Yonsei Med J.
2010 May;51(3):367-374. 10.3349/ymj.2010.51.3.367.
Risk Factors for Recurrent Hypoglycemia in Hospitalized Diabetic Patients Admitted for Severe Hypoglycemia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Emergency Medicine, Tri-Service General Hospital, National Defense Medical Center, Taipei, Taiwan. doc50024@ndmctsgh.edu.tw
- 2Department of Medicine, Taichung Veterans General Hospital, Taichung, Taiwan.
- 3Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Tri-Service General Hospital, National Defense Medical Center, Taipei, Taiwan.
- KMID: 1074988
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2010.51.3.367
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Severe hypoglycemia can result in neural damage, impaired cognitive function, coma, seizures, or death. The decision to admit diabetic patients after initial treatment in the emergency department remains unclear. Our purpose is to identify risk factors for developing recurrent hypoglycemia in diabetic patients admitted for severe hypoglycemia.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
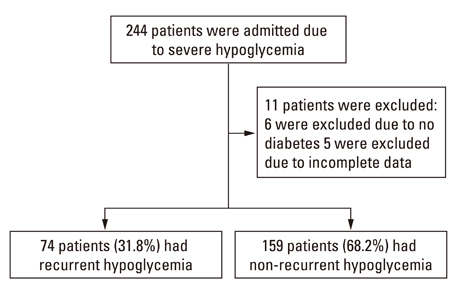
We reviewed the records of 233 subjects (92 males, 141 females; mean age, 74.1 +/- 9.8 years) with type 2 diabetes treated at a tertiary care teaching hospital and hospitalized for severe hypoglycemia.
RESULTS
Seventy-four (31.8%) patients were categorized with recurrent hypoglycemia and 159 (68.2%) with non-recurrent. Multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed that patients with loss of a recent meal, coronary artery disease, infection, and poor renal function (lower estimated glomerular filtration rate) were at risk for recurrent hypoglycemia. The use of calcium-channel blockers appeared to be a protective factor for the development of recurrent hypoglycemia.
CONCLUSION
There may be a subset of patients with severe hypoglycemia and certain risk factors for recurrent hypoglycemia that should be admitted.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Aged
Aged, 80 and over
Calcium Channel Blockers/adverse effects/therapeutic use
Coronary Artery Disease/complications
Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2/complications
Female
Glomerular Filtration Rate
Hospitalization
Humans
Hypoglycemia/*etiology/*prevention & control
Kidney Diseases/complications
Logistic Models
Male
Multivariate Analysis
Recurrence
Retrospective Studies
Risk Factors
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Hypoglycemia Revisited in the Acute Care Setting
Shih-Hung Tsai, Yen-Yue Lin, Chin-Wang Hsu, Chien-Sheng Cheng, Der-Ming Chu
Yonsei Med J. 2011;52(6):898-908. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2011.52.6.898.
Reference
-
1. Guettier JM, Gorden P. Hypoglycemia. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2006. 35:753–766. viii–ix.
Article2. Ben-Ami H, Nagachandran P, Mendelson A, Edoute Y. Drug-induced hypoglycemic coma in 102 diabetic patients. Arch Intern Med. 1999. 159:281–284.
Article3. Kearney T, Dang C. Diabetic and endocrine emergencies. Postgrad Med J. 2007. 83:79–86.4. The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1993. 329:977–986.5. Miller CD, Phillips LS, Ziemer DC, Gallina DL, Cook CB, El-kebbi IM. Hypoglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Arch Intern Med. 2001. 161:1653–1659.6. Socransky SJ, Pirrallo RG, Rubin JM. Out-of-hospital treatment of hypoglycemia: refusal of transport and patient outcome. Acad Emerg Med. 1998. 5:1080–1085.
Article7. Lobmann R, Smid HG, Pottag G, Wagner K, Heinze HJ, Lehnert H. Impairment and recovery of elementary cognitive function induced by hypoglycemia in type-1 diabetic patients and healthy controls. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000. 85:2758–2766.
Article8. Cryer P. Hypoglycemia: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment. 1997. New York: Oxford University Press.9. Shorr RI, Ray WA, Daugherty JR, Griffin MR. Incidence and risk factors for serious hypoglycemia in older persons using insulin or sulfonylureas. Arch Intern Med. 1997. 157:1681–1686.
Article10. The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. Clustering of long-term complications in families with diabetes in the diabetes control and complications trial. Diabetes. 1997. 46:1829–1839.11. Kuzuya T, Nakagawa S, Satoh J, Kanazawa Y, Iwamoto Y, Kobayashi M, et al. Report of the Committee on the classification and diagnostic criteria of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2002. 55:65–85.
