J Vet Sci.
2010 Dec;11(4):359-361. 10.4142/jvs.2010.11.4.359.
Elevated fructosamine concentrations caused by IgA paraproteinemia in two dogs
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Companion Animals and Horses, University of Veterinary Medicine, Vienna, Austria. florian.zeugswetter@vetmeduni.ac.at
- 2Department of Pathobiology, University of Veterinary Medicine, Vienna, Austria.
- 3Department of Biomedical Sciences, University of Veterinary Medicine, Vienna, Austria.
- KMID: 1072188
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2010.11.4.359
Abstract
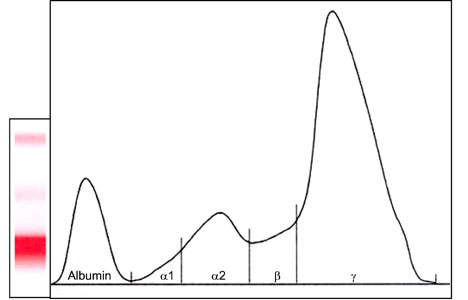
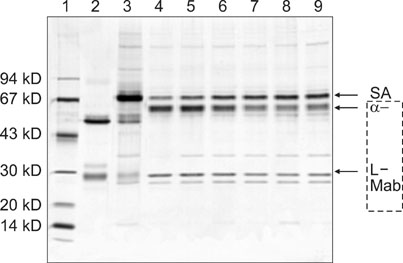
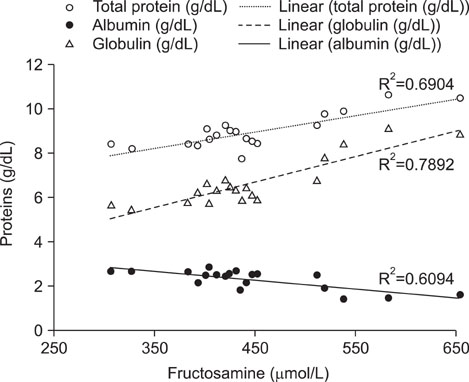
- An 8-year-old male Austrian Pinscher and a 14-year-old male Golden Retriever were presented for evaluation due to unexplainable high fructosamine values despite euglycemia and epistaxis in combination with polydipsia/polyuria, respectively. Blood analysis revealed severe hyperglobulinemia, hypoalbuminemia and markedly elevated fructosamine concentrations in both dogs. Multiple myeloma with IgA-monoclonal gammopathy was diagnosed by serum and urine electrophoresis including immunodetection with an anti-dog IgA antibody and bone marrow aspirations. Diabetes mellitus was excluded by repeated plasma and urine glucose measurements. Fructosamine values were positively correlated with globulin, but negatively correlated with albumin concentrations. These cases suggest that, as in human patients, monoclonal IgA gammopathy should be considered as a possible differential diagnosis for dogs with high fructosamine concentrations.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Fujita K, Curtiss LK, Sakurabayashi I, Kameko F, Okumura N, Terasawa F, Tozuka M, Katsuyama T. Identification and properties of glycated monoclonal IgA that affect the fructosamine assay. Clin Chem. 2003. 49:805–808.
Article2. Fujita K, Kameko F, Kato Y, Fukushima M, Okumura N, Terasawa F, Sugano M, Yamauchi K, Sato H, Kameko M, Sakurabayashi I. Mechanism of IgA-albumin complex formation that affects the fructosamine assay. J Electrophor. 2006. 50:19–23.
Article3. Griot-Wenk ME, Busato A, Welle M, Racine BP, Weilenmann R, Tschudi P, Tipold A. Total serum IgE and IgA antibody levels in healthy dogs of different breeds and exposed to different environments. Res Vet Sci. 1999. 67:239–243.
Article4. Kawamoto M, Kaneko JJ, Heusner AA, Feldman EC, Koizumi I. Relation of fructosamine to serum protein, albumin, and glucose concentrations in healthy and diabetic dogs. Am J Vet Res. 1992. 53:851–855.5. Laemmli UK. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970. 227:680–685.
Article6. Marca MC, Loste A, Ramos JJ. Effect of acute hyperglycaemia on the serum fructosamine and blood glycated haemoglobin concentrations in canine samples. Vet Res Commun. 2000. 24:11–16.7. Miller I, Goldfarb M. Smejkal GB, Lazarev A, editors. Immunoglobulin patterns in health and disease. Separation Methods in Proteomics. 2006. Boca Raton: CRC Taylor & Francis;235–267.
Article8. Reusch CE, Gerber B, Boretti FS. Serum fructosamine concentrations in dogs with hypothyroidism. Vet Res Commun. 2002. 26:531–536.9. Reusch CE, Haberer B. Evaluation of fructosamine in dogs and cats with hypo- or hyperproteinaemia, azotaemia, hyperlipidaemia and hyperbilirubinaemia. Vet Rec. 2001. 148:370–376.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Polyneuropathy Associated with IgA Paraproteinemia and Amyloidosis: A Case Report and Literature Review
- Evaluation of fructosamine tests and preanalytical errors
- HbA1c and serum fructosamine levels in hyperthyroidism
- Paraproteinemic neuropathy
- A case of monoclonal gammopathy of renal significance presenting as atypical amyloidosis with IgA lambda paraproteinemia