J Vet Sci.
2008 Dec;9(4):415-419. 10.4142/jvs.2008.9.4.415.
Ultrasonographic evaluation of renal dimension and resistive index in clinically healthy Korean domestic short-hair cats
- Affiliations
-
- 1Section of Diagnostic Imaging, School of Veterinary Medicine and Institute of Veterinary Science, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon 201-100, Korea.
- 2Section of Wildlife Medicine, School of Veterinary Medicine and Institute of Veterinary Science, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon 201-100, Korea.
- 3Section of Small Animal Internal Medicine, School of Veterinary Medicine and Institute of Veterinary Science, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon 201-100, Korea. hyun5188@kangwon.ac.kr
- 4Section of Obstetrics, College of Veterinary Medicine, Chonnam National University, Gwangju 500-757, Korea.
- KMID: 1104918
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2008.9.4.415
Abstract
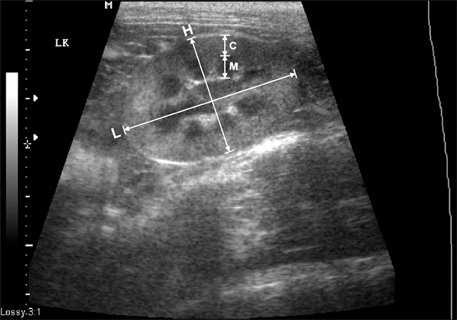
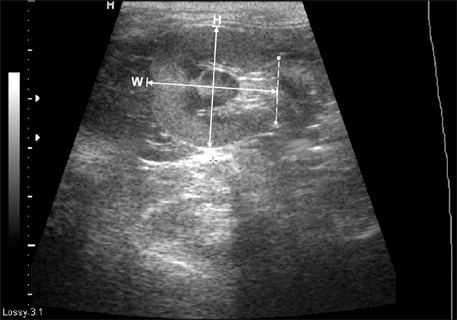
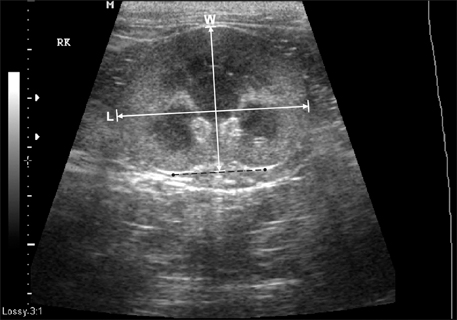
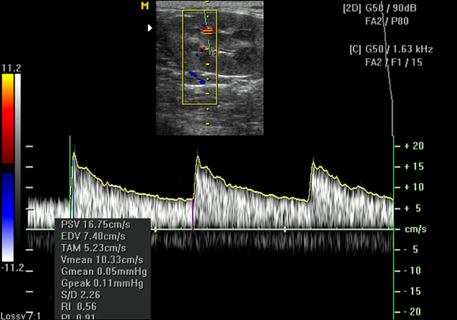
- Renal length, height, width, resistive index (RI), size of cortex, and medulla were determined by renal ultrasonography in 50 healthy Korean domestic short-hair cats. In the sagittal plane, the renal length was 3.83 +/- 0.51 cm (mean +/- SD) in the left kidney and 3.96 +/- 0.48 cm in the right kidney, whereas the renal height was 2.42 +/- 0.27 cm in the left kidney and 2.36 +/- 0.28 cm in the right kidney. In the transverse plane, the renal height was 2.42 +/- 0.28 cm in the left kidney and 2.38 +/- 0.27 cm in the right kidney, whereas the renal width was: 2.65 +/- 0.35 cm in the left kidney and 2.63 +/- 0.31 cm in the right kidney. In the dorsal plane, the renal length was 3.84 +/- 0.53 cm in the left kidney and 3.97 +/- 0.54 cm in the right kidney, whereas the renal width was 2.65 +/- 0.34 cm in the left kidney and 2.66 +/- 0.33 cm in the right kidney. There were no significant differences (p > 0.05) among the same structure sizes measured in different planes. In the sagittal plane, the size of the renal cortex was 0.47 +/- 0.08 cm in the left kidney and 0.47 +/- 0.08 cm in the right kidney, whereas of the size of the renal medulla was 0.55 +/- 0.30 cm in the left kidney and 0.50 +/- 0.07 cm in the right kidney. RI evaluated by pulsed wave Doppler sonography was 0.52 +/- 0.05 in the left kidney and 0.55 +/- 0.05 in the right kidney. The actual renal dimensions determined by gross examination were not statistically different from those determined by ultrasonography. Furthermore the renal dimensions and RI were statistically correlated to the body weight of cats.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Armbrust LJ, Biller DS, Hoskinson JJ, Meier HT, Lora-Michiels M. The basics of renal ultrasonography. Vet Med. 2001. 96:114–133.2. Genkins SM, Sanfilippo FP, Carroll BA. Duplex Doppler sonography of renal transplants: lack of sensitivity and specificity in establishing pathologic diagnosis. Am J Roentgenol. 1989. 152:535–539.
