J Vet Sci.
2009 Jun;10(2):115-120. 10.4142/jvs.2009.10.2.115.
Genetic variability of the prion protein gene (PRNP) in wild ruminants from Italy and Scotland
- Affiliations
-
- 1Istituto Zooprofilattico Sperimentale del Piemonte, Liguria e Valle d'Aosta, 10154 Turin, Italy. simone.peletto@izsto.it
- 2Neuropathogenesis Division, The Roslin Institute and Royal (Dick) School of Veterinary Studies, University of Edinburgh, Roslin, Midlothian, EH25 9PS, UK.
- 3Department of Animal Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, University of Zaragoza, 50013 Zaragoza, Spain.
- 4Moredun Research Institute, Pentlands Science Park, Bush Loan, Penicuik, Midlothian EH26 0PZ, UK.
- 5Department of Animal Productions, Epidemiology and Ecology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, University of Turin, 10095 Grugliasco, Italy.
- KMID: 1102967
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2009.10.2.115
Abstract
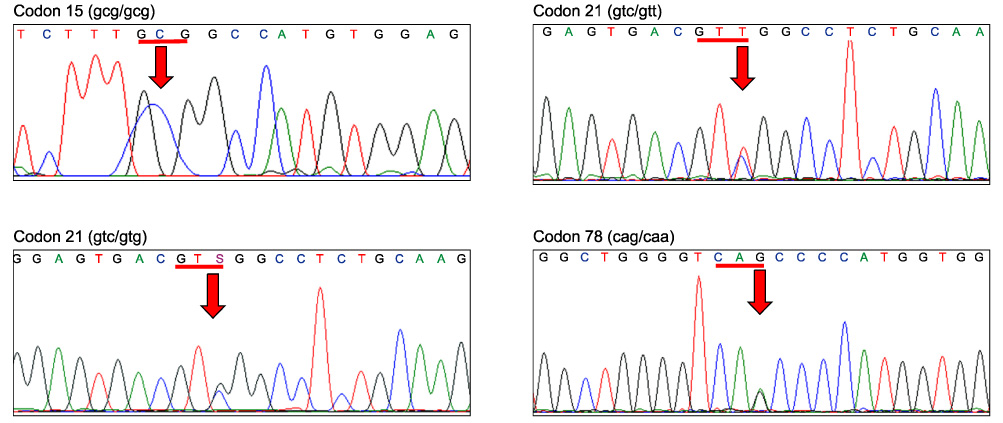
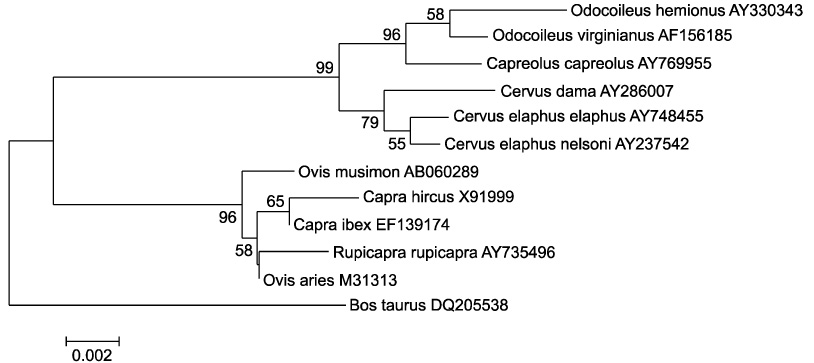
- The genetics of the prion protein gene (PRNP) play a crucial role in determining the relative susceptibility to transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs) in several mammalian species. To determine the PRNP gene variability in European red deer (Cervus elaphus), roe deer (Capreolus capreolus) and chamois (Rupicapra rupicapra), the PRNP open reading frame from 715 samples was analysed to reveal a total of ten single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). In red deer, SNPs were found in codons 15, 21, 59, 78, 79, 98, 136, 168 and 226. These polymorphisms give rise to 12 haplotypes, and one of which is identical to the PRNP of American wapiti (Rocky Mountain elk, Cervus elaphus nelsoni). One silent mutation at codon 119 was detected in chamois and no SNPs were found in roe deer. This analysis confirmed that European wild ruminants have a PRNP genetic background that is compatible with TSE susceptibility, including chronic wasting disease.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Belt PB, Muileman IH, Schreuder BE, Bos-de Ruijter J, Gielkens AL, Smits MA. Identification of five allelic variants of the sheep PrP gene and their association with natural scrapie. J Gen Virol. 1995. 76:509–517.
Article2. Cavalli-Sforza LL, Edwards AWF. Phylogenetic analysis. Models and estimation procedures. Am J Hum Genet. 1967. 19:233–257.
Article3. De Bosschere H, Saegerman C, Neukermans A, Berkvens D, Casaer J, Vanopdenbosch E, Roels S. First chronic wasting disease (CWD) surveillance of roe deer (Capreolus capreolus) in the northern part of Belgium. Vet Q. 2006. 28:55–60.4. Felsenstein J. Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol. 1981. 17:368–376.
Article5. Goldmann W, Houston F, Stewart P, Perucchini M, Foster J, Hunter N. Ovine prion protein variant A (136) R (154) L (168) Q (171) increases resistance to experimental challenge with bovine spongiform encephalopathy agent. J Gen Virol. 2006. 87:3741–3745.
Article6. Green KM, Browning SR, Seward TS, Jewell JE, Ross DL, Green MA, Williams ES, Hoover EA, Telling GC. The elk PRNP codon 132 polymorphism controls cervid and scrapie prion propagation. J Gen Virol. 2008. 89:598–608.
