Korean J Ophthalmol.
2006 Mar;20(1):33-40. 10.3341/kjo.2006.20.1.33.
Surgical Outcomes in Correction of Brown Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. earth317@yahoo.co.kr
- 2Department of Ophthalmology, Giessen University College of Medicine, Giessen, Germany.
- KMID: 1099070
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2006.20.1.33
Abstract
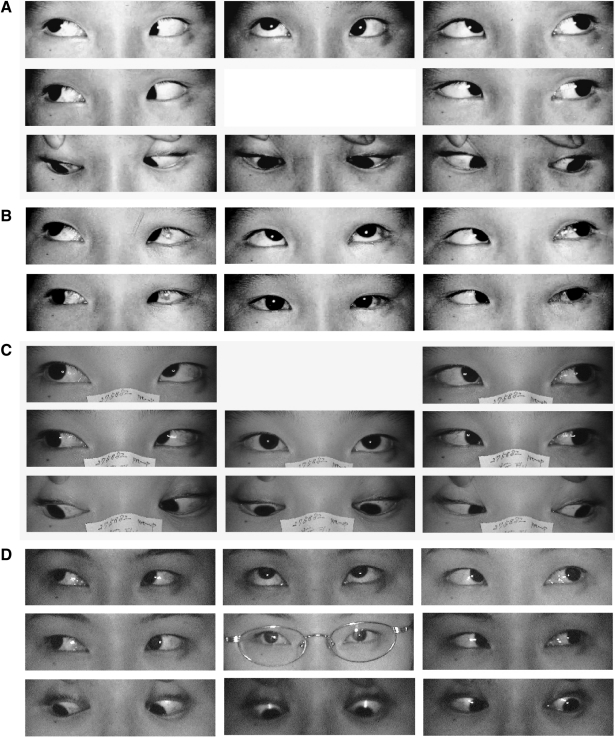
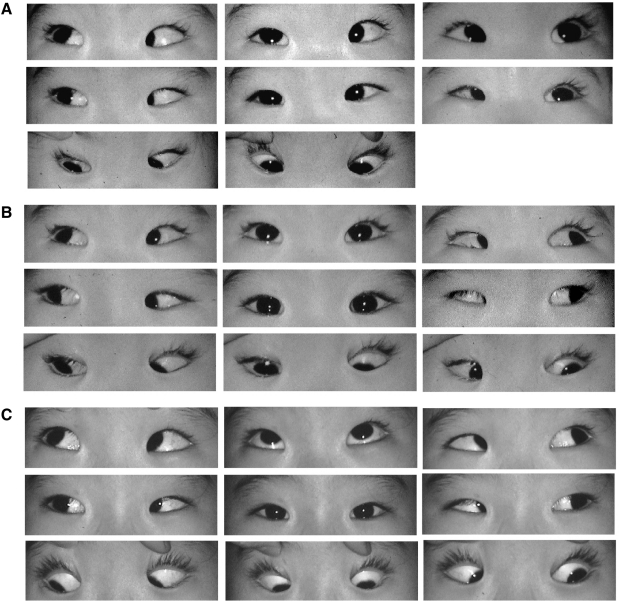
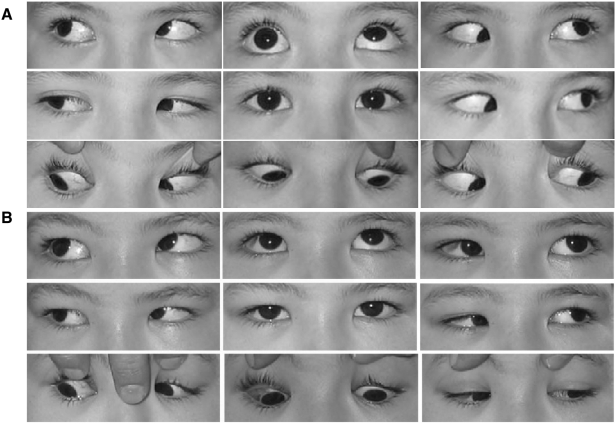
- PURPOSE: To evaluate the outcomes of surgery for Brown syndrome. METHODS: We reviewed the charts of 15 patients who underwent surgery for Brown syndrome. The limitation of elevation in adduction (LEA) ranged from -2 to -4 degrees. A superior oblique muscle (SO) tenotomy was performed in 4 patients, a silicone expander was inserted in the SO of 9 patients, and a SO recession was performed in 2 patients. The results of surgery were analyzed with a follow-up period of more than 6 months, 42.3+/-48.42 months on average. RESULTS: Nine female patients and 6 male patients with unilateral Brown syndrome were selected for this study. The left eye was the affected eye in 9 patients. The degree of preoperative LEA was -2 to -4 in 4 patients in whom SO tenotomy was performed, -3 to -4 in 9 patients treated with the silicone expander, and -2 to -4 in 2 patients treated with SO recession. The LEA was released after surgery in all patients without postoperative adhesion. However, unilateral overaction of the inferior oblique muscle due to excessive weakening of the SO occurred in 1 patient with tenotomy (25%) and in 1 patient with insertion of a silicone expander (11%). CONCLUSIONS: LEA was released after tenotomy, insertion of a silicone expander and recession of the SO in 13 of 15 patients with Brown syndrome. SO palsy due to overcorrection and under-correction with postoperative adhesion should be avoided.
