Korean J Radiol.
2007 Dec;8(6):545-547. 10.3348/kjr.2007.8.6.545.
Imaging Findings of Central Nervous System Vasculitis Associated with Goodpasture's Syndrome: a Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. Ahn-kj@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, Kangnam St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1089443
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2007.8.6.545
Abstract
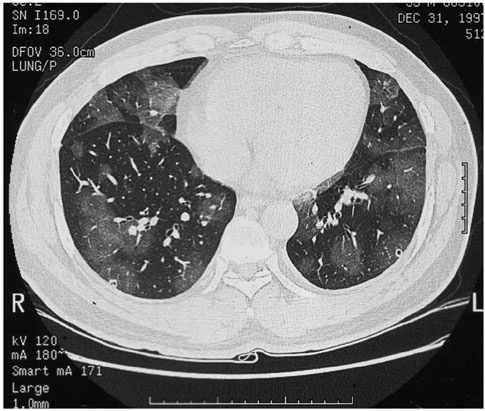
- Glomerulonephritis and pulmonary hemorrhage are features of Goodpasture's syndrome. Goodpasture's syndrome accompanied with central nervous system (CNS) vasculitis is extremely rare. Herein, we report a rare case of CNS vasculitis associated with Goodpasture's syndrome in a 34-year-old man, who presented with a seizure and sudden onset of right sided weakness. He also had recurrent hemoptysis of one month's duration. Goodpasture's syndrome is histologically diagnosed by intense linear deposits of IgG along the glomerular basement membrane in both renal and lung tissues.
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Anti-Glomerular Basement Membrane Disease/complications/*diagnosis/therapy
Anti-Inflammatory Agents/administration & dosage
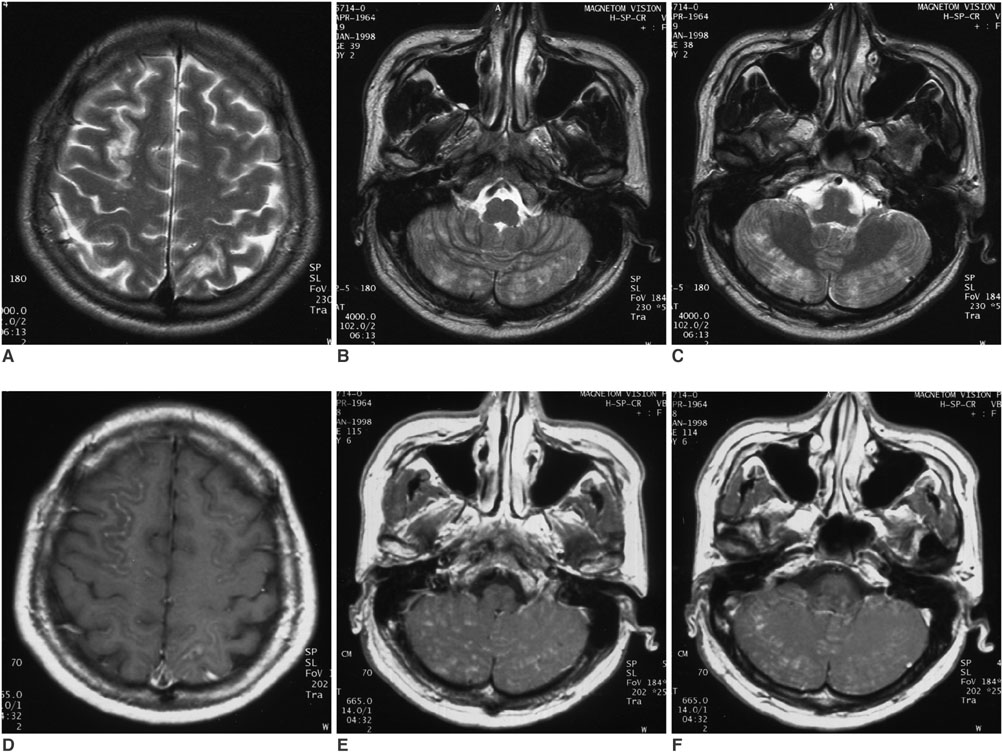
Brain/*pathology
Contrast Media/administration & dosage
Diagnosis, Differential
Fluorescent Antibody Technique
Hemoptysis/etiology
Humans
Image Enhancement/methods
Immunoglobulin G/immunology
Kidney/ultrasonography
Lung/pathology/*radiography
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Male
Methylprednisolone/administration & dosage
Muscle Weakness/etiology
Plasmapheresis
Rare Diseases
Seizures/etiology
Tomography, X-Ray Computed
Vasculitis, Central Nervous System/*diagnosis/etiology/therapy
Figure
Reference
-
1. Goodpasture EW. The significant of certain pulmonary lesions in relation to the etiology of influenza. Am J Med Sci. 1919. 7:863–870.2. Jayne DR, Marshall PD, Jones SJ, Lockwood CM. Autoantibodies to GBM and neutrophil cytoplasm in rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 1990. 37:965–970.3. Weber MFA, Andrassy K, Pullig O, Koderisch J, Netzer K. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies and anti glomerular basement membrane antibodies in Goodpasture's syndrome and in Wegener's granulomatosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1992. 2:1227–1234.4. O'Donoghue DJ, Short CD, Brenchley PE, Lawler W, Ballardie FW. Sequential development of systemic vasculitis with anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies complicating anti-glomerular basement membrane disease. Clin Nephrol. 1989. 32:251–255.5. Escolar Castellon JD, Roche PA, Escolar Castellon A, Minana Amda C. Goodpasture's syndrome due to exposure to cigarette smoke. Histol Histopathol. 1991. 6:535–547.6. Savage CO, Pusey CD, Bowman C, Rees AJ, Lockwood CM. Antiglomerular basement membrane antibody mediated disease in the British Isles 1980-4. Br Med J. 1986. 292:301–304.7. Wilson CB, Dixon FJ. Anti-glomerular basement membrane antibody-induced glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 1973. 3:74–89.8. Rydel JJ, Rodby RA. An 18-year-old man with Goodpasture's syndrome and ANCA-negative central nervous system vasculitis. Am J Kidney Dis. 1998. 31:345–349.9. Garnier P, Deprele C, Pilonchery B, Michel D. [Cerebral angiitis and Goodpasture's syndrome]. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2003. 159:68–70.10. Nicola G, Anna B, Janet E, Anil G, Nadeem M. Cerebral vasculitis in a teenager with Goodpasture's syndrome. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2004. 19:3168–3171.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Central Nervous System Involvement in Eosinophilia-Myalgia Syndrome Associated with L-tryptophan Ingestion: A case report
- Churg-Strauss Syndrome Presenting as Transverse Myelitis
- A Case of Overlap Syndrome of Systemic Sclerosis and Cryoglobulinemic Vasculitis With Central Nervous System Involvement
- Isolated Angiitis of Cntral Nervous System: A case Report
- Primary Angiitis of the Central Nervous System Presenting Tumefactive Lesions and Small Arteriolar Ectasias