Article12. Workgroup on Hypoglycemia, American Diabetes Association. Defining and reporting hypoglycemia in diabetes: a report from the American Diabetes Association Workgroup on Hypoglycemia. Diabetes Care. 2005. 28:1245–1249.13. Stevens LA, Coresh J, Greene T, Levey AS. Assessing kidney function--measured and estimated glomerular filtration rate. N Engl J Med. 2006. 354:2473–2483.
Article14. Mechem CC, Kreshak AA, Barger J, Shofer FS. The short-term outcome of hypoglycemic diabetic patients who refuse ambulance transport after out-of-hospital therapy. Acad Emerg Med. 1998. 5:768–772.
Article15. Carter AJ, Keane PS, Dreyer JF. Transport refusal by hypoglycemic patients after on-scene intravenous dextrose. Acad Emerg Med. 2002. 9:855–857.
Article16. Block MB, Rubenstein AH. Spontaneous hypoglycemia in diabetic patients with renal insuff-iciency. JAMA. 1970. 213:1863–1866.
Article17. Rutsky EA, McDaniel HG, Tharpe DL, Alred G, Pek S. Spontaneous hypoglycemia in chronic renal failure. Arch Intern Med. 1978. 138:1364–1368.
Article18. Kreisberg RA. Diabetic dyslipidemia. Am J Cardiol. 1998. 82:67U–73U.
Article19. McGuinness OP. Defective glucose homeostasis during infection. Annu Rev Nutr. 2005. 25:9–35.20. Fong YM, Marano MA, Moldawer LL, Wei H, Calvano SE, Kenney JS, et al. The acute splanchnic and peripheral tissue metabolic response to endotoxin in humans. J Clin Invest. 1990. 85:1896–1904.21. Bell DS. Inflammation, insulin resistance, infection, diabetes, and atherosclerosis. Endocr Pract. 2000. 6:272–276.22. Saeed M, Carlson GL, Little RA, Irving MH. Selective impairment of glucose storage in human sepsis. Br J Surg. 1999. 86:813–821.23. Tsukuda K, Mogi M, Li JM, Iwanami J, Min LJ, Sakata A, et al. Diabetes-associated cognitive impairment is improved by a calcium channel blocker, nifedipine. Hypertension. 2008. 51:528–533.
Article24. Müller D, Zimmering M, Roehr CC. Should nifedipine be used to counter low blood sugar levels in children with persistent hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia? Arch Dis Child. 2004. 89:83–85.25. Fuhrman MP, Charney P, Mueller CM. Hepatic proteins and nutrition assessment. J Am Diet Assoc. 2004. 104:1258–1264.
Article26. Weinsier RL, Hunker EM, Krumdieck CL, Butterworth CE Jr. Hospital malnutrition. A prospective evaluation of general medical patients during the course of hospitalization. Am J Clin Nutr. 1979. 32:418–426.
Article27. Giordano R, Grottoli S, Brossa P, Pellegrino M, Destefanis S, Lanfranco F, et al. Alprazolam (a benzodiazepine activating GABA receptor) reduces the neuroendocrine responses to insulin-induced hypoglycaemia in humans. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2003. 59:314–320.
Article28. Stratton JR, Halter JB. Effect of a benzodiazepine (alprazolam) on plasma epinephrine and norepinephrine levels during exercise stress. Am J Cardiol. 1985. 56:136–139.
Article29. Morris AD, Boyle DI, McMahon AD, Pearce H, Erans JM, Newton RW, et al. ACE inhibitor use is associated with hospitalization for severe hypoglycemia in patients with diabetes. DARTS/MEMO Collaboration. Diabetes Audit and Research in Tayside, Scotland. Medicines Monitoring Unit. Diabetes Care. 1997. 20:1363–1367.
Article30. Weidmann P, Boehlen LM, de Courten M, Ferrari P. Antihypertensive therapy in diabetic patients. J Hum Hypertens. 1992. 6:Suppl 2. S23–S36.31. Chelliah A, Burge MR. Hypoglycaemia in elderly patients with diabetes mellitus: causes and strategies for prevention. Drugs Aging. 2004. 21:511–530.32. Kotler MN, Berman L, Rubenstein AH. Hypoglycaemia precipitated by propranolol. Lancet. 1966. 2:1389–1390.33. Barnett AH, Leslie D, Watkins PJ. Can insulin-treated diabetics be given beta-adrenergic blocking drugs? Br Med J. 1980. 280:976–978.
Article34. Pandit MK, Burke J, Gustafson AB, Minocha A, Peivis AN. Drug-induced disorders of glucose tolerance. Ann Intern Med. 1993. 118:529–539.
Article35. Swislocki AL, Hoffman BB, Reaven GM. Insulin resistance, glucose intolerance and hyperinsulinemia in patients with hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 1989. 2(6 Pt 1):419–423.
Article36. Murphy MB, Lewis PJ, Kohner E, Schumer B, Dollery CT. Glucose intolerance in hypertensive patients treated with diuretics; a fourteen-year follow-up. Lancet. 1982. 2:1293–1295.
Article