Korean J Lab Med.
2009 Oct;29(5):384-389. 10.3343/kjlm.2009.29.5.384.
A Case of Light Chain Deposition Disease Involving Kidney and Bone Marrow with Microangiopathic Hemolytic Anemia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Eulji University School of Medicine, Eulji General Hospital, Seoul, Kerea.
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, University of Ulsan, College of Medicine and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. hschi@amc.seoul.kr
- 3Department of Pathology, University of Ulsan, College of Medicine and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, University of Ulsan, College of Medicine and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1077412
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/kjlm.2009.29.5.384
Abstract
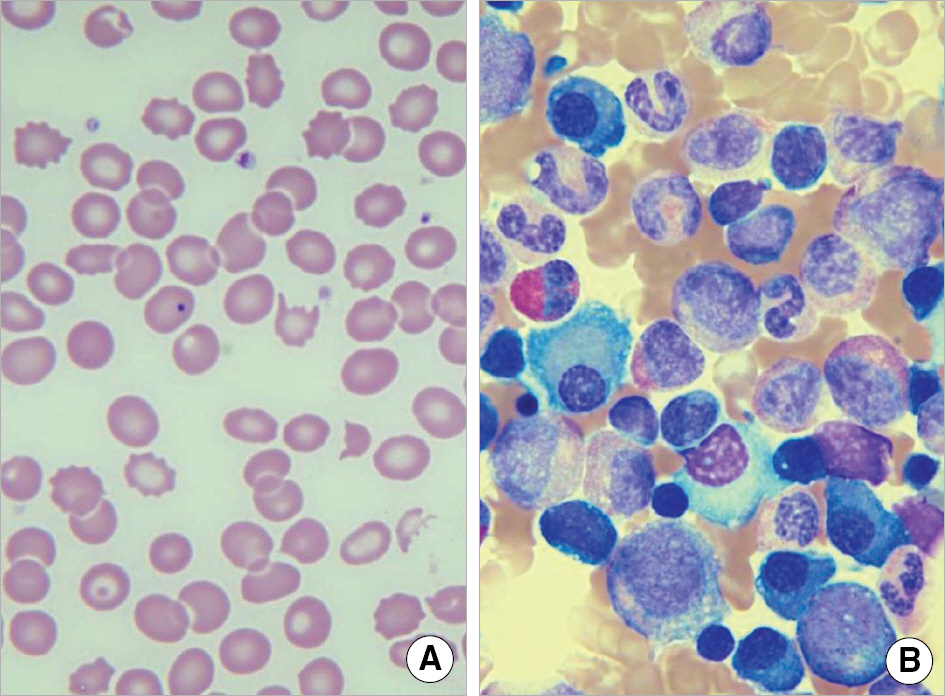
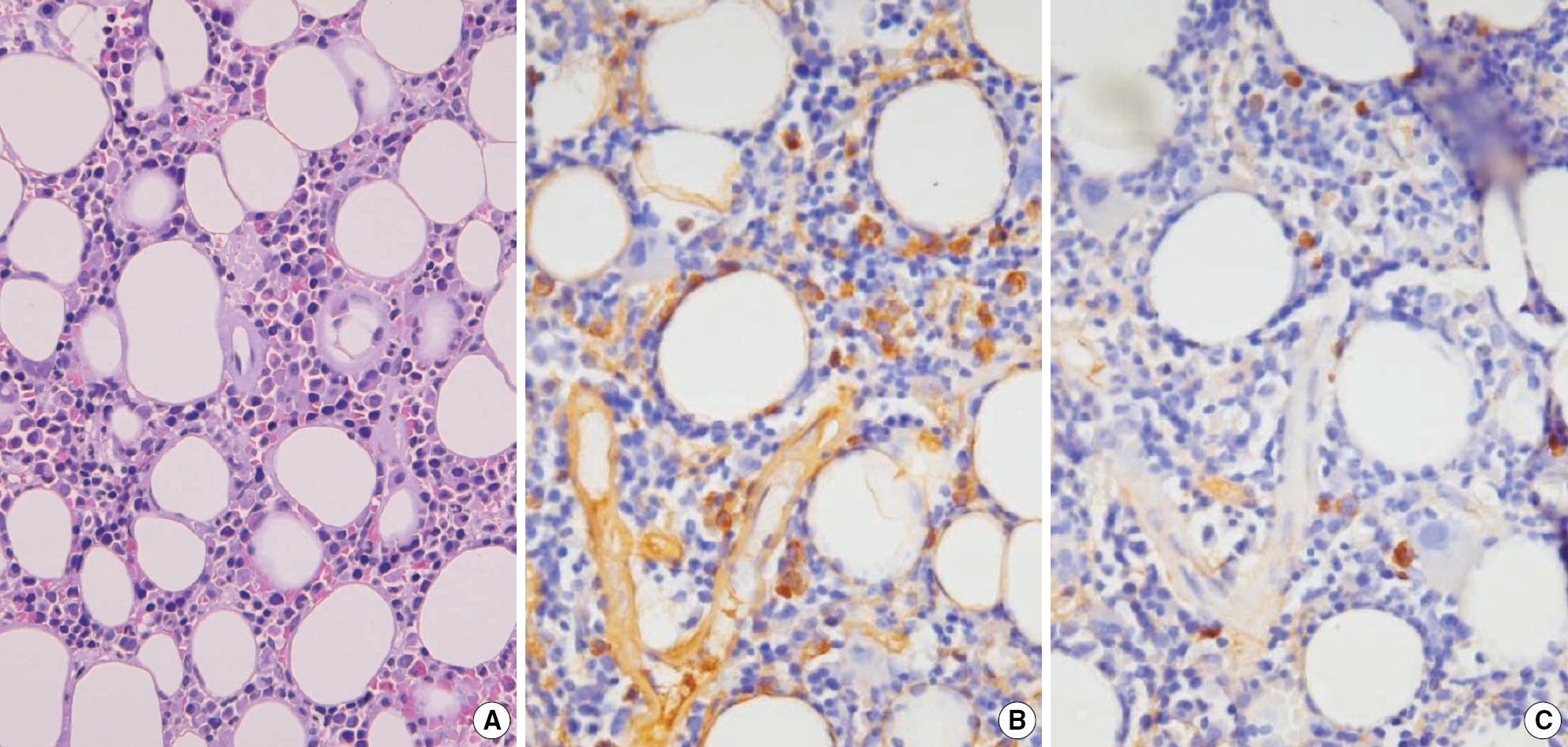
- We report a case of light chain deposition disease in a 59-yr-old female showing deposition of monoclonal light chain in the kidney and bone marrow accompanied with a schistocytosis, the morphologic finding of microangiopathic hemolytic anemia. The immunofluorescence examination of the kidney revealed strongly stained kappa-light chain deposits on the glomerular mesangium and capillary wall, tubules, and vessel wall. The electron microscopy demonstrated electron-dense deposits on the glomerular basement membrane and mesangium. Anemia was observed with schistocytosis