sanders GT, Huijgen HJ, Sanders R. Magnesium in disease: a review with special emphasis on the serum ionized magnesium. Clin Chem Lab Med. 1999. 37:1011–1033.6. Huijgen HJ, Soesan M, Sanders R, Mairuhu WM, Kesecioglu J, Sanders GT. Magnesium levels in critically ill patients. What should we measure? Am J Clin Pathol. 2000. 114:688–695.7. van Ingen HE, Huijgen HJ, Kok WT, Sanders GT. Analytical evaluation of Kone Microlyte determination of ionized magnesium. Clin Chem. 1994. 40:52–55.8. Maj-Zurawska M. Clinical findings on human blood with the KONE ISE for Mg2+. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1994. 217:69–76.9. Chantler J, Cox DJ. Self-prepared heparinized syringes for measuring ionized magnesium in critical care patients. Br J Anaesth. 1999. 83:810–812.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Evaluation of D-Phenylalanyl-L-prolyl-L-arginine Chloromethyl Ketone(PPACK) as an Alternative Anticoagulant to Heparin Salts for Analysis of ionized Calcium, Blood Gas, Electrolytes
- Frequency of Serum Ionized Hypomagnesemia in Patient with Ionized Hypocalcemia
- Relationship between Direct Measured and Calculated Ionized Calcium in Maintenance Hemodialysis Patients
- The Significance of Sample Preparation in Measurement of Ionized Calcium
- Whole blood versus serum ionized calcium concentrations in dialysis patients