MeSH Terms
-
Treatment Outcome
Time Factors
Syndrome
Silicone Elastomers
Prosthesis Implantation/instrumentation
Ophthalmologic Surgical Procedures/*methods
Oculomotor Muscles/physiopathology/*surgery
Ocular Motility Disorders/physiopathology/*surgery
Male
Humans
Follow-Up Studies
Female
Eye Movements/physiology
Child, Preschool
Child
Adult
Figure
Reference
-
1. Brown HW. Allen JH, editor. Congenital structural muscle anomalies. Strabismus Ophthalmic Symposium. 1950. St. Louis: Mosby;p. 205.2. Brown HW. True and simulated superior oblique tendon sheath syndromes. Doc Ophthalmol. 1973; 34:123–136. PMID: 4706084.
Article3. Von noorden GK, Campos EC. Binocular Vision and Ocular Motility. 2002. 6th ed. St.Louis: Mosby;p. 466–471.4. Jacobi KW. Tenectomy of the superior oblique in the tendon sheath syndrome (Brown). Klin Monatsbl Augenheilkd. 1972; 160:669–674. PMID: 4662719.5. Crawford JS. Surgical treatment of true Brown's syndrome. Am J Ophthalmol. 1976; 81:289–295. PMID: 1258952.
Article6. Parks MM. Ocular Motility and Strabismus. 1975. Hagerstown: Harper & Row;p. 147.7. Parks MM, Eustis HS. Simultaneous superior oblique tenotomy and inferior oblique recession in Brown's syndrome. Ophthalmology. 1987; 94:1043–1047. PMID: 3658365.
Article8. Wright KW. Superior oblique silicone expander for Brown syndrome and superior oblique overaction. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1991; 28:101–107. PMID: 2051286.
Article9. Caldeira JA. Bilateral recession of the superior oblique in "A" pattern tropias. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1978; 15:306–311.10. Von Kaufmann H. Strabismus. 2003. 3rd ed. Stuttgart: Georg Thieme Verlag;p. 510.11. Parks MM. Surgery for Brown syndrome. Symposium on Strabismus, Transactions of the New Orleans Academy of Ophthalmology. 1978. St Louis: Mosby;p. 157–177.12. Parks MM. Atlas of Strabismus Surgery. 1983. 1st ed. Philadelphia: Harper & Row;p. 190–195.13. Prieto-Diaz J. Superior oblique overaction. Int Ophthalmol Clin. 1989; 29:43–50. PMID: 2645237.14. Reynolds JD, Wackerhagen MV. Bilateral superior oblique tenotomy for A-pattern strabismus in patients with fusion. Binocular Vision. 1988; 3:33–38.15. Parks MM. Commentary on "Bilateral superior oblique tenotomy for A-pattern strabismus in patients with fusion". Binocular Vision. 1988; 3:39.16. Wright KW, Min BM, Park C. Comparison of superior oblique tendon expander to superior oblique tenotomy for the management of superior oblique overaction and Brown syndrome. J Pediatric Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1992; 29:92–97.17. Wright KW. Wright KW, editor. Superior oblique tendon silicon expander in strabismus. Color Atlas of Ophthalmic Surgery Strabismus. 1991. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott;chap. 12.18. Wright KW. Results of the superior oblique tendon elongation procedure for severe brown's syndrome. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 2000; 98:41–48. PMID: 11190035.19. Stager DR Jr, Parks MM, Stager DR Sr, Pesheva M. Long-term results of silicone expander for moderate and severe Brown syndrome (Brown syndrome "plus"). J AAPOS. 1999; 3:328–332. PMID: 10613574.
Article20. Wilson ME, Sinatra RB, Saunders RA. Downgaze restriction after placement of superior oblique tendon spacer for Brown syndrome. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1995; 32:29–34. PMID: 7752031.21. Romano P, Roholt P. Measured graduated recession of the superior oblique muscle. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1983; 20:134–140. PMID: 6350556.
Article22. Buckley EG, Flynn JT. Superior oblique recession versus tenotomy: a comparison of surgical results. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1983; 20:112–117. PMID: 6864426.
Article23. Gräf M, Kloss S, Kaufmann H. Results of surgery for congenital Brown's syndrome. Klin Monatsbl Augenheilkd. 2005; 223:630–637.24. Parks MM. The superior oblique tendon. 33rd Doyne memorial lecture. Trans Ophthalmol Soc U.K. 1977; 97:288–304. PMID: 345531.25. Parks MM. Management of overaction superior oblique muscles. Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus, Transactions of the New Orleans Academy of Ophthalmology. 1986. New York: Raven Press;p. 409–418.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Three Cases of Acquired Simulated Brown Syndrome after Blowout Fracture Operations
- Brown-Sequard Syndrome due to Herniated Cervical Disc
- Typical and A typical Brown's Syndrome
- A Brown-Sequard Syndrome Resulting from a Ruptured Cervical Disc Herniation: A Case Report
- Extradural Cervical Disc Herniation Causing Sudden Brown-se'quard Syndrome: A Case Report