and Howell-Jolly body in the peripheral blood smears. The immunohistochemical examination of the bone marrow showed the presence of kappa-light chain deposits in scattered plasma cells and thickened vessel wall in the absence of a prominent plasma cell proliferation. Although an immunofixation electrophoresis failed to detect a monoclonal gammopathy, the presence of monoclonal protein could be identified by an abnormal kappa/lambda ratio on the serum free light chain analysis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1.Ronco P., Alyanakian MA., Mougenot B., Aucouturier P. Light chain deposition disease: a model of glomerulosclerosis defined at the molecular level. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2001. 12:1558–65.
Article2.Ronco P., Plaisier E., Mougenot B., Aucouturier P. Immunoglobulin light (heavy)-chain deposition disease: from molecular medicine to pathophysiology-driven therapy. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006. 1:1342–50.
Article3.Grogan TM., Van Camp B, et al. Plasma cell neoplasms. Jaffe ES, Harris NL, editors. World Heath Organization classification of tumours. Pathology and genetics of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. Lyon: IARC Press;2001. p. 150–4.4.Elghetany MT., Banki K. Erythrocytic disorders. McPherson RA, Pincus MR, editors. Henry's clinical diagnosis and management by laboratory methods. 21st ed.Philadelphia: Saunders;2007. :535.
