Remifentanil Prevents Withdrawal Movements Caused by Intravenous Injection of Rocuronium
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kylee504@yuhs.ac
- 2Anesthesia and Pain Research Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1084492
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2008.49.2.211
Abstract
- PURPOSE
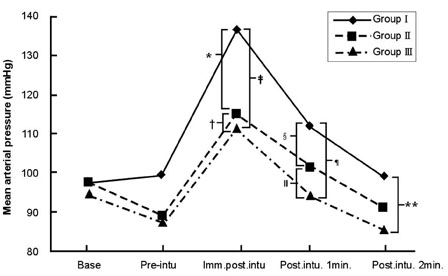
The incidence of pain induced withdrawal movement following intravenous injection of rocuronium is high. This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study was designed to evaluate the effect of pretreatment of remifentanil on the withdrawal movements due to intravenous injection of rocuronium during anesthetic induction. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Ninety adult female patients undergoing thyroidectomy were randomly allocated to three groups. Each patient intravenously received one of three solutions of equal volume (4 mL): normal saline (Group I, n=30), 0.5 microgram/kg remifentanil (Group II, n=30) or 1 microgram/kg remifentanil (Group III, n=30). Thirty seconds after remifentanil administration, anesthesia was induced with 5 mg/kg IV thiopental. Twenty seconds after thiopental injection, 0.6 mg/kg IV rocuronium was administered (injection rate of 0.5 mL/sec) and patients' withdrawal movements were assessed. Mean arterial pressure (MAP) and heart rate were assessed on arrival in the operation room, before the tracheal intubation and immediately, 1 and 2 min after the tracheal intubation. RESULTS: The incidence of withdrawal movements was significantly lower in both of the remifentanil groups (3 and 0% in Group II and III, respectively) than in the saline group (70%). Remifentanil attenuated the increase of heart rate and MAP immediately and 1 min after the tracheal intubation. CONCLUSION: The pretreatment with 0.5 and 1.0 microgram/kg remifentanil of bolus doses prevented the withdrawal movements caused by rocuronium injection, and effectively blunted cardiovascular activation following tracheal intubation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Antihistamine Pretreatment to Reduce Incidence of Withdrawal Movement After Rocuronium Injection
Ho Jun Lee, Sung Jin Han, Heezoo Kim, Il Ok Lee, Myoung Hoon Kong, Nan Suk Kim, Sang Ho Lim, Mi Kyoung Lee
J Korean Med Sci. 2009;24(5):879-882. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.5.879.The influence of age and gender on remifentanil EC50 for preventing rocuronium induced withdrawal movements
So Jin Park, Hye Jin Park, Ju Youn Choi, Hyo Seok Kang, Hong Seok Choi
Korean J Anesthesiol. 2010;58(3):244-248. doi: 10.4097/kjae.2010.58.3.244.Pharmacological and non-pharmacological intervention for rocuronium-induced withdrawal movement in the Korean population: a meta-analysis of 41 studies including 4,742 subjects
Geun Joo Choi, Sangseok Lee, Jeoung Hyuk Lee, Seul Gi Park, Hyun Kang
Korean J Anesthesiol. 2014;66(6):419-432. doi: 10.4097/kjae.2014.66.6.419.EC50 and EC95 of remifentanil to prevent rocuronium-induced withdrawal movements in children
Hye Jin Park, Hyoseok Kang, Eu-Gene Kim, Juyoun Choi, Jeong Sung Seo
Korean J Anesthesiol. 2014;66(6):433-438. doi: 10.4097/kjae.2014.66.6.433.
Reference
-
1. Steegers MA, Robertson EN. Pain on injection of rocuronium bromide. Anesth Analg. 1996. 83:203.
Article2. Borgeat A, Kwiatkowski D. Spontaneous movements associated with rocuronium: is pain on injection the cause? Br J Anaesth. 1997. 79:382–383.
Article3. Morishima T, Sobue K, Arima H, Tanaka S, So M, Ando H, et al. Profound pain due to propofol injection triggered myocardial ischemia in a patient with a suspected pheochromocytoma. Anesth Analg. 2003. 96:631.
Article4. Cheong KF, Wong WH. Pain on injection of rocuronium: influence of two doses of lidocaine pretreatment. Br J Anaesth. 2000. 84:106–107.
