J Vet Sci.
2008 Jun;9(2):197-202. 10.4142/jvs.2008.9.2.197.
Percutaneous heartworm removal from dogs with severe heart worm (Dirofilaria immitis) infestation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Section of Small Animal Internal Medicine, Institute of Veterinary Medicine, School of Veterinary Medicine, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon 200-701, Korea. hyun5188@kangwon.ac.kr
- KMID: 1106236
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2008.9.2.197
Abstract
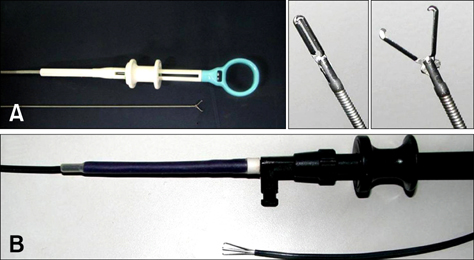
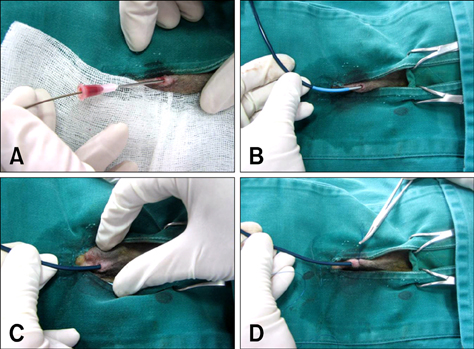
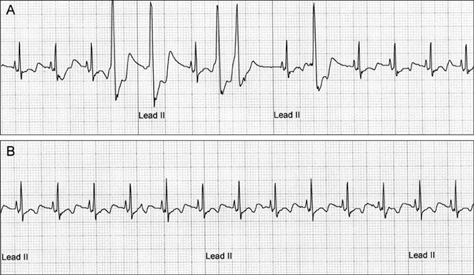
- Canine heart worm disease is often life-threatening due to its various complications, including right side heart failure, caval syndrome and pulmonary eosinophilic granulomatosis. Several preventive medications and melarsomine have been developed and they are very effective to control heartworm infestation. However, in a case of severe infestation, melarsomine therapy often results in an unfavorable outcome because of the severe immune reaction caused by rapid killing of the adult worm. Surgical removal and an interventional method using flexible alligator forceps have been well described in the literature. Despite the usefulness of mechanical removal using flexible alligator forceps, the methodology still needs to be upgraded for increasing the applicability for treating dogs with severe infestation. We describe herein a newly developed percutaneous removal method for heartworms and this was successfully applied to 4 dogs with severe heartworm infestation. The follow-up studies also showed favorable outcomes with no complications.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Atkins C. Ettinger SJ, Feldman EC, editors. Canine heartworm disease. Textbook of Veterinary Internal Medicine. 2004. 6th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders;1118–1136.2. Atwell RB, Litster AL. Surgical extraction of transplanted adult Dirofilaria immitis in cats. Vet Res Commun. 2002. 26:301–308.3. Glaus TM, Jacobs GJ, Rawlings CA, Watson ED, Calvert CA. Surgical removal of heartworms from a cat with caval syndrome. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1995. 206:663–666.4. Grieve RB, Frank GR, Stewart VA, Parsons JC, Belasco DL, Hepler DI. Chemoprophylactic effects of milbemycin oxime against larvae of Dirofilaria immitis during prepatent development. Am J Vet Res. 1991. 52:2040–2042.5. Paul AJ, Todd KS Jr, Sundberg JP, DiPietro JA, McCall JW. Efficacy of ivermectin against Dirofilaria immitis larvae in dogs 30 and 45 days after induced infection. Am J Vet Res. 1986. 47:883–884.6. Polizopoulou ZS, Koutinas AF, Saridomichelakis MN, Patsikas MN, Leontidis LS, Roubies NA, Desiris AK. Clinical and laboratory observations in 91 dogs infected with Dirofilaria immitis in northern Greece. Vet Rec. 2000. 146:466–469.
Article7. Rawlings CA, Raynaud JP, Lewis RE, Duncan JR. Pulmonary thromboembolism and hypertension after thiacetarsamide vs melarsomine dihydrochloride treatment of Dirofilaria immitis infection in dogs. Am J Vet Res. 1993. 54:920–925.8. Sasaki Y, Kitagawa H, Ishihara K, Masegi T. Improvement in pulmonary arterial lesions after heartworm removal using flexible alligator forceps. Nippon Juigaku Zasshi. 1990. 52:743–752.
Article9. Strickland KN, Atkins CE. Cote E, editor. Heartworm disease, dog. Clinical Veterinary Advisor: Dogs and Cats. 2007. 6th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders;465–467.10. Yoon HY, Jeong SW, Kim JY, Han HJ, Jang HY, Lee B, Namkang HS. The efficacy of surgical treatment with flexible alligator forceps in dogs with heartworm infection. J Vet Clin. 2005. 22:309–313.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Catheter-guided percutaneous heartworm removal using a nitinol basket in dogs with caval syndrome
- Periodicity exhibited by Dirofilaria immitis microfilariae identified in dogs of Korea
- Evaluation of improved transvenous heartworm extraction brush in dogs with caval syndrome
- Studies on the anti-parasitic efficacy and safety of ivermectin and pyrantel pamoate compound against Dirofilaria immitis in dogs
- Serum cardiac troponin I concentrations in clinically normal and Dirofilaria immitis infected Korean Jindo dogs