J Vet Sci.
2007 Sep;8(3):269-273. 10.4142/jvs.2007.8.3.269.
Clinical and pathological assessment of different suture techniques for microvascular anastomosis in rat femoral artery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Assiut University, Assiut 71526, Egypt. khaledradad@hotmail.com
- 2Department of Plastic Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, Assiut University, Assiut 71526, Egypt.
- KMID: 1090802
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2007.8.3.269
Abstract
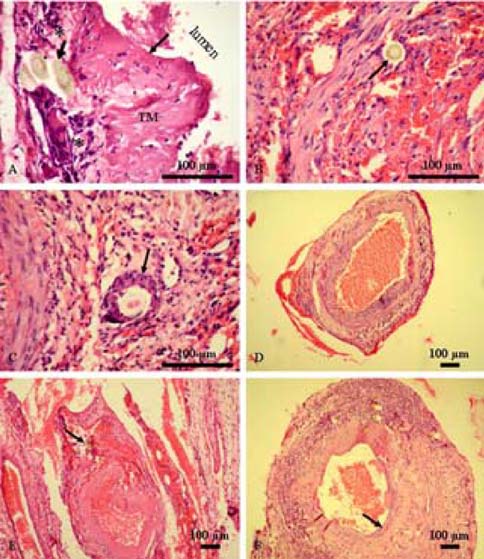
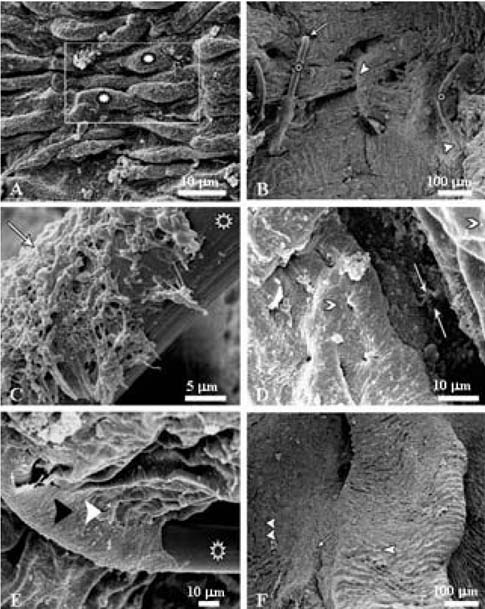
- This study examined the clinical and pathologicalfeatures after a microvascular anastomosis of a ratfemoral artery using four different suture techniques.Sixty Sprage-Dawely rats were divided randomly into 4groups. Fifteen bisected arteries (one from each animal) inGroup I, II, III and IV were sutured with the simpleinterrupted suture, continuous suture, sleeve suture andcuff suture, respectively. The anastomosis times in GroupI, II, III and IV were 28.67, 14.67, 15.47 and 15.93 min,respectively. Immediate bleeding that stopped withoutintervention (grade I) was observed in 67%, 73% and60% of the anastomosed vessels in Groups II, III and IV,respectively, while 60% of the vessels in Group I showedlight bleeding that was inhibited by gentile pressure(grade II). All vessels examined appeared to be patent at 5and 15min after the anastomosis. On the 7th daypostoperatively, the vessels of Group I showed the highestpatency rate (93%) compared with Groups II (67%), III(73%) and IV (87%). Moreover, there were morepronounced pathological changes in Group I than in theother groups. These changes included endothelial loss,endothelial proliferation, degeneration and necrosis of thetunica media. Suture materials surrounded by aninflammatory reaction were also observed. In conclusion,the simple interrupted suture is preferable formicrovascular anastomosis due to its highest patency rate.The other techniques investigated can be good alternativesbecause of their short anastomotic time and moderatepathological changes.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Acland RD, Trachtenberg L. The histopathology of small arteries following experimental microvascular anastomosis. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1977. 60:868–875.
Article2. Bancroft JD, Stevens A. Theory and Practice of Histological Techniques. 1990. 3rd ed. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone;113–305.3. Chen YX, Chen LE, Seaber AV, Urbaniak JR. Comparison of continuous and interrupted suture techniques in microvascular anastomosis. J Hand Surg [AM]. 2001. 26:530–539.
Article4. Ching S, Thoma A, Monkman S, Kelton JG. Inhibition of microsurgical thrombosis by the platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa antagonist SR121566A. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003. 112:177–185.
Article5. Cobbett J. Small vessel anastomosis. A comparison of suture techniques. Br J Plast Surg. 1967. 20:16–20.6. Furka I, Brath E, Nemeth N, Miko I. Learning microsurgical suturing and knotting techniques: comparative data. Microsurgery. 2006. 26:4–7.
Article7. Harris GD, Finseth F, Buncke HJ. The microvascular anastomotic autogenous cuff. Br J Plast Surg. 1981. 34:50–52.
Article8. Hung LK, Au KK, Ho YF. Comparative study of artery cuff and fat wrap in microvascular anastomosis in the rat. Br J Plast Surg. 1988. 41:278–283.
Article9. Kanaujia RR. Micro-arterial anastomosis using only two sutures and an autogenous cuff. J Hand Surg [Br]. 1988. 13:44–49.
Article10. Lauritzen C. A new and easier way to anastomose microvessels. An experimental study in rats. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg. 1978. 12:291–294.
Article11. Lauritzen C, Bagge U. A technical and biomechanical comparison between two types of microvascular anastomoses. An experimental study in rats. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg. 1979. 13:417–421.
Article12. Lee BY, Thoden WR, Brancato RF, Kavner D, Shaw W, Madden JL. Comparison of continuous and interrupted suture techniques in microvascular anastomosis. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1982. 155:353–357.13. Lidman D, Daniel RK. The normal healing process of microvascular anastomoses. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg. 1981. 15:103–110.
Article14. Moscona AR, Owen ER. Continuous anastomotic technique in microsurgery. Isr J Med Sci. 1978. 14:979–983.15. Schubert HM, Hohlrieder M, Falkensammer P, Jeske HC, Moser PL, Kolbitsch C, Biebl M. Bipolar anastomosis technique (BAT) enables "fast-to-do", high-quality venous end-to-end anastomosis in a new vascular model. J Craniofac Surg. 2006. 17:772–778.
Article16. Simsek T, Eroglu L, Engin MS, Kaplan S, Yildiz L. End-to-end microvascular anastomosis in the rat carotid artery using continuous horizontal mattress sutures. J Reconstr Microsurg. 2006. 22:631–640.
Article17. Sully L, Nightingale MG, O'Brien BM, Hurley JV. An experimental study of the sleeve technique in microarterial anastomoses. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1982. 70:186–192.
Article18. Tetik C, Unal MB, Kocaoglu B, Erol B. Use of continuous horizontal mattress suture techniques in microsurgery: an experimental study in rats. J Hand Surg. 2005. 30:587–595.
Article19. Wieslander JB, Aberg M. Stenosis following end-in-end microarterial anastomosis: an angiographic comparison with the end-to-end technique. J Microsurg. 1982. 3:151–155.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Microvascular Anastomosis Using Horizontal Mattress Suture Technique
- Microvascular Polytetrafluoroethylene Graft in the Rat
- Experimental Study on Microvascular Anastomosis without Sutures Using Fibrin Glue
- AN EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON PATENCY RATE OF MICROVASCULAR ANASTOMOSIS USING FIBRIN GLUE
- Experimental Study for Microvascular Anastomosis