Article5.Kim G., Chang KY., Baek SH., Kim KD., Bae SJ., Kim JS, et al. A case of light chain deposition disease associated with renal amyloidosis. Korean J Nephrol. 1997. 16:783–7. (김구, 장광열, 백상현, 김광동, 배성진, 김재석등. 신유전분증을동반한경쇄침착질환1예. 대한신장학회지 1997;16:783-7.).6.Chung SJ., Ko JM., Kim HK., Kim CH., Park SK., Kim WK, et al. A case of adult Fanconi syndrome and osteomalacia associated with β-light chain monoclonal gammopathy. J Korean Soc Endocrinol. 1998. 13:99–107. (정시정, 고정민, 김홍규, 김철희, 박수길, 김우건 등. κ-Light Chain Monoclonal Gammopathy 에 병발된 성인형 Fanconi 증 후군과골연화증1예. 대한내분비학회지 1998;13:99-107.).7.Lim YH., Kim YG., Baek HJ., Yeo HM., Sin SC., Kim JA, et al. A case of light chain deposition disease without significant proteinuria. Korean J Nephrol. 2003. 22:581–5. (임영환, 김윤구, 백현정, 여호명, 신성철, 김정아등. 단백뇨가동반되지않은고질소혈증으로발현한경쇄침착질환. 대한신장학회지 2003;22:581-5.).8.Ko GJ., Kim JY., Kim MK., Choi HM., Hyun YY., Boo CS, et al. A case of lambda-type light chain deposition disease manifested as acute renal failure and multiple organ dysfunction by embolic events. Korean J Nephrol. 2004. 23:975–81. (고강지, 김정엽, 김명규, 최혜민, 현영율, 부창수 등. 급성 신부전으로 발현되어 다발성 장기부전을 동반한 λ형경쇄침착질환1예. 대한신장학회지 2004;23:975-81.).9.Lee KW., Lee HK., Lee YM., Na KR., Suh KS., Shin YT. A case of idiopathic light chain deposition disease. Korean J Nephrol. 2005. 24:146–51. (이강욱, 이한규, 이영모, 나기량, 서광선, 신영태. Monoclonal Gammopathy of Undetermined Significance (MGUS) 와관련된경쇄침착질환1예. 대한신장학회지 2005;24:146-51.).10.Kang J., Kim J., Shin SJ., Han K. A case of IgA kappa light chain deposition disease and combined adult Fanconi syndrome with Auer rod-like intracytoplasmic inclusions in plasma cells and proximal renal tubular cells. Korean J Lab Med. 2007. 27:248–52. (강지민, 김진아, 신석준, 한경자. 형질 세포와 근위 신세관 세포내 Auer rod 양 봉입체를 함유한 판코니 증후군 동반 IgA kappa 형 경쇄침착질환 1예보고. 대한진단검사의학회지 2007;27:248-52.).11.Kanjanabuch T., Bunruang R., Srisawat N., Lewsuwan S., Kittikovit V., Eiam-Ong S. The combination of thrombotic microangiopathy and nodular sclerosis in light chain deposition disease. J Med Assoc Thai. 2006. 89:S248–52.12.Herrera GA., Joseph L., Gu X., Hough A., Barlogie B. Renal pathologic spectrum in an autopsy series of patients with plasma cell dyscrasia. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2004. 128:875–9.
Article13.Gokden N., Barlogie B., Liapis H. Morphologic heterogeneity of renal light-chain deposition disease. Ultrastruct Pathol. 2008. 32:17–24.
Article14.Alpay N., Uzun S., Bahat G., Yavuz S., Erten N., Tascioglu C. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura associated with multiple myeloma. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2008. 19:439–41.
Article15.Katzmann JA., Clark RJ., Abraham RS., Bryant S., Lymp JF., Bradwell AR, et al. Serum reference intervals and diagnostic ranges for free κ and free λ immunoglobulin light chains: relative sensitivity for detection of monoclonal light chains. Clin Chem. 2002. 48:1437–44.
Article16.Lachmann HJ., Gallimore R., Gillmore JD., Carr-Smith HD., Bradwell AR., Pepys MB, et al. Outcome in systemic AL amyloidosis in relation to changes in concentration of circulating free immunoglobulin light chains following chemotherapy. Br J Haematol. 2003. 122:78–84.
Article17.Abraham RS., Katzmann JA., Clark RJ., Bradwell AR., Kyle RA., Gertz MA. Quantitative analysis of serum free light chains. A new marker for the diagnostic evaluation of primary systemic amyloidosis. Am J Clin Pathol. 2003. 119:274–8.18.Katzmann JA., Abraham RS., Dispenzieri A., Lust JA., Kyle RA. Diagnostic performance of quantitative κ and λ free light chain assays in clinical practice. Clin Chem. 2005. 51:878–81.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Seven Cases of Monoclonal Gammopathies Involving Kidney
- A Case of Microangiopathic Hemolytic Anemia after Myxoma Excision and Mitral Valve Repair Presenting as Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome
- Two Cases of Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemic
- Microangiopathic Hemolytic Anemia as the First Manifestation of Metastatic Signet Ring Cell Carcinoma of Unknown Origin: A Case Report and Review of Literature
- Microangiopathic Hemolytic Anemia: A Rare Complication of Acute Pancreatitis