Yonsei Med J.
2008 Apr;49(2):217-223. 10.3349/ymj.2008.49.2.217.
The Effect of Lowering the Threshold for Diagnosis of Impaired Fasting Glucose
- Affiliations
-
- 1Departments of Internal Medicine, Inha University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea. namms@inha.ac.kr
- 2Occupational and Environmental Medicine, Inha University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- 3Preventive and Social Medicine, Inha University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- 4Center for Advanced Medical Education (BK 21 project), Inha University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- KMID: 1084493
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2008.49.2.217
Abstract
- PURPOSE
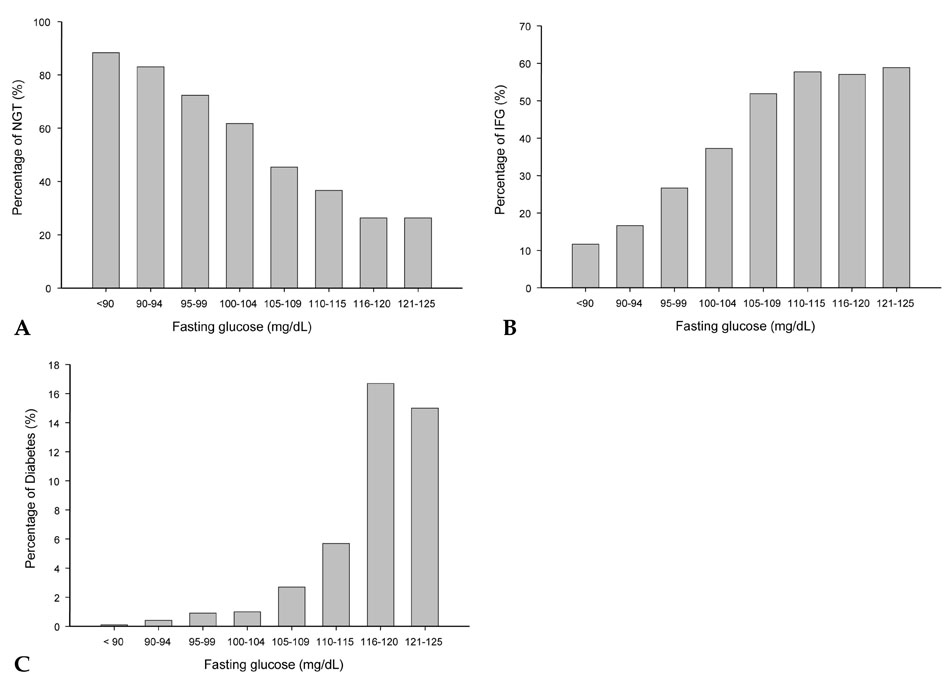
The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of lowering the fasting plasma glucose (FPG) criteria for impaired fasting glucose (IFG) on the prevalence of IFG and the risk for the development of diabetes associated with IFG in Koreans. MATERIALS AND METHODS: A total of 7,211 subjects who had normal glucose tolerance (NGT) or IFG were recruited. Subjects were evaluated at baseline and after two years follow up. Clinical data including total cholesterol, FPG and blood pressure were examined. RESULTS: Lowering the criteria for IFG from 6.1 mmol/L (110 mg/dL) to 5.6 mmol/L (100 mg/dL) increased the prevalence of IFG from 6.6% (494 subjects) to 24.4% (1829 subjects). After the 2 years follow up period, 91 subjects (1.3%) developed diabetes. Twenty one (0.3%) subjects developed diabetes among 5,382 NGT subjects and 70 (3.8%) subjects developed diabetes among 1,829 IFG (5.6-7.0 mmol/L) subjects. Lowering the IFG threshold from 6.1 mmol/L to 5.6 mmol/L resulted in a 18.4% decrease in specificity and 23.9% increase in sensitivity for predicting diabetes. The baseline FPG for predicting the development of diabetes after 2 years at a point on the receiver operating characteristic curve that was closest to the ideal 100% sensitivity and 100% specificity was 5.7 mmol/L (103 mg/dL). CONCLUSION: Lowering the FPG criterion of IFG should have benefits in predicting new onset type 2 diabetes mellitus in Koreans. The economic and health benefits of applying the new IFG criteria should be evaluated in future studies.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Report of the Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Care. 1997. 20:1183–1197.2. World Health Organization. Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications; report of a WHO consultation. Part 1: Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. 1999. Geneva: WHO.3. Genuth S, Alberti KG, Bennett P, Buse J, Defronzo R, Kahn R, et al. Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Follow-up report on the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2003. 26:3160–3167.4. Gabir MM, Hanson RL, Dabelea D, Imperatore G, Roumain J, Bennett PH, et al. The 1997 American Diabetes Association and 1999 World Health Organization criteria for hyperglycemia in the diagnosis and prediction of diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2000. 23:1108–1112.