Article3. Jurriaans E, Dubbins PA. Renal transplantation: the normal morphological and Doppler ultrasound examination. J Clin Ultrasound. 1992. 20:495–506.
Article4. Morrow KL, Salman MD, Lappin MR, Wrigley R. Comparison of the resistive index to clinical parameters in dogs with renal disease. Vet Radiol Ultrasound. 1996. 37:193–199.
Article5. Nyland TG, Fisher PE, Doverspike M, Hornof WJ, Olander HJ. Diagnosis of urinary tract obstruction in dogs using duplex Doppler ultrasonography. Vet Radiol Ultrasound. 1993. 34:348–352.
Article6. Osborne CA, Finco DR. Canine and Feline Nephrology and Urology. 1995. 8th ed. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins;370–464.7. Platt JF. Duplex Doppler evaluation of native kidney dysfunction: obstructive and nonobstructive disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1992. 158:1035–1042.
Article8. Pollard R, Nyland TG, Bernsteen L, Gregory CR, Hornof WJ. Ultrasonographic evaluation of renal autografts in normal cats. Vet Radiol Ultrasound. 1999. 40:380–385.
Article9. Quarto di Palo F, Rivolta R, Elli A, Castagnone D. The well-functioning renal graft evaluated by color Doppler flowmetry. Nephron. 1995. 70:314–318.
Article10. Rifkin MD, Needleman L, Pasto ME, Kurtz AB, Foy PM, McGlynn E, Canino C, Baltarowich OH, Pennell RG, Goldberg BB. Evaluation of renal transplant rejection by duplex Doppler examination: value of the resistive index. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1987. 148:759–762.
Article11. Rivers BJ, Walter PA, Letourneau JG, Finlay DE, Ritenour ER, King VL, O'Brien TD, Polzin DJ. Duplex Doppler estimation of resistive index in arcuate arteries of sedated, normal female dogs: implications for use in the diagnosis of renal failure. J Am Anim Hosp Assoc. 1997. 33:69–76.
Article12. Rivers BJ, Walter PA, O'Brien TD, Polzin DJ. Duplex Doppler estimation of Pourcelot resistive index in arcuate arteries of sedated normal cats. J Vet Intern Med. 1996. 10:28–33.
Article13. Walter PA, Feeney DA, Johnston GR, Fletcher TF. Feline renal ultrasonography: quantitative analyses of imaged anatomy. Am J Vet Res. 1987. 48:596–599.14. Walter PA, Johnston GR, Feeney DA, O'Brien TD. Renal ultrasonography in healthy cats. Am J Vet Res. 1987. 48:600–607.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pelvis dilatation and mucosal thickening of transplanted kidney: comparative study of resistive index and ultrasonographic finding
- Serial Changes of Serum Creatinine and Resistive Index to Predict Acute Rejection after Renal Transplantation
- Evaluation of Factors Affecting the Renal Doppler Waveform with the Use of an Electrical Circuit Model
- Resistive Index Analysis Using Doppler Ultrasonography in Patients with Acute Stroke
- The Value of Intrarenal Resistive Index in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis