Korean J Radiol.
2008 Apr;9(2):182-185. 10.3348/kjr.2008.9.2.182.
Embolization of a Bleeding Maxillary Arteriovenous Malformation via the Superficial Temporal Artery after External Carotid Artery Ligation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, People's Republic of China. chaohuawang@sina.com
- KMID: 1098199
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2008.9.2.182
Abstract
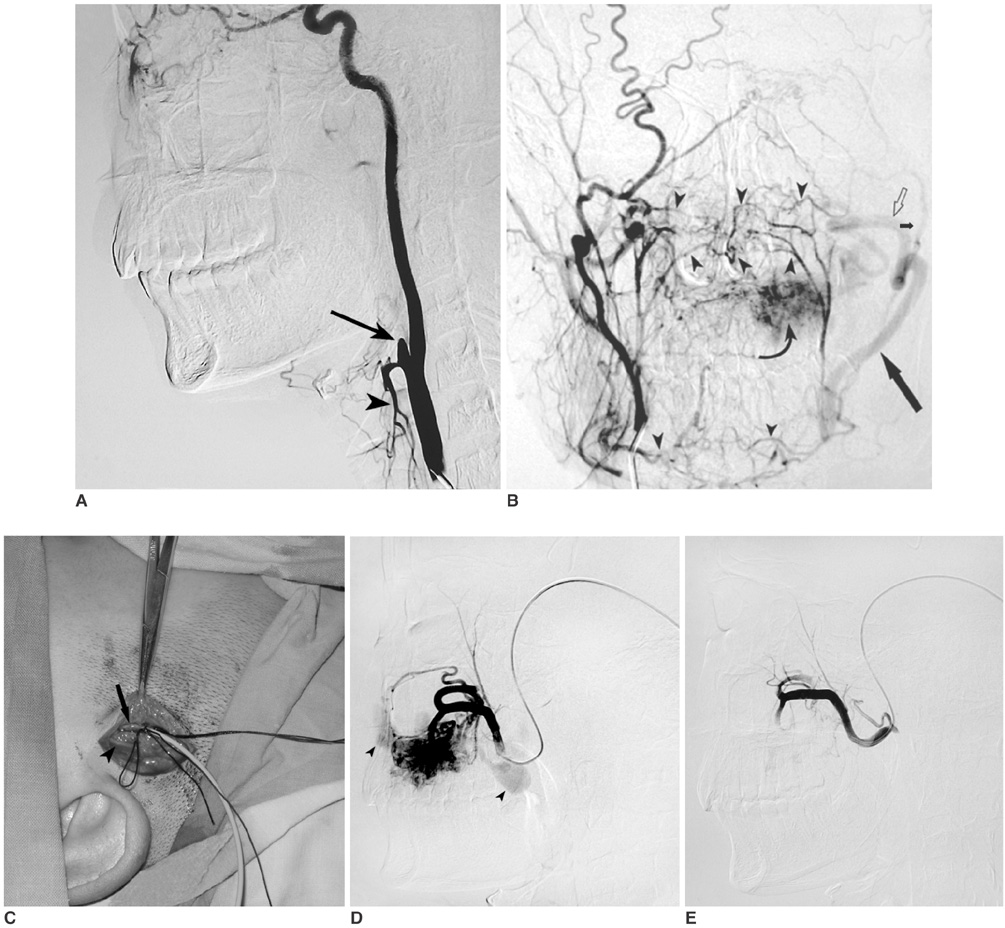
- We report a new approach of embolization in a 15-year-old boy that presented with a massive hemorrhage from a maxillary arteriovenous malformation. Re-bleeding occurred after emergent ligation of the external carotid artery. The bleeding was successfully controlled by embolization via the superficial temporal artery.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Siu WW, Weill A, Gariepy JL, Moret J, Marotta T. Arteriovenous malformation of the mandible: embolization and direct injection therapy. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2001. 12:1095–1098.2. Benndorf G, Campi A, Hell B, Holzle F, Lund J, Bier J. Endovascular management of a bleeding mandibular arteriovenous malformation by transfemoral venous embolization with NBCA. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001. 22:359–362.3. Han MH, Seong SO, Kim HD, Chang KH, Yeon KM, Han MC. Craniofacial arteriovenous malformation: preoperative embolization with direct puncture and injection of n-butyl cyanoacrylate. Radiology. 1999. 211:661–666.4. Li X, Wang YX, Zhou X, Guan Y, Tang C. Catheterization of the hepatic artery via the left common carotid artery in rats. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2006. 29:1073–1076.5. Remonda L, Schroth G, Ozdoba C, Lovblad K, Ladrach K, Huber P. Facial intraosseous arteriovenous malformations: CT and MR features. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1995. 19:277–281.6. Liu D, Ma X. Assessment of efficacy of endovascular embolization for central arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) in the jaw. Chin J Stomatol. 2002. 37:340–342.7. Gobin YP, Pasco A, Merland JJ, Aymard AA, Casasco A, Houdart E. Percutaneous puncture of the external carotid artery or its branches after surgical ligation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1994. 15:79–82.8. Pinar YA, Govsa F. Anatomy of the superficial temporal artery and its branches: its importance and surgery. Surg Radiol Anat. 2006. 28:248–253.9. Smith TP. Embolization in the external carotid artery. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2006. 17:1897–1913.10. Vardiman AB, Kopitnik TA, Purdy PD, Batjer HH, Samson DS. Treatment of traumatic arterial vasospasm with intraarterial papaverine infusion. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1995. 16:319–321.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Cirsoid Aneurysm of the Scalp
- Posterior Fossa Dural Arteriovenous Malformation: Case Report
- Massive Postoperative Bleeding: A Case Report
- Traumatic False Aneurysm of the Lingual Artery: A Case Report
- Scalp Arteriovenous Malformation Feeding from External Carotid Artery and Internal Carotid Artery Concurrently: Case Report