Article5. Davidson MB, Landsman PB, Alexander CM. Lowering the criterion for impaired fasting glucose will not provide clinical benefit. Diabetes Care. 2003. 26:3329–3330.
Article6. Vaccaro O, Riccardi G. Changing the definition of impaired fasting glucose: impact on the classification of individuals and risk definition. Diabetes Care. 2005. 28:1786–1788.7. Schriger DL, Lorber B. Lowering the cut point for impaired fasting glucose: where is the evidence? Where is the logic? Diabetes Care. 2004. 27:592–601.8. Borch-Johnsen K, Colagiuri S, Balkau B, Glümer C, Carstensen B, Ramachandran A, et al. Creating a pandemic of prediabetes: the proposed new diagnostic criteria for impaired fasting glycaemia. Diabetologia. 2004. 47:1396–1402.
Article9. Kim SM, Lee JS, Lee J, Na JK, Han JH, Yoon DK, et al. Prevalence of diabetes and impaired fasting glucose in Korea: Korean National Health and Nutrition Survey 2001. Diabetes Care. 2006. 29:226–231.10. American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2005. 28:Suppl 1. S37–S42.11. Park JY, Lee KU, Kim CH, Kim HK, Hong SK, Park KS, et al. Past and current obesity in Koreans with noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1997. 35:49–56.
Article12. Min HK. Non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) in Korea. Diabet Med. 1996. 13:S13–S15.
Article13. Nathan DM, Davidson MB, DeFronzo RA, Heine RJ, Henry RR, Pratley R, et al. American Diabetes Association. Impaired fasting glucose and impaired glucose tolerance: implications for care. Diabetes Care. 2007. 30:753–759.14. Yoon KH, Lee JH, Kim JW, Cho JH, Choi YH, Ko SH, et al. Epidemic obesity and type 2 diabetes in Asia. Lancet. 2006. 368:1681–1688.
Article15. Knowler WC, Barrett-Conner E, Fowler SE, Hamman RF, Lachin JM, Walker EA, et al. Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group. Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle intervention or metformin. N Engl J Med. 2002. 346:393–403.
Article16. Vendrame F, Gottlieb PA. Prediabetes: prediction and prevention trials. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2004. 33:75–92. ix
Article17. Larsson H, Lindgärde F, Berglund G, Ahrén B. Prediction of diabetes using ADA or WHO criteria in post-menopausal women: a 10-year follow-up study. Diabetologia. 2004. 43:1224–1228.
Article18. Santaguida PL, Balion C, Hunt D, Morrison K, Gerstein H, Raina P, et al. Diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of impaired glucose tolerance and impaired fasting glucose. Evid Rep Technol Assess (Summ). 2005. 128:1–11.19. Shaw JE, Zimmet PZ, de Courten M, Dowse GK, Chitson P, Gareeboo H, et al. Impaired fasting glucose or impaired glucose tolerance. What best predicts future diabetes in Mauritius? Diabetes Care. 1999. 22:399–402.
Article20. De Vegt F, Dekker JM, Jager A, Hienkens E, Kostense PJ, Stehouwer CD, et al. Relation of impaired fasting and postload glucose with incident type 2 diabetes in a Dutch population: The Hoorn Study. JAMA. 2001. 285:2109–2113.
Article21. Song KH, Nam-Goomg IS, Han SM, Kim MS, Lee EJ, Lee YS, et al. Change in prevalence and 6-year incidence of diabetes and impaired fasting glucose in Korean subjects living in a rural area. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2007. 78:378–384.
Article22. Shaw JE, Zimmet PZ, Hodge AM, de Courten M, Dowse GK, Chitson P, et al. Imparied fasting glucose: how low should it go? Diabetes Care. 2000. 23:34–39.23. Lorenzo C, Okoloise M, Williams K, Stern MP, Haffner SM. San Antonio Heart Study. The metabolic syndrome as predictor of type 2 diabetes: the San Antonio heart study. Diabetes Care. 2003. 26:3153–3159.24. Choi KM, Lee J, Kim DR, Kim SK, Shin DH, Kim NH, et al. Comparison of ADA and WHO criteria for the diagnosis of diabetes in elderly Koreans. Diabet Med. 2002. 19:853–857.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Significance of Fasting Glucose Criteria in Metabolic Syndrome
- Prevalence and Risk Factors for Diabetes Mellitus and Impaired Fasting Glucose of Adults
- The Effect of Red-Yeast-Rice Supplement on Serum Lipid Profile and Glucose Control in Subjects with Impaired Fasting Glucose or Impaired Glucose Tolerance
- Erratum: The Effect of Lowering the Threshold for Diagnosis of Impaired Fasting Glucose
- Risk Factors of Impaired Fasting Glucose and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Using Datamining