Article5. Memiş D, Turan A, Karamanlioğlu B, Süt N, Pamukçu Z. The prevention of pain from injection of rocuronium by ondansetron, lidocaine, tramadol, and fentanyl. Anesth Analg. 2002. 94:1517–1520.
Article6. Reddy MS, Chen FG, Ng HP. Effect of ondansetron pretreatment on pain after rocuronium and propofol injection: a randomised, double-blind controlled comparison with lidocaine. Anaesthesia. 2001. 56:902–905.
Article7. Ramaswamy S, Bapna JS. Analgesic effect of metoclopramide and its mechanism. Life Sci. 1986. 38:1289–1292.
Article8. Turan A, Memis D, Karamanlioglu B, Sut N, Pamukcu Z. The prevention of pain from injection of rocuronium by magnesium sulphate, lignocaine, sodium bicarbonate and alfentanil. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2003. 31:277–281.
Article9. Mahajan R, Batra YK, Kumar S. Pain on injection of rocuronium: influence of ketamine pretreatment. Can J Anaesth. 2005. 52:111–112.
Article10. Chiarella AB, Jolly DT, Huston CM, Clanachan AS. Comparison of four strategies to reduce the pain associated with intravenous administration of rocuronium. Br J Anaesth. 2003. 90:377–379.
Article11. Tuncali B, Karci A, Tuncali BE, Mavioglu O, Olguner CG, Ayhan S, et al. Dilution of rocuronium to 0.5 mg/mL with 0.9% NaCl eliminates the pain during intravenous injection in awake patients. Anesth Analg. 2004. 99:740–743.
Article12. Egan TD. Remifentanil pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. A preliminary appraisal. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1995. 29:80–94.13. Egan TD, Minto CF, Hermann DJ, Barr J, Muir KT, Shafer SL. Remifentanil versus alfentanil: comparative pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in healty adult male volunteers. Anesthesiology. 1996. 84:821–833.14. Mazurek AJ, Rae B, Hann S, Kim JI, Castro B, Coté CJ. Rocuronium versus succinylcholine: are they equally effective during rapid-sequence induction of anesthesia? Anesth Analg. 1998. 87:1259–1262.15. Borgeat A, Kwiatkowski D, Ruetsch YA. Spontaneous movements associated with rocuronium injection: the effects of prior administration of fentanyl. J Clin Anesth. 1997. 9:650–652.
Article16. Iyilikci L, Balkan BK, Gökel E, Günerli A, Ellidokuz H. The effects of alfentanil or remifentanil pretreatment on propofol injection pain. J Clin Anesth. 2004. 16:499–502.
Article17. Höhne C, Donaubauer B, Kaisers U. Opioids during anesthesia in liver and renal failure. Anaesthesist. 2004. 53:291–303.18. Bilgin H, Basanğan Moğol E, Bekar A, Işçimen R, Korfali G. A comparison of effects of alfentanil, fentanyl, and remifentanil on hemodynamic and respiratory parameters during stereotactic brain biopsy. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 2006. 18:179–184.
Article19. Hall AP, Thompson JP, Leslie NA, Fox AJ, Kumar N, Rowbotham DJ. Comparison of different doses of remifentanil on the cardiovascular response to laryngoscopy and tracheal intubation. Br J Anaesth. 2000. 84:100–102.
Article20. Shevchenko Y, Jocson JC, McRae VA, Stayer SA, Schwartz RE, Rehman M, et al. The use of lidocaine for preventing the withdrawal associated with the injection of rocuronium in children and adolescents. Anesth Analg. 1999. 88:746–748.
Article21. Mencke T, Beerhalter U, Fuchs-Buder T. Spontaneous movements, local reactions and pain on injection of rocuronium. A comparison between female and male patients. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2001. 45:1002–1005.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The efficacy of sevolflurane inhalation alone or its combination with intravenous remifentanil against withdrawal movements on rocuronium injection in children
- EC50 and EC95 of remifentanil to prevent rocuronium-induced withdrawal movements in children
- The influence of age and gender on remifentanil EC(50) for preventing rocuronium induced withdrawal movements
- Dilution and slow injection reduces the incidence of rocuronium-induced withdrawal movements in children
- The dose-dependent effect of remifentanil for withdrawal responses on injection of recuronium in children