J Vet Sci.
2006 Mar;7(1):93-95. 10.4142/jvs.2006.7.1.93.
Application of a temporary palatal prosthesis in a puppy suffering from cleft palate
- Affiliations
-
- 1Laboratory of Veterinary Surgery, College of Veterinary Medicine, Chungnam National University, Daejeon 305-764, Korea. hongsu@mail.nih.gov
- 2Department of Dental Laboratory Technology, Daejeon Health Sciences College, Daejeon 300-090, Korea.
- 3Kayang Animal Hospital, Daejeon 300-090, Korea.
- KMID: 1103564
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2006.7.1.93
Abstract
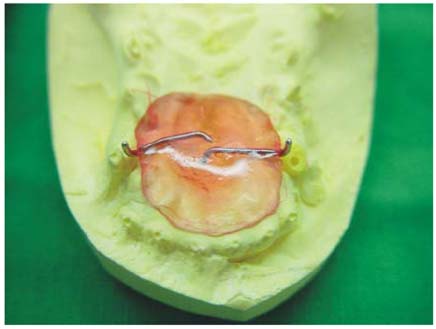
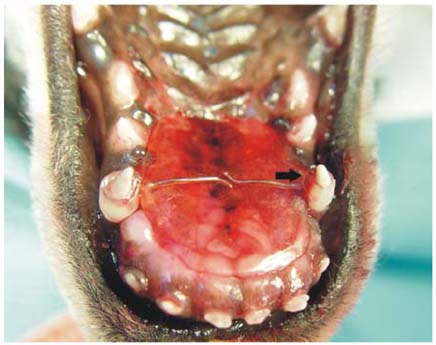
- A 3-month-old Schnauzer was presented with congenital defects of the secondary palate. On the clinical examination, coughing, sneezing, drainage of nasal discharge from the external nares and poor growth were found. Vital signs and results of blood examination were within normal ranges. Thoracic radiography revealed mild pneumonia in the right lung lobes. In a puppy suffering from cleft palates, a palatal prosthesis was applied to the hard palate in order to protect the surgical wound, because a routine surgery was not successful. A palatal prosthesis was applied and held in place using the instant glue and plastic bands to protect the surgical wound following the third repeated surgery. Although a small oronasal fistula still remained, there was no functional defect. This prosthesis was easy to apply and helpful to protect the surgical wound. In addition, this implant could be placed or adjusted without or sedation/anesthesia.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bardach J, Mooney M, Bardach E. The influence of two flap palatoplasty on facial growth in beagles. Plast Reconst Surg. 1982. 69:927–936.2. Forbes DP, Kaminski EJ, Perry HT. Repair of surgical clefts of the hard palate in beagles. Cleft Palate. 1988. 25:270–281.3. Griffiths LG, Sullivan M. Bilateral overlapping mucosal single-pedicle flaps for correction of soft palate defects. J Am Anim Hosp Assoc. 2001. 37:183–186.
Article4. Hawkins BJ. Hoskins JD, editor. Dental disease and care. Veterinary Pediatrics. 2001. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Saunders;135–146.
Article5. Holmstrom SE. Veterinary Dentistry for the Technician and Office Staff. 2000. Philadelphia: Saunders;270–280.6. Howard DR, Davis DG, Merkley DF, Krahwinkel DJ, Schirmer RG, Brinker WO. Mucoperiosteal flap technique for cleft palate repair in dogs. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1974. 165:352–354.7. Ishikawa Y, Goris RC, Nagaoka K. Use of a corticocancellous bone graft in the repair of a cleft palate in a dog. Vet Surg. 1994. 23:201–205.
Article8. Latham RA, Deaton TG, Calabrese CT. A question of the role of the vomer in the growth of the premaxillary segment. Cleft Palate. 1975. 12:351–355.9. Lippincott CL. Surgical correction of cleft hard and soft palate in the dog. Vet Med Small Anim Clin. 1974. 1:58–67.10. Meijer R, Prahl B. Influences of different surgical procedures on growth of dentomaxillary complex in dogs with artificially created cleft palate. Ann Plast Surg. 1978. 1:460–465.
Article11. Nelson AW. Slatter D, editor. Cleft Palate. Textbook of Small Animal Surgery. 2002. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Saunders;814–823.12. Sager M, Nefen S. Use of buccal mucosal flaps for the correction of congenital soft palate defects in three dogs. Vet Surg. 1998. 27:358–363.
Article13. Sinibaldi KR. Cleft palate. Vet Clin North Am. 1979. 9:245–257.
Article14. Thoday KL, Charlton DA, Graham-Jones O, Frost PL, Pullen-Warner E. The successful use of a prosthesis in the correction of a palatal defect in a dog. J small Anim Pract. 1975. 16:487–494.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Congenital Palatal Fistula with Submucous Cleft Palate
- Acquired Palatal Fistula in Patients with Submucous and Incomplete Cleft Palate before Surgery
- Palatal obturator restoration of a cleft palate patient with velopharyngeal insufficiency: a clinical report
- A Case of Congenital Palatal Teratoma Associated with Cleft Palate
- Incidence of fistula after primary cleft palate repair: a 25-year assessment of one surgeon’s experience