Korean J Radiol.
2008 Jul;9(Suppl):S48-S51. 10.3348/kjr.2008.9.s.s48.
Solitary Fibrous Tumor of the Pancreas: Imaging Findings
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology & Research Institute of Radiology, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. jhbyun@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1100104
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2008.9.s.s48
Abstract
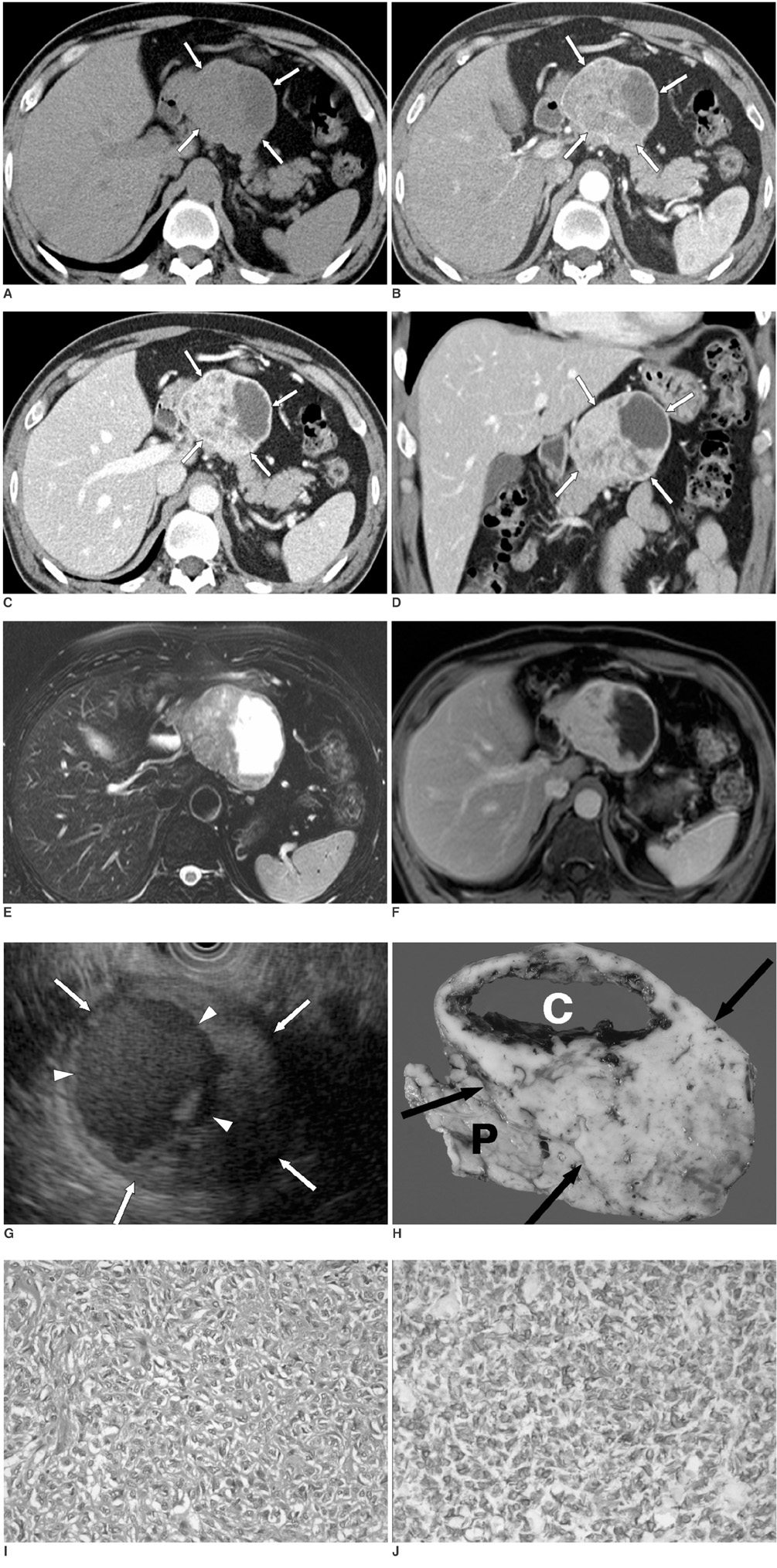
- We report here a case of a pathologically proven solitary fibrous tumor of the pancreas. A 54-year-old man was referred to our hospital for further evaluation of a pancreatic mass that was found incidentally. CT, MR imaging, and endoscopic ultrasonography showed a well-defined, enhancing mass with cystic portions of the pancreas body. MR cholangiopancreatography showed no pancreatic duct dilatation. A solitary fibrous tumor of the pancreas is a very rare lesion.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Luttges J, Mentzel T, Hubner G, Kloppel G. Solitary fibrous tumour of the pancreas: a new member of the small group of mesenchymal pancreatic tumours. Virchows Arch. 1999. 435:37–42.2. Young RH, Clement PB, McCaughey WT. Solitary fibrous tumors ('fibrous mesotheliomas') of the peritoneum. A report of three cases and a review of the literature. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1990. 114:493–495.3. Goodlad JR, Fletcher CD. Solitary fibrous tumour arising at unusual sites: analysis of a series. Histopathology. 1991. 19:515–522.4. Cardinale L, Allasia M, Ardissone F, Borasio P, Familiari U, Lausi P, et al. CT features of solitary fibrous tumour of the pleura: experience in 26 patients. Radiol Med (Torino). 2006. 111:640–650.5. Tateishi U, Nishihara H, Morikawa T, Miyasaka K. Solitary fibrous tumor of the pleura: MR appearance and enhancement pattern. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2002. 26:174–179.6. Miyamoto H, Molena DA, Schoeniger LO, Haodong Xu. Solitary fibrous tumors of the pancreas: a case report. Int J Surg Pathol. 2007. 15:311–314.7. Horton KM, Hruban RH, Yeo C, Fishman EK. Multi-detector row CT of pancreatic islet cell tumors. Radiographics. 2006. 26:453–464.8. Sheth S, Hruban RK, Fishman EK. Helical CT of islet cell tumors of the pancreas: typical and atypical manifestations. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002. 179:725–730.9. Coleman KM, Doherty MC, Bigler SA. Solid-pseudopapillary tumor of the pancreas. Radiographics. 2003. 23:1644–1648.10. Buetow PC, Buck JL, Pantongrag-Brown L, Beck KG, Ros PR, Adair CF. Solid and papillary epithelial neoplasm of the pancreas: imaging-pathologic correlation in 56 cases. Radiology. 1996. 199:707–711.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Imaging Findings of a Solitary Fibrous Tumor in Pancreas: A Case Report
- Solitary Fibrous Tumor of the Pancreas: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
- A Case of Solitary Fibrous Tumor in the Cheek
- Solitary Fibrous Tumor of the Adrenal Gland: A Case Report
- Intramedullary Solitary Fibrous Tumor of Cervicothoracic Spinal Cord