Article7. Hamir AN, Miller JM, Cutlip RC, Kunkle RA, Jenny AL, Stack MJ, Chaplin MJ, Richt JA. Transmission of sheep scrapie to elk (Cervus elaphus nelsoni) by intracerebral inoculation: final outcome of the experiment. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2004. 16:316–321.
Article8. Hamir AN, Gidlewski T, Spraker TR, Miller JM, Creekmore L, Crocheck M, Cline T, O'Rourke KI. Preliminary observations of genetic susceptibility of elk (Cervus elaphus nelsoni) to chronic wasting disease by experimental oral inoculation. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2006. 18:110–114.
Article9. Heaton MP, Leymaster KA, Freking BA, Hawk DA, Smith TP, Keele JW, Snelling WM, Fox JM, Chitko-McKown CG, Laegreid WW. Prion gene sequence variation within diverse groups of U.S. sheep, beef cattle, and deer. Mamm Genome. 2003. 14:765–777.
Article10. Li L, Coulthart MB, Balachandran A, Chakrabartty A, Cashman NR. Species barriers for chronic wasting disease by in vitro conversion of prion protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007. 364:796–800.
Article11. Meng LP, Zhao DM, Liu HX, Yang JM, Ning ZY, Wu CD, Han CX. Polymorphisms of the prion protein gene (PRNP) in Chinese domestic sika deer (Cervus nippon hortulorum). Anim Genet. 2005. 36:266–267.
Article12. Jeong HJ, Lee JB, Park SY, Song CS, Kim BS, Rho JR, Yoo MH, Jeong BH, Kim YS, Choi IS. Identification of single-nucleotide polymorphisms of the prion protein gene in sika deer (Cervus nippon laiouanus). J Vet Sci. 2007. 8:299–301.
Article13. Jewell JE, Conner MM, Wolfe LL, Miller MW, Williams ES. Low frequency of PrP genotype 225SF among free-ranging mule deer (Odocoileus hemionus) with chronic wasting disease. J Gen Virol. 2005. 86:2127–2134.14. Johnson C, Johnson J, Clayton M, McKenzie D, Aiken J. Prion protein gene heterogeneity in free-ranging white-tailed deer within the chronic wasting disease affected region of Wisconsin. J Wildl Dis. 2003. 39:576–581.
Article15. Johnson C, Johnson J, Vanderloo JP, Keane D, Aiken JM, McKenzie D. Prion protein polymorphisms in white-tailed deer influence susceptibility to chronic wasting disease. J Gen Virol. 2006. 87:2109–2114.
Article16. Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M. MEGA3: integrated software for Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis and sequence alignment. Brief Bioinform. 2004. 5:150–163.
Article17. Moore RA, Vorberg I, Priola SA. Species barriers in prion diseases--brief review. Arch Virol. 2005. 19:Suppl. 187–202.18. O'Rourke KI, Besser TE, Miller MW, Cline TF, Spraker TR, Jenny AL, Wild MA, Zebarth GL, Williams ES. PrP genotypes of captive and free-ranging Rocky Mountain elk (Cervus elaphus nelsoni) with chronic wasting disease. J Gen Virol. 1999. 80:2765–2769.19. O'Rourke KI, Spraker TR, Hamburg LK, Besser TE, Brayton KA, Knowles DP. Polymorphisms in the prion precursor functional gene but not the pseudogene are associated with susceptibility to chronic wasting disease in white-tailed deer. J Gen Virol. 2004. 85:1339–1346.20. Perucchini M, Griffin K, Miller MW, Goldmann W. PrP genotypes of free-ranging wapiti (Cervus elaphus nelsoni) with chronic wasting disease. J Gen Virol. 2008. 89:1324–1328.
Article21. Raymond M, Rousset F. GENEPOP (version 1.2): population genetics software for exact tests and ecumenicism. J Hered. 1995. 86:248–249.
Article22. Roels S, Saegerman C, De Bosschere H, Berkvens D, Gregoire F, Hoyoux A, Mousset B, Desmecht D, Vanopdenbosch E, Linden A. First results of chronic wasting disease (CWD) surveillance in the south-eastern part of Belgium. Vet Q. 2005. 27:98–104.
Article23. Saitou N, Nei M. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol. 1987. 4:406–425.24. Schettler E, Steinbach F, Eschenbacher-Kaps I, Gerst K, Muessdoerffer F, Risch K, Streich WJ, Frölich K. Surveillance for prion disease in cervids, Germany. Emerg Infect Dis. 2006. 12:319–322.
Article25. Sigurdson CJ, Aguzzi A. Chronic wasting disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007. 1772:610–618.
Article26. Stahl N, Borchelt DR, Hsiao K, Prusiner SB. Scrapie prion protein contains a phosphatidylinositol glycolipid. Cell. 1987. 51:229–240.
Article27. Wood JL, Lund LJ, Done SH. The natural occurrence of scrapie in moufflon. Vet Rec. 1992. 130:25–27.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Genetic Studies in Human Prion Diseases
- Sequence variations of the bovine prion protein gene (PRNP) in native Korean Hanwoo cattle
- No association of prion protein gene polymorphisms with Alzheimer's disease in Korean population
- Molecular analysis of prion protein gene (PRNP) in Korean patients with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
- Identification of single-nucleotide polymorphisms of the prion protein gene in sika deer (Cervus nippon laiouanus)