Korean J Ophthalmol.
2006 Jun;20(2):79-81. 10.3341/kjo.2006.20.2.79.
Ultrasonographic Measurement of Upper Eyelid Thickness in Korean Children with Epicanthus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Pochun CHA University College of Medicine, Pundang CHA Hospital, Sungnam, Korea. eye@cha.ac.kr
- KMID: 1099039
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2006.20.2.79
Abstract
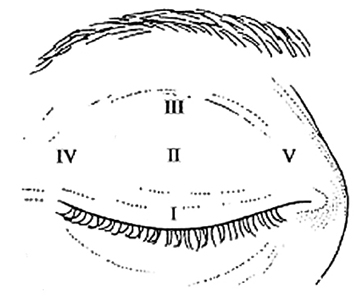
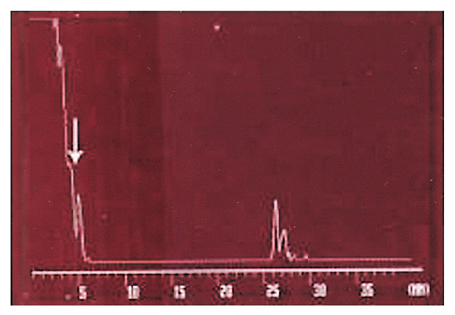
- PURPOSE: Upper eyelid thickness was measured to determine whether there is a difference in the thickness of the upper eyelids in children with and without epicanthus. METHODS: Children were enrolled into the epicanthus group or non-epicanthus (control) group. The children with epicanthus were classified into four subgroups according to the Duke-Elder's classification. The thickness of the upper eyelid was measured at five points with A-scan ultrasonography. RESULTS: There was no significant difference in upper eyelid thickness between the epicanthus group and control group (P>0.05) or between the subgroups of the epicanthus group (P>0.05). CONCLUSIONS: This result suggests that the etiology of epicanthus may not be hypertrophy of soft tissue.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Nesi FA, Lisman RD, Levine MR. Smith's ophthalmic plastic and reconstructive surgery. 1998. 2nd ed. St. Louis: Mosby;982–987.2. Johnson CC. Epicanthus and Epiblepharon. Arch Ophthalmol. 1978. 96:1030–1033.3. Wu W, Xu J, He B. Correction of severe congenital epicanthus using the modified square-flap method. Br J Plast Surg. 2000. 53:667–668.4. Duke-Elder S. System of ophthalmology. 1964. Vol 3. St. Louis: Mosby;851–856.5. Cha SC, Jang YS, Lee JH. Mutational analysis of forkhead transcriptional factor 2 (FOXL2) in Korean patients with blepharophimosis-ptosis-epicanthus inversus syndrome. Clin Genet. 2003. 64:485–490.6. Yang SW, Choi WC, Kim SY. Refractive changes of congenital entropion and epiblepharon on surgical correction. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2001. 15:32–37.7. Kim JH, Hwang JM, Kim HJ, et al. Characteristic ocular findings in Asian children with Down syndrome. Eye. 2002. 16:710–714.8. Mair MH, Geley T, Judmaier W, et al. Using orbital sonography to diagnose and monitor treatment of acute swelling of the eyelids in pediatric patients. Am J Roentgenol. 2002. 179:1529–1534.9. Schrom T, Bloching M, Wernecke K, et al. Measurement of upper eyelid implants curvature by ultrasound. Laryngoscope. 2005. 115:884–888.10. Hosal BM, Ayer NG, Zilelioglu G, Elhan AH. Ultrasound biomicroscopy of the levator aponeurosis in congenital and aponeurotic blepharoptosis. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004. 20:308–311.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Metric and Non -metric Characteristics of Korean Eyes Using Satadardized Photographs
- Morphological Evaluation of Upper Eyelid in Korean Children
- Epicanthus as a Cause of Pruritis
- Morphological Evaluation of Upper Eyelid in Korean
- Comparison of Skin Thickness in Lymphedema Using Ultrasonography and Skin Biopsy